SCHEME OF WORK
WEEK TOPIC
1. Revision of last term examination question.
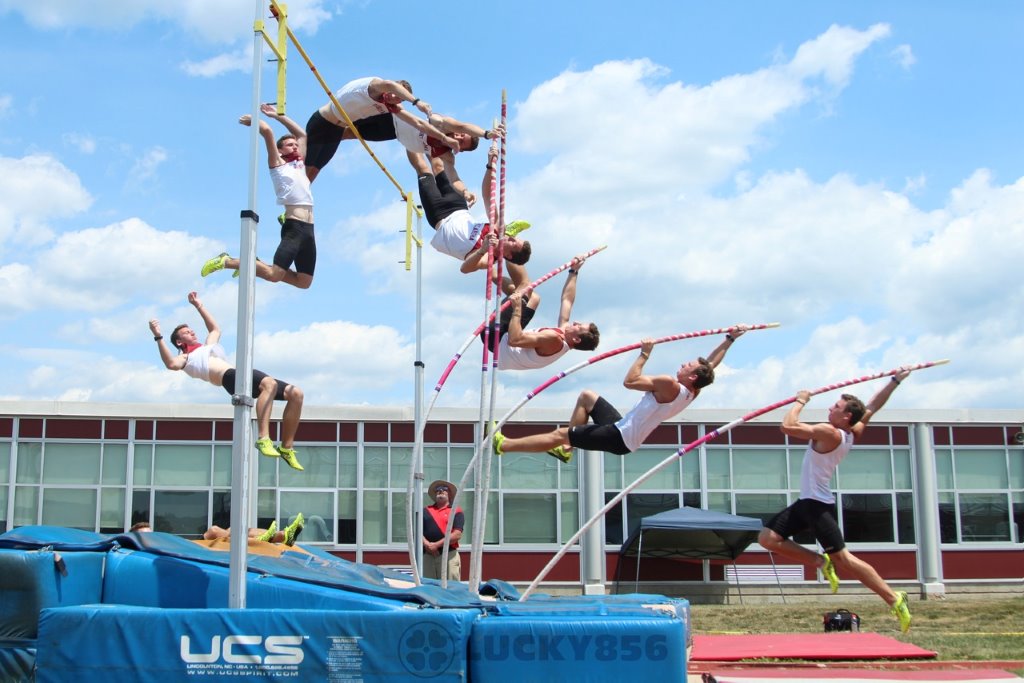
2. Field Events (Pole Vault): Pole Vault Skills – grip, run-up, pole carrying, take off, hang, swing up, pull-up and bar clearance, Landing, recovery.
3. Field Events (Throws – Javelin): Basic Javelin skills – grip, carriage, run up, release, follow through, recovery.
4. Combined Events; Pentathlon, Decathlon: (a) Group of combined events: (i) Pentathlon (ii) Decathlon. (b) List the various events under: decathlon. (b) List the various events under: decathlon and pentathlon. (c) The duration of the competition of decathlon and pentathlon. (d)Scoring the events. (e) Facilities and equipment, (f) Rules and regulations (g) Officiating (h) Exposure to practice of various events should be emphasized.
5. Ball Games (Hockey): (a) History and development of Hockey. (b) Basic skill and techniques e.g. hit, stop, drive, dribble, pass, flick, push, bully/centre pass. (c) Rules and regulations. (d) Officials and their duties. (e) Facilities and equipment. (f) Values of the games. (g) Draw and label the hockey stick and hockey pitch.’
6. Common Sports Injuries and First Aid: (a) Common Sports Injuries – dislocation, sprains, strains, fractures. (b) First Aid Treatment for each sports’ injury.
7. Family Life Education: (a) Meaning and types of families. (b) Duties of members of the family. (c) Puberty in boys and girls. (d) Pre-marital sex and its health consequences. (e) Assertiveness and Communication skills.
8. Physical Education, Health Education Agencies and Career Opportunities: (a) Sports promotion agencies and bodies in Nigeria. (i) Sports Associations (ii) NAPHER (iii) Nigeria Institute of Sports (b) Agencies/organizations promoting health education in Nigeria. (i)NSHA (ii) NAHET (iii) Ministry of Health (iv) NDLEA (v) Road Safety Corps. (vi) NAFDAC (vii) UNESCO (viii) USAID (ix) WHO (x) JICA (xi) UNWEF (c) Career Opportunities in Health Education.
9. Ageing and Death Education: (a) Description of ageing and death (b) Life enhancing measure against ageing: exercise, nutrition, rest and sleep. (c) Supporting a dying person. (d) Supporting a grieving and ageing person.
10. Revision.
1ST TERM
WEEK 1
LESSON 1
TOPIC: FIELD EVENTS: Pole Vault
CONTENT: (a) Definition (b) Requirements/qualities for/of a Pole Vaulter. (c) Equipment for Pole Vault
(e) Basic skills/Techniques for Pole Vault (e) Rules and Regulations. (e) The officials.
POLE VAULT
DEFINITION: Pole Vault is a field event which involves jumping over a horizontal placed obstacle (bar) that is supported by two uprights. The competition is performed by both male and female athletes, and the competitor is called a Pole Vaulter.

REQUIREMENTS/QUALITIES OF A GOOD POLE VAULTER.
(1) Flexibility
(2) Agility
(3) Speed
(4) Courage
(5) Muscular Strength
(6) Concentration
(7) Determination
(C) THE EQUIPMENT USED IN POLE VAULT
(1) The uprights (2) The cross bar (3) The supports for the crossbar (4) The landing foam
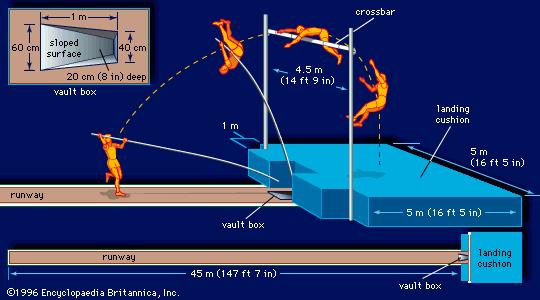
Specifications of the Equipment
(1) The uprights;
The components are made of iron metal.
Strength and height; the two uprights must be rigid and sufficiently high.
Spacing: positioned at least 3.66m apart.
Movability: movable up to 60cm forward and backward from the back of the box.
Supports of the crossbar: must be uniform and of 13mm in diameter. Must extend 7.5mm
horizontally in the direction of the landing area.
The crossbar: It is made of aluminium metal. It can be circular or triangular in shape.
The length should be between 4.48m—4.52m. It should have a minimum weight of 2.25kilos.
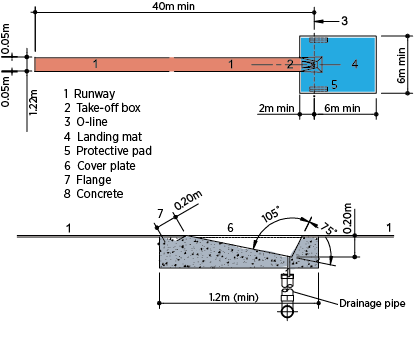
The runaway: It shall be between 40m and 45m long. It shall have a width of 1.22m and 1.25m
(maximum). It shall be marked by white lines of 5cm wide.
The box: It shall be 1m long. It shall be 60cm wide. And should have an angle of 105 formed
between the base and the stop board.
PHASES OF POLE VAULT.
This is the order of Pole Vaulting;
(1) The grip (2) run up (3) The plant (4) The take off (5) The bar clearance and (6) The landing.
EVALUATION.
1. State 5 basic requirements/qualities of a good Pole Vaulter.
2. Itemize in order the six phases of Pole Vaulting.
3. Mention four features of the crossbar in Pole Vault.
LESSON 2
TECHNIQUES/SKILLS INVOLVED IN POLE VAULT
(1) The grip
(2) The run- up
(3) The hand shift and plant
(4) The take off
(5) The hang
(6) The swing up
(7) The turning
(8) the clearance
(9) the landing.
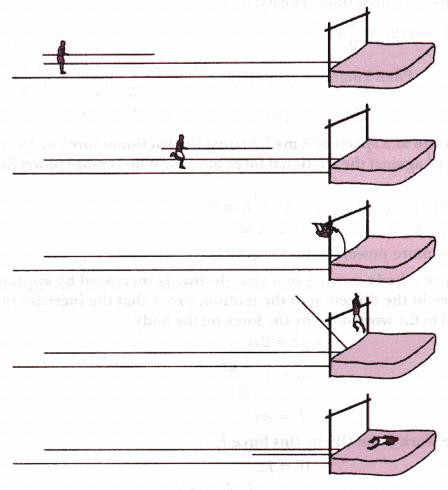
DESCRIPTION OF POLE VAULT TECHNIQUES/SKILLS.
(1) The Grip: for a right hand athlete, right hand placed at the top of the pole with the palm holding
Over and the thumb kept outside. The left hand holds the lower part of the pole with the fingers curling round it.
(2) Carriage: Pole must be kept at the right hand side. (ii) At the hip joint level (iii) the pole is not swayed while running.
(3) Run up: (i) feet should be parallel when starting off. (ii) Take off foot is taken first and acceleration gradual. (ii) Running action is similar to printing. (iii) Length of the run up is about 11---15 strides.
(4) Hand shift and the plant: (i) lower hand is brought up, close to the upper hand and during the last three steps. (ii) The pole is planted in the box, while the take off leg is slightly flexed at the take off.
(5) Take off: Take off is planted flat,should not be far from the box as the free leg is brought forward and backward.
(6) The hang: The vaulter leaves the ground with the pole in front, then hangs on to the pole as the body is elongated.
(7) The swing up: As the pole assumes vertical position, the vaulter flexes his legs and swing them up to clear the pole.
(8) The pull – up: As the pelvis reaches the grip level, the arms are flexed to pull up the body.
(9) The turn: As the body is pulled up, the body is also turned, so that he faces downward.
(10) The push up: The arms are extended to get the body to a hand- stand position on the pole immediately after the turn.
(11) The clearance: as the leg start to descend, the pole is released and clears over the crossbar.
(12) The landing: \the legs are permitted to swing downward so that the back faces downward and allow the body to land in a semi- sitting position.
RULES AND REGULATIONS ON POLE VAULT.
(1) Take off should be from one foot (single take off).
(2) A vaulter should continue jumping until he/she has forfeited the right to continue further.
(3) A failure is recorded if a vaulter, dislodges the bar, touch the ground or touch the landing area without clearing the bar.
(4) A vaulter is out of competition when he dislodges the bar three consecutive times at a particular height.
(5) Measurement is made from the ground to the middle of the bar.

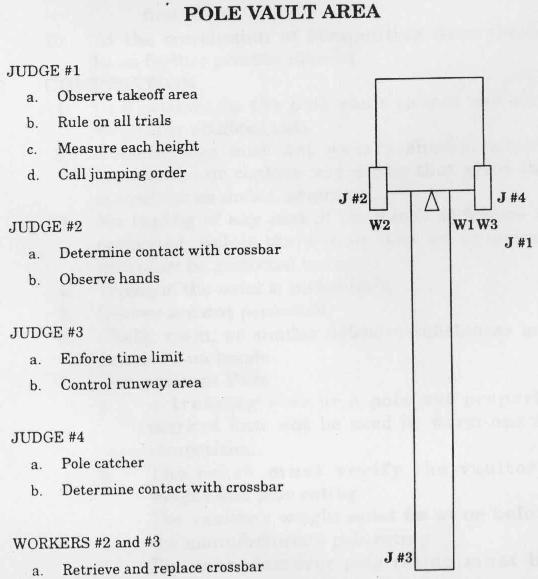
OFFICIALS IN POLE VAULT.
(1) The Referee (2) The chief field judge and (3) the two field judge.
https://youtu.be/2ByLsiNcsv0
EVALUATION.
(1) List out 5 skills allowed in pole vault.
(2) Mention 5 rules and regulations governing pole vault as a field event.
TOPIC: FIELD EVENTS: Pole Vault
CONTENT: (a) Definition (b) Requirements/qualities for/of a Pole Vaulter. (c) Equipment for Pole Vault
(e) Basic skills/Techniques for Pole Vault (e) Rules and Regulations. (e) The officials.
POLE VAULT
DEFINITION: Pole Vault is a field event which involves jumping over a horizontal placed obstacle (bar) that is supported by two uprights. The competition is performed by both male and female athletes, and the competitor is called a Pole Vaulter.

REQUIREMENTS/QUALITIES OF A GOOD POLE VAULTER.
(1) Flexibility
(2) Agility
(3) Speed
(4) Courage
(5) Muscular Strength
(6) Concentration
(7) Determination
(C) THE EQUIPMENT USED IN POLE VAULT
(1) The uprights (2) The cross bar (3) The supports for the crossbar (4) The landing foam

Specifications of the Equipment
(1) The uprights;
The components are made of iron metal.
Strength and height; the two uprights must be rigid and sufficiently high.
Spacing: positioned at least 3.66m apart.
Movability: movable up to 60cm forward and backward from the back of the box.
Supports of the crossbar: must be uniform and of 13mm in diameter. Must extend 7.5mm
horizontally in the direction of the landing area.
The crossbar: It is made of aluminium metal. It can be circular or triangular in shape.
The length should be between 4.48m—4.52m. It should have a minimum weight of 2.25kilos.
The runaway: It shall be between 40m and 45m long. It shall have a width of 1.22m and 1.25m
(maximum). It shall be marked by white lines of 5cm wide.
The box: It shall be 1m long. It shall be 60cm wide. And should have an angle of 105 formed
between the base and the stop board.
PHASES OF POLE VAULT.
This is the order of Pole Vaulting;
(1) The grip (2) run up (3) The plant (4) The take off (5) The bar clearance and (6) The landing.

EVALUATION.
1. State 5 basic requirements/qualities of a good Pole Vaulter.
2. Itemize in order the six phases of Pole Vaulting.
3. Mention four features of the crossbar in Pole Vault.
LESSON 2
TECHNIQUES/SKILLS INVOLVED IN POLE VAULT
(1) The grip
(2) The run- up
(3) The hand shift and plant
(4) The take off
(5) The hang
(6) The swing up
(7) The turning
(8) the clearance
(9) the landing.

DESCRIPTION OF POLE VAULT TECHNIQUES/SKILLS.
(1) The Grip: for a right hand athlete, right hand placed at the top of the pole with the palm holding
Over and the thumb kept outside. The left hand holds the lower part of the pole with the fingers curling round it.
(2) Carriage: Pole must be kept at the right hand side. (ii) At the hip joint level (iii) the pole is not swayed while running.
(3) Run up: (i) feet should be parallel when starting off. (ii) Take off foot is taken first and acceleration gradual. (ii) Running action is similar to printing. (iii) Length of the run up is about 11---15 strides.
(4) Hand shift and the plant: (i) lower hand is brought up, close to the upper hand and during the last three steps. (ii) The pole is planted in the box, while the take off leg is slightly flexed at the take off.
(5) Take off: Take off is planted flat,should not be far from the box as the free leg is brought forward and backward.
(6) The hang: The vaulter leaves the ground with the pole in front, then hangs on to the pole as the body is elongated.
(7) The swing up: As the pole assumes vertical position, the vaulter flexes his legs and swing them up to clear the pole.
(8) The pull – up: As the pelvis reaches the grip level, the arms are flexed to pull up the body.
(9) The turn: As the body is pulled up, the body is also turned, so that he faces downward.
(10) The push up: The arms are extended to get the body to a hand- stand position on the pole immediately after the turn.
(11) The clearance: as the leg start to descend, the pole is released and clears over the crossbar.
(12) The landing: \the legs are permitted to swing downward so that the back faces downward and allow the body to land in a semi- sitting position.

RULES AND REGULATIONS ON POLE VAULT.
(1) Take off should be from one foot (single take off).
(2) A vaulter should continue jumping until he/she has forfeited the right to continue further.
(3) A failure is recorded if a vaulter, dislodges the bar, touch the ground or touch the landing area without clearing the bar.
(4) A vaulter is out of competition when he dislodges the bar three consecutive times at a particular height.
(5) Measurement is made from the ground to the middle of the bar.

OFFICIALS IN POLE VAULT.
(1) The Referee (2) The chief field judge and (3) the two field judge.
https://youtu.be/2ByLsiNcsv0
EVALUATION.
(1) List out 5 skills allowed in pole vault.
(2) Mention 5 rules and regulations governing pole vault as a field event.
WEEK 2
LESSON 3
Topic: FIELD EVENTS: Javelin Throwing
Contents: (a) Definition (b) Requirements/qualities of a good Javelin thrower (c) Facility and Equipment (d) The skills/techniques of Javelin (e) Rules and Regulation of Javelin (f) Safety precautions for Javelin events. (g) Officials for Javelin event.
JAVELIN
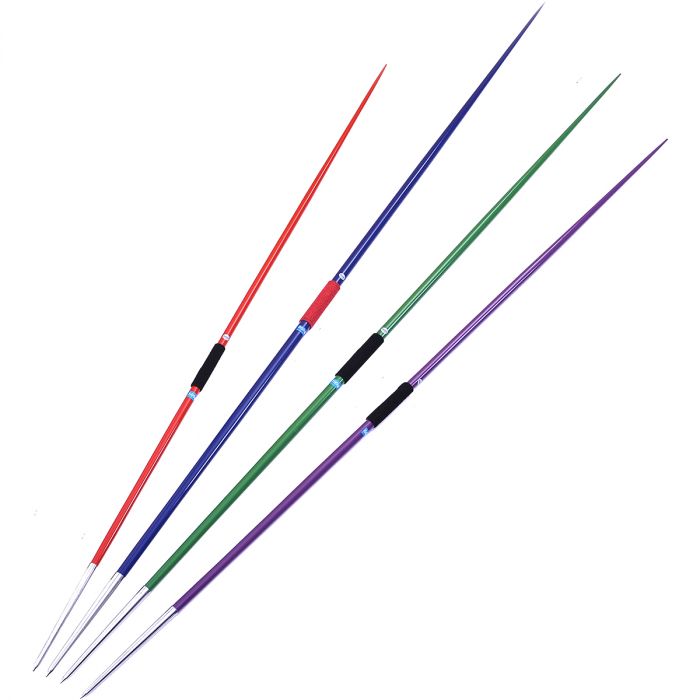
(a) Definition: Javelin is a field event which involves the throwing of an implement with one hand for distance over a horizontal surface. The competition is performed by both male and female athletes and competitor is called a Javelin thrower.

(b) Qualities/Requirements of a good Javelin thrower:
(i) Ability to run fast.
(ii) Must possess a good arm extension before release.
(iii) Possession of a good sense of balance.
(iv) Must have a good sense of coordination.
(v) Must possess a good muscular strength.
(vi) Must be physically fit.

(c) FACILITY IN JAVELIN.
(1) The Javelin pitch.
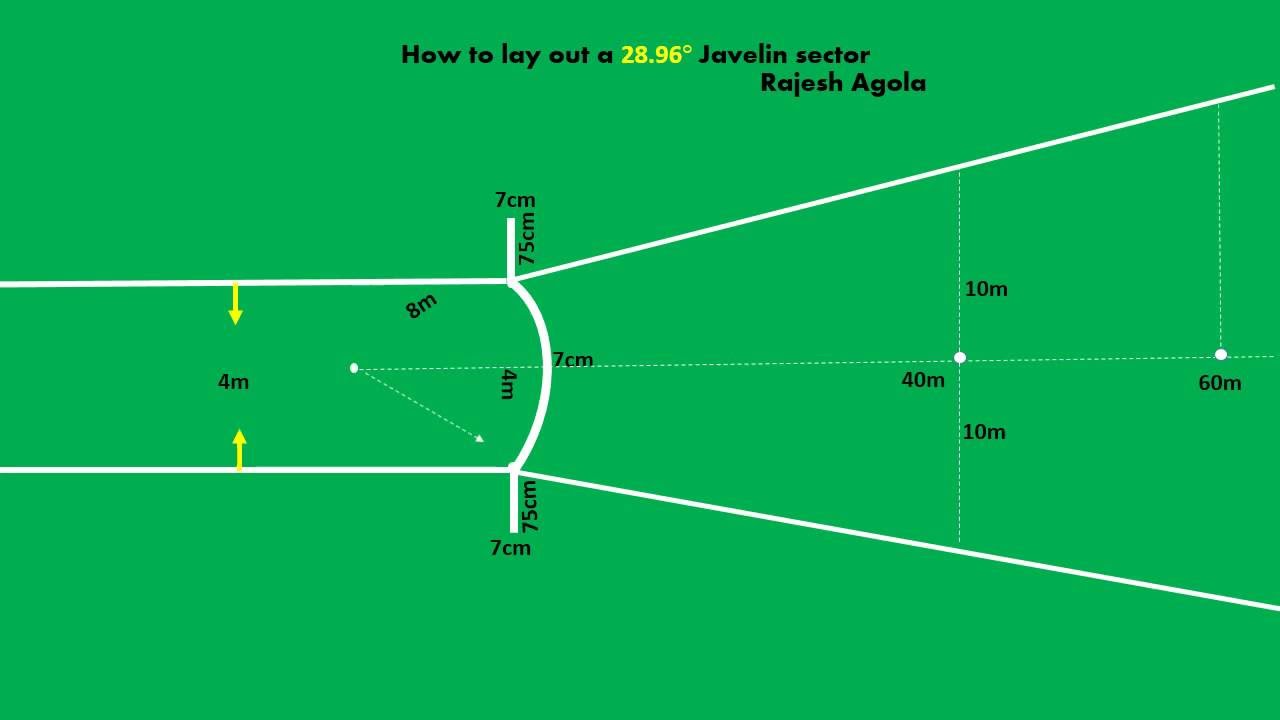
THE EQUIPMENT IN JAVELIN.
These are : (i) The Javelin (ii) The red flag and white flag. (iii) The writing materials (iv) The score sheets. (v) The measuring spike (vi) The measuring tape.
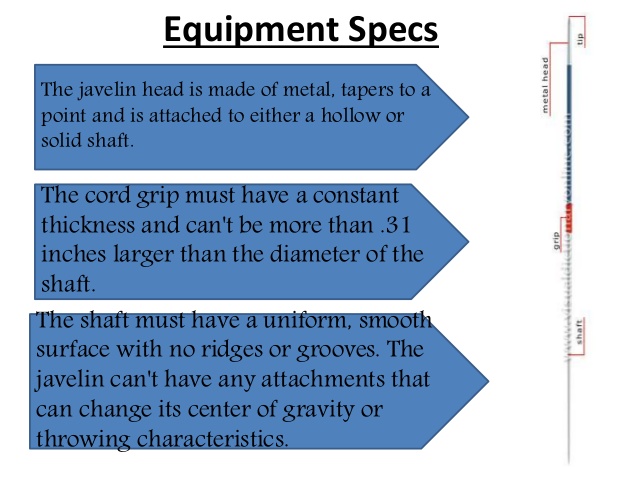
The Javelin (the implement) ----------showing the shaft, cord grip and the metal head.
(2) Javelin runway and graduating landing sector.
https://youtu.be/OhwRrPKFec4
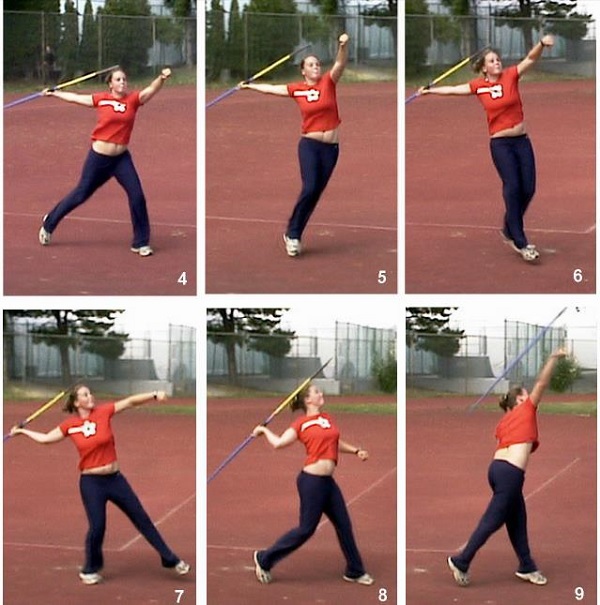
THE PHASES/STEPS INVOLVE IN THROWING JAVELIN:
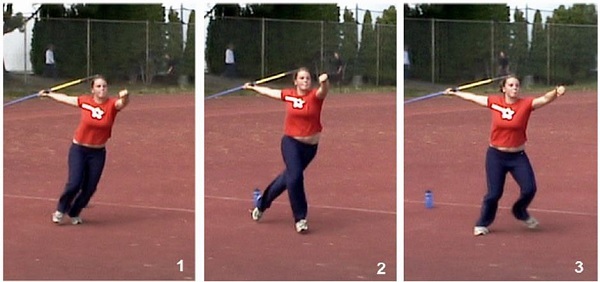
(i) The stance/stand (ii) The run up/The approach (iii) The cross step (iv) The release (v) The follow through and (vi) The recovery.

EVALUATION:
(1) List out 5 qualities of a good Javelin thrower.
(2) Mention 5 equipment used in Javelin.
(3) State 5 steps/phases in order involve in throwing Javelin.
LESSON 4
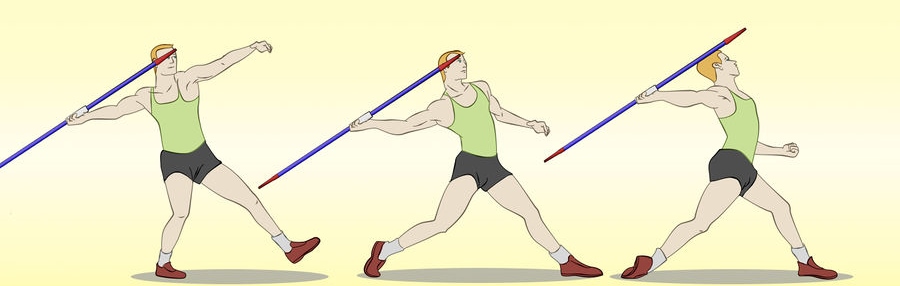
SKILLS/TECHNIQUES INVOLVE IN JAVELIN:
(i) The Grip (ii) The carriage (iii) The approach run (iv) The release (v) The follow through and (vi) The recovery.
DESCRIPTION OF THE SKILLS.
(1) The Grip---- some methods of grip are;
(i) The American/Hungarian grip (ii) The tennis grip (iii) The finnish grip (iv) The fork/claw grip.
(2) The carriage: There are two ways of carrying the Javelin, (i) The over- shoulder carriage (ii) The over- head carriage.
(3) The approach run: The run- up should be relaxed and fast enough to get the thrower to a powerful throwing position, covering the “ five stride rhythm.”
(4) The release:
During the release, the left side of the body is fixed to provide a base.
(5) The recovery:
To recover and avoid going over the scratch line, the right leg is brought forward. The left foot is brought back and thrower stands on his right foot.
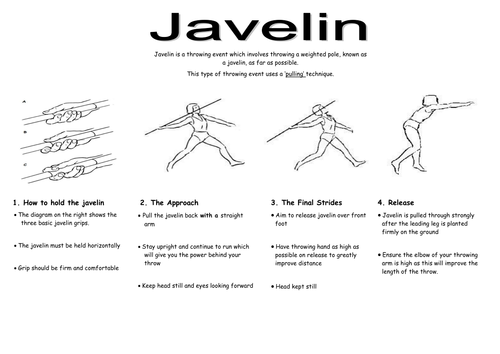
Types of throw: (i) The standing throw and the running throw.
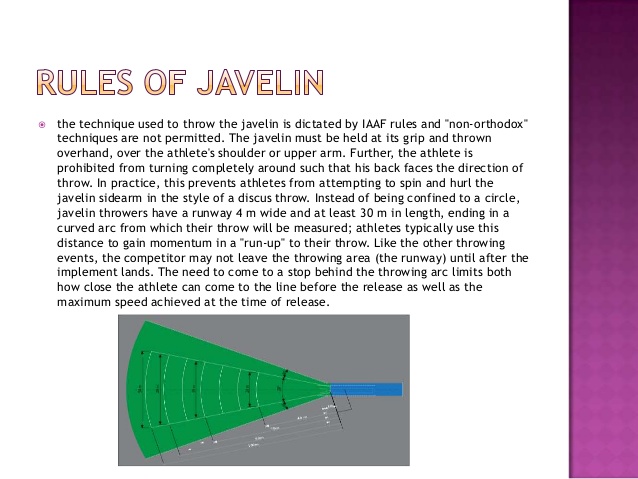
(e) THE RULES AND REGULATIONS OF JAVELIN.
(i) Throws are made behind an arc of circle 8metres in radius.
(ii) The hold of the Javelin must be at the grip/cord part.
(iii) The tip of the metal must strike the ground before any other part of the Javelin to make a good throw.
(iv) No parts of the body of the competitor should cross the arc to the landing sector immediately after throw.
(v) All throws must fall between the landing sector to be counted as valid.
(vi) The throws is not counted valid if the Javelin breaks in the air.
(vii) A horn is blown to warn people that are around.
(viii) A three trials are allowed in a throw in which the best is used to place the competitor.
(f) SAFETY PRECAUTIONS FOR JAVELIN EVENT.
(i) Do not slung or hurled the Javelin.
(ii) The landing area before releasing the Javelin must not be backed by the thrower.
(iii) The steward must not throw the Javelin while returning it but must carry it back.
(iv) Landing area has to be cleared when the event is in progress.
(v) A horn must be blown to warn the spectators.
(g) OFFICIALS FOR JAVELIN:
(i) The Referee (ii) The Chief field judge (iii) Two field judges.
https://youtu.be/z01uou_tbH0
EVALUATION:
(1) Itemize 5 techniques/skills in Javelin.
(2) Mention 5 rules and Regulations of Javelin.
(3) State 5 safety rules for Javelin event.
Topic: FIELD EVENTS: Javelin Throwing
Contents: (a) Definition (b) Requirements/qualities of a good Javelin thrower (c) Facility and Equipment (d) The skills/techniques of Javelin (e) Rules and Regulation of Javelin (f) Safety precautions for Javelin events. (g) Officials for Javelin event.
JAVELIN
(a) Definition: Javelin is a field event which involves the throwing of an implement with one hand for distance over a horizontal surface. The competition is performed by both male and female athletes and competitor is called a Javelin thrower.

(b) Qualities/Requirements of a good Javelin thrower:
(i) Ability to run fast.
(ii) Must possess a good arm extension before release.
(iii) Possession of a good sense of balance.
(iv) Must have a good sense of coordination.
(v) Must possess a good muscular strength.
(vi) Must be physically fit.

(c) FACILITY IN JAVELIN.
(1) The Javelin pitch.

THE EQUIPMENT IN JAVELIN.
These are : (i) The Javelin (ii) The red flag and white flag. (iii) The writing materials (iv) The score sheets. (v) The measuring spike (vi) The measuring tape.

The Javelin (the implement) ----------showing the shaft, cord grip and the metal head.
(2) Javelin runway and graduating landing sector.
https://youtu.be/OhwRrPKFec4
THE PHASES/STEPS INVOLVE IN THROWING JAVELIN:
(i) The stance/stand (ii) The run up/The approach (iii) The cross step (iv) The release (v) The follow through and (vi) The recovery.


EVALUATION:
(1) List out 5 qualities of a good Javelin thrower.
(2) Mention 5 equipment used in Javelin.
(3) State 5 steps/phases in order involve in throwing Javelin.
LESSON 4
SKILLS/TECHNIQUES INVOLVE IN JAVELIN:
(i) The Grip (ii) The carriage (iii) The approach run (iv) The release (v) The follow through and (vi) The recovery.
DESCRIPTION OF THE SKILLS.
(1) The Grip---- some methods of grip are;
(i) The American/Hungarian grip (ii) The tennis grip (iii) The finnish grip (iv) The fork/claw grip.
(2) The carriage: There are two ways of carrying the Javelin, (i) The over- shoulder carriage (ii) The over- head carriage.
(3) The approach run: The run- up should be relaxed and fast enough to get the thrower to a powerful throwing position, covering the “ five stride rhythm.”
(4) The release:
During the release, the left side of the body is fixed to provide a base.
(5) The recovery:
To recover and avoid going over the scratch line, the right leg is brought forward. The left foot is brought back and thrower stands on his right foot.

Types of throw: (i) The standing throw and the running throw.

(e) THE RULES AND REGULATIONS OF JAVELIN.
(i) Throws are made behind an arc of circle 8metres in radius.
(ii) The hold of the Javelin must be at the grip/cord part.
(iii) The tip of the metal must strike the ground before any other part of the Javelin to make a good throw.
(iv) No parts of the body of the competitor should cross the arc to the landing sector immediately after throw.
(v) All throws must fall between the landing sector to be counted as valid.
(vi) The throws is not counted valid if the Javelin breaks in the air.
(vii) A horn is blown to warn people that are around.
(viii) A three trials are allowed in a throw in which the best is used to place the competitor.

(f) SAFETY PRECAUTIONS FOR JAVELIN EVENT.
(i) Do not slung or hurled the Javelin.
(ii) The landing area before releasing the Javelin must not be backed by the thrower.
(iii) The steward must not throw the Javelin while returning it but must carry it back.
(iv) Landing area has to be cleared when the event is in progress.
(v) A horn must be blown to warn the spectators.
(g) OFFICIALS FOR JAVELIN:
(i) The Referee (ii) The Chief field judge (iii) Two field judges.
https://youtu.be/z01uou_tbH0
EVALUATION:
(1) Itemize 5 techniques/skills in Javelin.
(2) Mention 5 rules and Regulations of Javelin.
(3) State 5 safety rules for Javelin event.
WEEK 3
LESSON 5
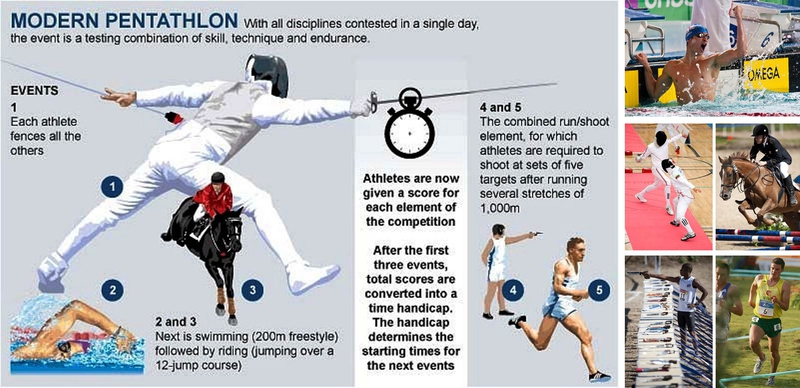
Topic: COMBINED EVENTS; PENTATHLON, DECATHLON AND HEPTATHLON.
CONTENT: (a) Definition of combined events (b) Group of combined events (c) List the various events under each group (d) The duration of the competition of (i) Pentathlon (ii) Decathlon and (iii) Heptathlon (e) Scoring the events (f) facilities and equipment (g) Rules and Regulation (h) Officiating (i) Exposure to practice of various events should be emphasized.
Definition of Combined events; Combined events are combination of track and field events. It originated from the ancient Olympic games to test the total fitness of competitors.
Group or Types of combined events: There are three types of combined events,
(i) Pentathlon (for men)
(ii) Decathlon (for men)
(iii) Heptathlon (for women)
EVENTS UNDER EACH GROUP/TYPE.
(1) Pentathlon: There are 5 events done in it, these are (i) Long Jump (ii) Javelin throw (iii) 200m race
(iv) Discus throw and (v) 1500m race. These events are held in a day.
(2) Decathlon: There are 10 events done in it and they are held in two consecutive days as follows;
DAY ONE DAY TWO
(1) 100m race 110m hurdles
(2) Long Jump Discus throws
(3) Shot put Pole Vault
(4) High Jump Javelin throws
(5) 400m race 1500m race

(3) Heptathlon: There are seven (7) events done in it and they are held on two consecutive days as
follows:
DAY ONE DAY TWO
(1) 100m hurdles Long Jump
(2) High Jump Javelin
(3) Shot put 800m race
(4) 200m race --------------
https://youtu.be/QNLQWtNrb3Y
OFFICIALS IN ATHLETICS EVENTS.
These are the officials in athletic events;
(1) The Referee
(2) The chief track judge
(3) The track judges
(4) The chief field judge
(5) The field judges
(6) The Starter
(7) The recall starter
(8) The lap recorders
(9) The marksman/assistant starter
(10) The announcer
(11) The umpires
(12) The recorders (table and cb)
(13) The time keepers
(14) The press
(15) The security officers
(16) The stewards
(17) The first aiders
(18) The clerk of the course.


SCORING IN COMBINED COMPETITIONS: The scoring is done by calculating the number of medals
Scored in order of importance as gold, silver and bronze.
EVALUATION:
(1) Mention the name of the two groups of combined events for men.
(2) State five events held on Heptathlon group of combined events for women
(3) How many events are being held on Heptathlon group?
Topic: COMBINED EVENTS; PENTATHLON, DECATHLON AND HEPTATHLON.
CONTENT: (a) Definition of combined events (b) Group of combined events (c) List the various events under each group (d) The duration of the competition of (i) Pentathlon (ii) Decathlon and (iii) Heptathlon (e) Scoring the events (f) facilities and equipment (g) Rules and Regulation (h) Officiating (i) Exposure to practice of various events should be emphasized.
Definition of Combined events; Combined events are combination of track and field events. It originated from the ancient Olympic games to test the total fitness of competitors.
Group or Types of combined events: There are three types of combined events,
(i) Pentathlon (for men)
(ii) Decathlon (for men)
(iii) Heptathlon (for women)
EVENTS UNDER EACH GROUP/TYPE.
(1) Pentathlon: There are 5 events done in it, these are (i) Long Jump (ii) Javelin throw (iii) 200m race
(iv) Discus throw and (v) 1500m race. These events are held in a day.

(2) Decathlon: There are 10 events done in it and they are held in two consecutive days as follows;
DAY ONE DAY TWO
(1) 100m race 110m hurdles
(2) Long Jump Discus throws
(3) Shot put Pole Vault
(4) High Jump Javelin throws
(5) 400m race 1500m race

(3) Heptathlon: There are seven (7) events done in it and they are held on two consecutive days as
follows:
DAY ONE DAY TWO
(1) 100m hurdles Long Jump
(2) High Jump Javelin
(3) Shot put 800m race
(4) 200m race --------------

https://youtu.be/QNLQWtNrb3Y
OFFICIALS IN ATHLETICS EVENTS.
These are the officials in athletic events;
(1) The Referee
(2) The chief track judge
(3) The track judges
(4) The chief field judge
(5) The field judges
(6) The Starter
(7) The recall starter
(8) The lap recorders
(9) The marksman/assistant starter
(10) The announcer
(11) The umpires
(12) The recorders (table and cb)
(13) The time keepers
(14) The press
(15) The security officers
(16) The stewards
(17) The first aiders
(18) The clerk of the course.


SCORING IN COMBINED COMPETITIONS: The scoring is done by calculating the number of medals
Scored in order of importance as gold, silver and bronze.
EVALUATION:
(1) Mention the name of the two groups of combined events for men.
(2) State five events held on Heptathlon group of combined events for women
(3) How many events are being held on Heptathlon group?
WEEK 4
LESSON 6
Topic: Ball Games (Hockey)
Content: (a) History and development of Hockey. (b) Basic skills and techniques e:g hit, stop,
drive, dribble, pass, flick, push, bully/centre pass. (c) Rules and Regulations (d) Officials and their
duties. (e) Facilities and Equipment (f) Values of the games (g) Draw and label the hockey stick
and hockey pitch.
HISTORY AND DEVELOPMENT OF HOCKEY
There was no clear record on the origin of hockey, but record shows that the people of ancient Greece, Romans and Persians played the game as at 541BC. Modern Hockey started in 1876AD when new set of rules and regulations were formed.
In 1887, first women hockey club formed in England
In 1900, the International Federation of Hockey formed in England.
In 1901, Hockey was introduced to USA
In 1952, the first major International Competition held.
Hokey is a field event played between two teams comprising of eleven players each. The game is played with hockey sticks and ball.
(b) Basic skills and techniques used in Hockey:
(i) The dribble/dribbling
(ii) The drive/hit/hitting
(iii) The stopping
(iv) The passing
(v) The Scooping
(vi) The flick
(vii) The goal keeping
(viii) The tackling.
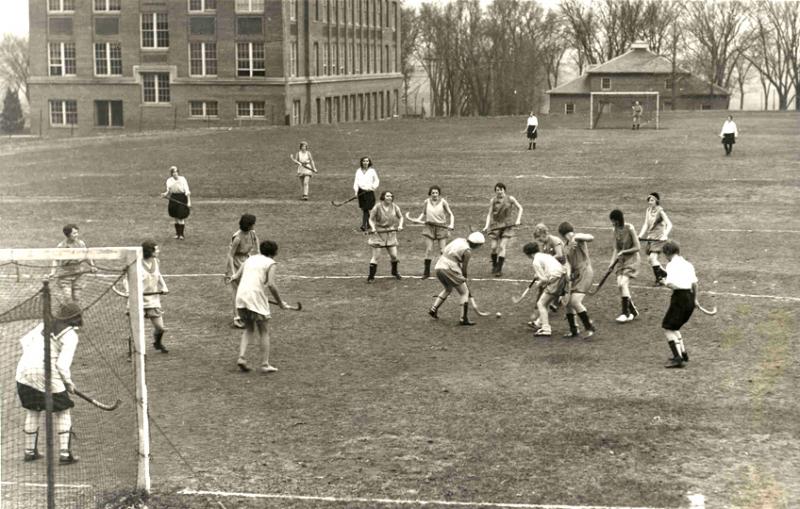


(c) FACILITIES USED IN HOCKEY GAME.
(i) The hockey pitch (ii) The goal posts (iii) The side boards (iv) The back boards (v) The nets
(vi) The flag posts.
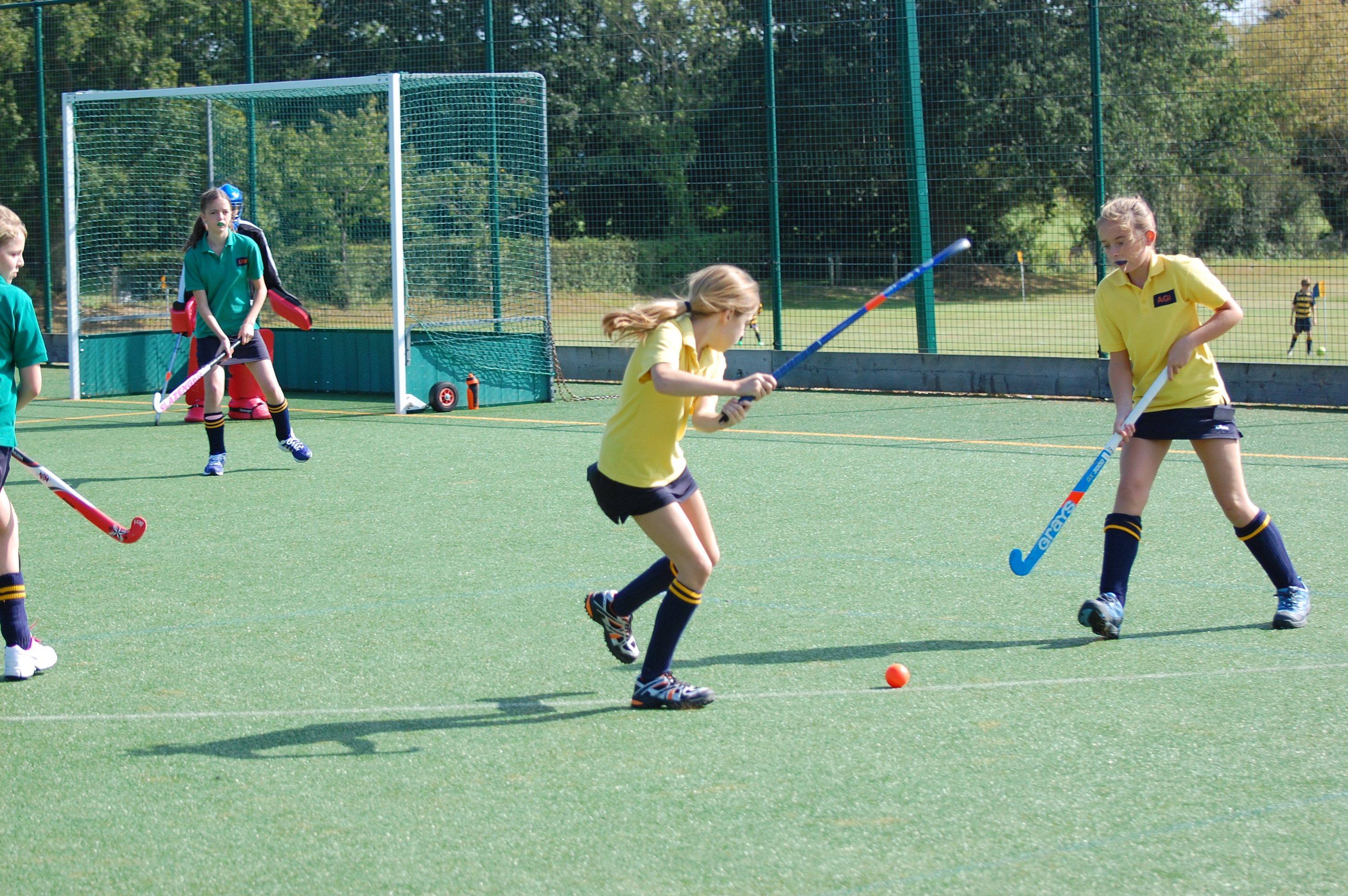

EQUIPMENT USED IN HOCKEY:
(i) The hockey sticks (ii) The hockey balls (iii) The pads (iv) The gloves (v) The studded shoes
(vi) The knee caps (vii) the groin protectors (viii) The shin guards (ix) The face mask (x) The chest
Pad (xi) the kickers.

https://youtu.be/IZCzbslH8jo
EVALUATION:
(1) Trace the history of hockey by filling the following;
(i) The first three nations that played hockey and when?
(ii) When did the modern hockey started and where?
(iii) The date of the first International hockey competition.
(2) State 5 skills used in hockey.
LESSON 7
RULES AND REGULATIONS IN HOCKEY:
(1) A team consists of 11 players while a squad is made up of 16 players. 22 players play the game
at a time.
(2) The game is started by a centre pass.
(3) Goals can be scored from within the striking circle.
(4) Players jerseys are numbered front and back.
(5) No player is allowed to play without stick.
(6) The ball must not be deliberately kicked by a player.
(7) All player must be at their own half of the pitch during the centre pass.
(8) A player is not allowed to throw the stick at the ball.
(9) The rounded side of the stick must not be used to hit the ball.
(10) The stick must not be raised above the shoulder while playing.
(11) A player must not under cut or turn in order to hit the ball.

OFFICIALS AND THEIR DUTIES.
Officials in hockey games are:
(i) Two umpires, one for each half of the field. (ii) Two assistant umpires. (iii) The Referee.

DUTIES OF THE TWO UMPIRES:
(1) They give final verdict (decision)
(2) Inspect the equipment for eligibility.
(3) Conduct toss for the choice of ends.
(4) Blow the whistles to indicate any foul.
(5) Authorised to disqualify any player for unsportsmanlike behavior.

DUTIES OF THE ASSISTANT UMPIRES:
(1) Assist the umpires.
(2) Indicate with the flags when the ball is out.
(3) Indicate any other infringements.
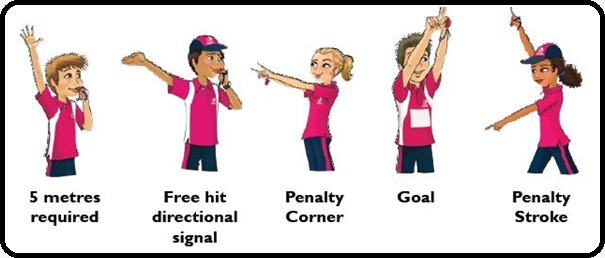
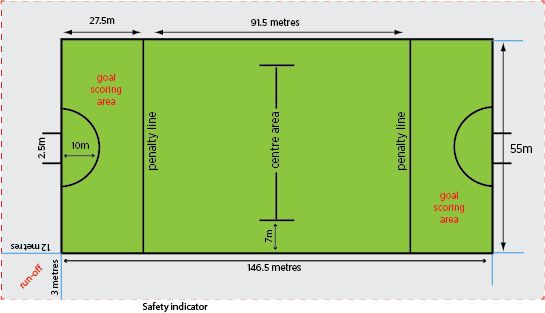
THE HOCKEY STICK AND HOCKEY PITCH.

EVALUATION:
(1) State 5 rules and regulations in Hockey.
(2) Mention 5 duties of the two umpires in Hockey.
Topic: Ball Games (Hockey)
Content: (a) History and development of Hockey. (b) Basic skills and techniques e:g hit, stop,
drive, dribble, pass, flick, push, bully/centre pass. (c) Rules and Regulations (d) Officials and their
duties. (e) Facilities and Equipment (f) Values of the games (g) Draw and label the hockey stick
and hockey pitch.
HISTORY AND DEVELOPMENT OF HOCKEY
There was no clear record on the origin of hockey, but record shows that the people of ancient Greece, Romans and Persians played the game as at 541BC. Modern Hockey started in 1876AD when new set of rules and regulations were formed.
In 1887, first women hockey club formed in England
In 1900, the International Federation of Hockey formed in England.
In 1901, Hockey was introduced to USA
In 1952, the first major International Competition held.
Hokey is a field event played between two teams comprising of eleven players each. The game is played with hockey sticks and ball.
(b) Basic skills and techniques used in Hockey:
(i) The dribble/dribbling
(ii) The drive/hit/hitting
(iii) The stopping
(iv) The passing
(v) The Scooping
(vi) The flick
(vii) The goal keeping
(viii) The tackling.


(c) FACILITIES USED IN HOCKEY GAME.
(i) The hockey pitch (ii) The goal posts (iii) The side boards (iv) The back boards (v) The nets
(vi) The flag posts.

EQUIPMENT USED IN HOCKEY:
(i) The hockey sticks (ii) The hockey balls (iii) The pads (iv) The gloves (v) The studded shoes
(vi) The knee caps (vii) the groin protectors (viii) The shin guards (ix) The face mask (x) The chest
Pad (xi) the kickers.

https://youtu.be/IZCzbslH8jo
EVALUATION:
(1) Trace the history of hockey by filling the following;
(i) The first three nations that played hockey and when?
(ii) When did the modern hockey started and where?
(iii) The date of the first International hockey competition.
(2) State 5 skills used in hockey.
LESSON 7
RULES AND REGULATIONS IN HOCKEY:
(1) A team consists of 11 players while a squad is made up of 16 players. 22 players play the game
at a time.
(2) The game is started by a centre pass.
(3) Goals can be scored from within the striking circle.
(4) Players jerseys are numbered front and back.
(5) No player is allowed to play without stick.
(6) The ball must not be deliberately kicked by a player.
(7) All player must be at their own half of the pitch during the centre pass.
(8) A player is not allowed to throw the stick at the ball.
(9) The rounded side of the stick must not be used to hit the ball.
(10) The stick must not be raised above the shoulder while playing.
(11) A player must not under cut or turn in order to hit the ball.

OFFICIALS AND THEIR DUTIES.
Officials in hockey games are:
(i) Two umpires, one for each half of the field. (ii) Two assistant umpires. (iii) The Referee.

DUTIES OF THE TWO UMPIRES:
(1) They give final verdict (decision)
(2) Inspect the equipment for eligibility.
(3) Conduct toss for the choice of ends.
(4) Blow the whistles to indicate any foul.
(5) Authorised to disqualify any player for unsportsmanlike behavior.

DUTIES OF THE ASSISTANT UMPIRES:
(1) Assist the umpires.
(2) Indicate with the flags when the ball is out.
(3) Indicate any other infringements.

THE HOCKEY STICK AND HOCKEY PITCH.


EVALUATION:
(1) State 5 rules and regulations in Hockey.
(2) Mention 5 duties of the two umpires in Hockey.
WEEK 5
LESSON 8
Topic: COMMON SPORTS INJURIES AND FIRST AID
CONTENT: (a) Common sports injuries
i. dislocation
ii. String
iii. Fracture
(b) First Aid treatment for each sport injury.
INJURY
Injury is damage to any part of the body that may allow the escape of blood as a result of accident.

Factors that cause injury:
Injuries are caused by two major factors:
• The human/man-made elements
• The natural or environmental elements
THE HUMAN ELEMENTS:- These are due to human behavior such as:- ignorance, risk taken, carelessness, overconfidence, inadequate warm-up, miscalculation, disregard to safety rules, drunkenness, effects of drugs, mistakes, and faulty judgments. It is otherwise known as avoidable or man-made accident
THE NATURAL OR ENVIRONMENTAL ELEMENTS: - These are brought about by nature; as a result, they are difficult to control e.g. cyclone, flood, tornado, hurricane, earthquake, land slide, volcanic eruption, heavy rain, thunderstorm, tidal waves etc. However, human elements sometimes aid natural factors. It is otherwise known as unavoidable accident.
Factors that can cause injuries during sports
• Carelessness.
• Fatigue/tiredness
• Poor lighting/ poor visibility in activity area.
• Lack of skills/ lack of knowledge
• Unsafe physical environment/ hazard
• Faulty equipment/ apparatus/ inappropriate costume.
• Lack of instruction/negligence
• Effects of drugs e.g. alcohol
SPORTS INJURIES
What are sports injuries? Sports injuries are the injuries that occur during participation in sports and games due to accident.
Common sports injuries
• dislocation
• strain
• fracture
• wounds
• sprain
• drowning
• muscles cramp
• bleeding

Description of common sports injuries
DISLOCATION: - It is the displacement of one or more bone ends at a joint as a result of injury to the Joint. Common sites of dislocation are – elbow, shoulder, ankle, hip, wrist, toe and finger joints.
Signs and symptoms of dislocation
• Pain
• Swelling
• Discoloration (change in color)
• Tenderness.
• High temperature at the area
• Subluxation (out of alignment)
• Loss of movement
• Bone displacement
• Deformity
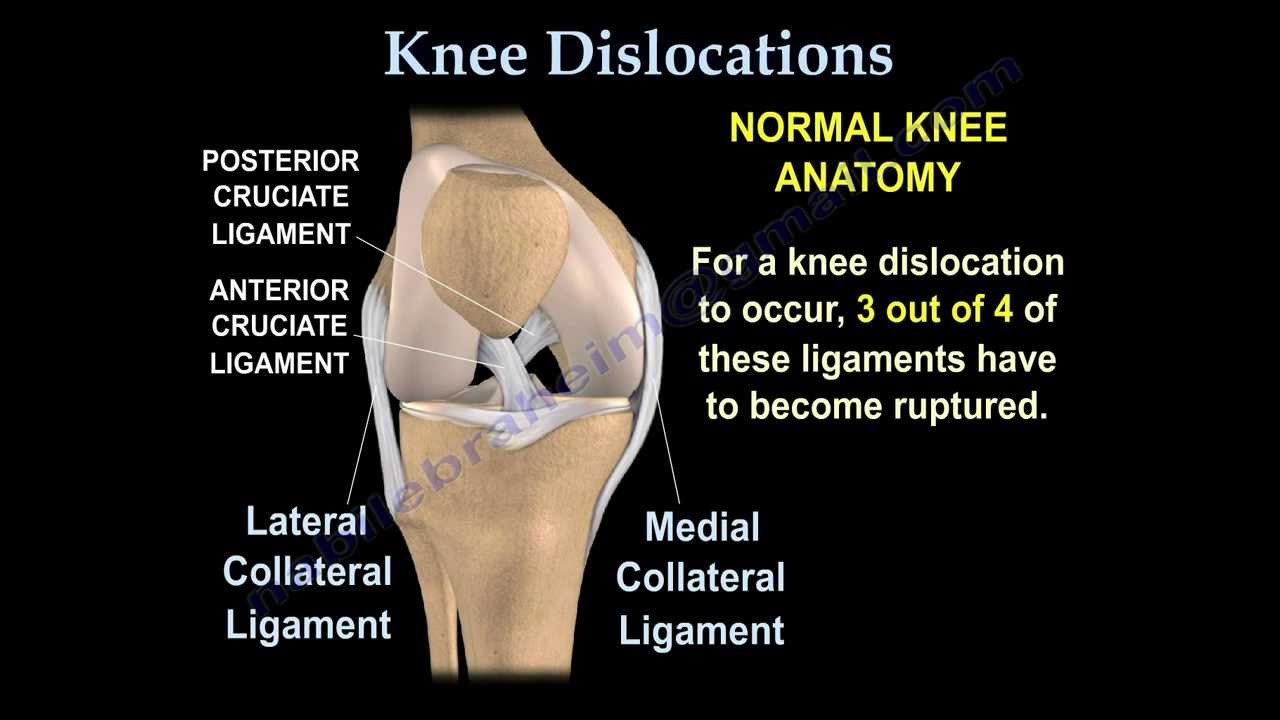
First Aid Treatment
Bandage the affected joint
Rub with cold compress
Never attempt to put back the bones
Seek medical attention
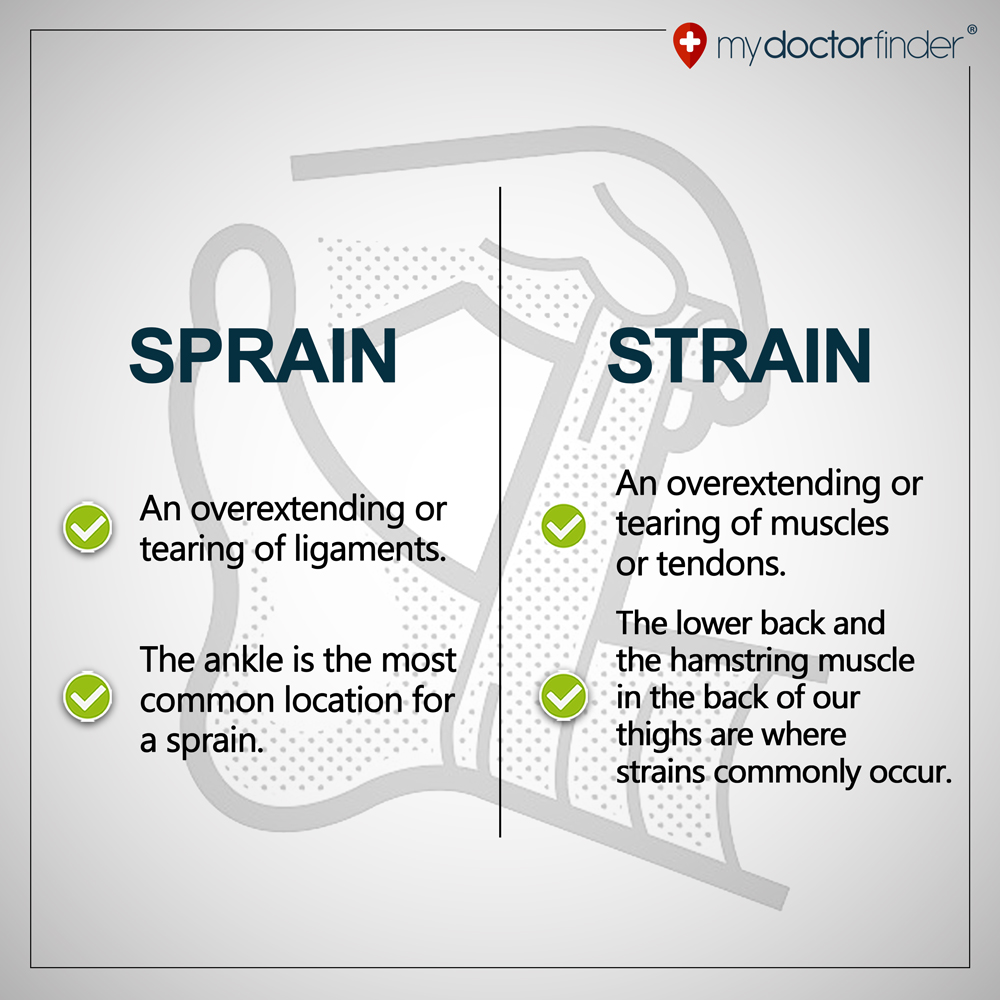
STRAIN: It is an injury to the muscle. It occurs in the muscle when a group of muscle is overstretched, the fibers may tear thereby causing an internal bleeding.
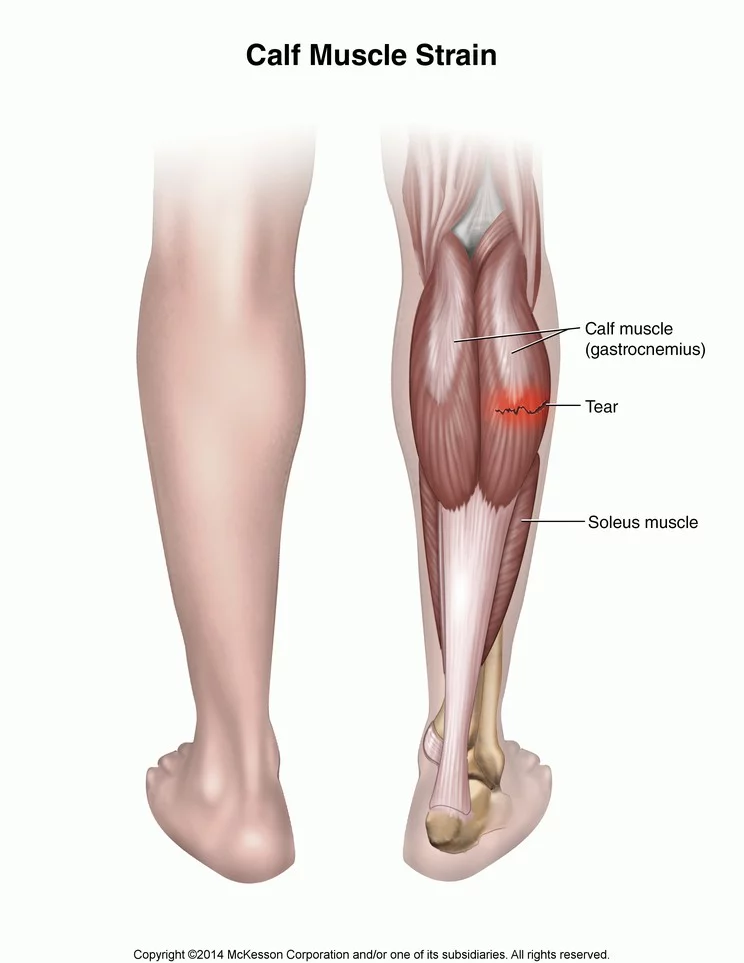
Causes
• Lifting of heavy weight.
• Forceful stretching of the muscle
• Action of antagonizing muscle. (opposite muscle)
• Overstretching of muscle
• Lack of adequate warm-up before activity.
Muscles mostly affected
• Hamstring muscles.
• Quadriceps muscles
• Triceps extensors
Signs and symptoms of strain
• Sharp pain
• Muscle tenderness
• Inability
• Swelling of muscle
First Aid Treatment
• Position the victim comfortably
• Apply a cold compress
• Bandage the affected part
• Seek medical attention
Differences between a sprain and a strain
• Sprain occurs in the joint while strain occurs in the muscle
• In sprain, the ligament is either overstretched or turned while in strain, the muscle fibers are either overstretched or turned.
FRACTURE: - Fracture is a break in the bone of the body. It may be simple or complicated otherwise called compound.
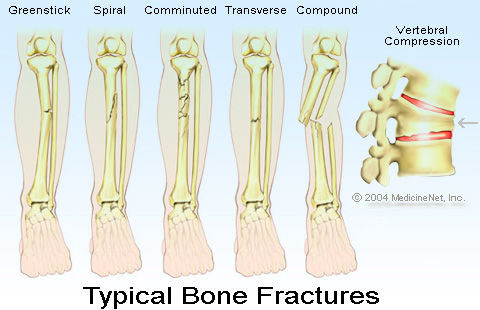
Differences between simple and compound fractures
• In a simple fracture, a bone only broken while in a compound fracture, a broken bone pierces (cut) the skin or tissue.
Type of fracture
• Greenstick fracture
• Simple fracture
• Compound or complicated fracture
• Comminuted fracture
• Impacted fracture
• Depressed fracture
Signs and symptoms of fracture
• Pains
• Deformity
• Abnormal mobility
• Loss of mobility
• Crepitus (sound of bones)
• Bone tenderness
• Discoloration of skin (change of color)
• Bleeding.

https://youtu.be/2v8vlXgGXwE
Evaluation:
(1) What are sports injuries?
(2) List five common sports injuries.
(3) What is fracture?
(4) Name five signs and symptom of fracture.
Assignment:
Objective Test:
(1) The injuries that occur during participation in sports and games due to accident are called ……………. (a) Sport accident (b) Sports injuries (c) Sports hazards (d) Sport dangers
(2) A break in the skin or damage to mucous membrane is ….... (a) Dislocation (b) Cramps (c)Wound (d) Fracture
(3) The displacement one or more bones at a joint is ……… (a) Dislocation (b) Wound (c) Shock (d) Fracture
(4) The twisting or over stretching of the joint is …………… (a) Strain (b) Sprain (c) Fracture (d) Cramps
Essay Test:
(1) Mention six types of wound.
(2) Differentiate between a sprain and a strain.
(3) Explain the following
(a) Impacted fracture
(b) Depressed fracture
(c) Greenstick fracture
(4) Itemize six types of fractures
Topic: COMMON SPORTS INJURIES AND FIRST AID
CONTENT: (a) Common sports injuries
i. dislocation
ii. String
iii. Fracture
(b) First Aid treatment for each sport injury.
INJURY
Injury is damage to any part of the body that may allow the escape of blood as a result of accident.

Factors that cause injury:
Injuries are caused by two major factors:
• The human/man-made elements
• The natural or environmental elements
THE HUMAN ELEMENTS:- These are due to human behavior such as:- ignorance, risk taken, carelessness, overconfidence, inadequate warm-up, miscalculation, disregard to safety rules, drunkenness, effects of drugs, mistakes, and faulty judgments. It is otherwise known as avoidable or man-made accident
THE NATURAL OR ENVIRONMENTAL ELEMENTS: - These are brought about by nature; as a result, they are difficult to control e.g. cyclone, flood, tornado, hurricane, earthquake, land slide, volcanic eruption, heavy rain, thunderstorm, tidal waves etc. However, human elements sometimes aid natural factors. It is otherwise known as unavoidable accident.
Factors that can cause injuries during sports
• Carelessness.
• Fatigue/tiredness
• Poor lighting/ poor visibility in activity area.
• Lack of skills/ lack of knowledge
• Unsafe physical environment/ hazard
• Faulty equipment/ apparatus/ inappropriate costume.
• Lack of instruction/negligence
• Effects of drugs e.g. alcohol
SPORTS INJURIES
What are sports injuries? Sports injuries are the injuries that occur during participation in sports and games due to accident.
Common sports injuries
• dislocation
• strain
• fracture
• wounds
• sprain
• drowning
• muscles cramp
• bleeding

Description of common sports injuries
DISLOCATION: - It is the displacement of one or more bone ends at a joint as a result of injury to the Joint. Common sites of dislocation are – elbow, shoulder, ankle, hip, wrist, toe and finger joints.
Signs and symptoms of dislocation
• Pain
• Swelling
• Discoloration (change in color)
• Tenderness.
• High temperature at the area
• Subluxation (out of alignment)
• Loss of movement
• Bone displacement
• Deformity

First Aid Treatment
Bandage the affected joint
Rub with cold compress
Never attempt to put back the bones
Seek medical attention
STRAIN: It is an injury to the muscle. It occurs in the muscle when a group of muscle is overstretched, the fibers may tear thereby causing an internal bleeding.

Causes
• Lifting of heavy weight.
• Forceful stretching of the muscle
• Action of antagonizing muscle. (opposite muscle)
• Overstretching of muscle
• Lack of adequate warm-up before activity.
Muscles mostly affected
• Hamstring muscles.
• Quadriceps muscles
• Triceps extensors
Signs and symptoms of strain
• Sharp pain
• Muscle tenderness
• Inability
• Swelling of muscle
First Aid Treatment
• Position the victim comfortably
• Apply a cold compress
• Bandage the affected part
• Seek medical attention
Differences between a sprain and a strain
• Sprain occurs in the joint while strain occurs in the muscle
• In sprain, the ligament is either overstretched or turned while in strain, the muscle fibers are either overstretched or turned.

FRACTURE: - Fracture is a break in the bone of the body. It may be simple or complicated otherwise called compound.

Differences between simple and compound fractures
• In a simple fracture, a bone only broken while in a compound fracture, a broken bone pierces (cut) the skin or tissue.
Type of fracture
• Greenstick fracture
• Simple fracture
• Compound or complicated fracture
• Comminuted fracture
• Impacted fracture
• Depressed fracture
Signs and symptoms of fracture
• Pains
• Deformity
• Abnormal mobility
• Loss of mobility
• Crepitus (sound of bones)
• Bone tenderness
• Discoloration of skin (change of color)
• Bleeding.

https://youtu.be/2v8vlXgGXwE
Evaluation:
(1) What are sports injuries?
(2) List five common sports injuries.
(3) What is fracture?
(4) Name five signs and symptom of fracture.
Assignment:
Objective Test:
(1) The injuries that occur during participation in sports and games due to accident are called ……………. (a) Sport accident (b) Sports injuries (c) Sports hazards (d) Sport dangers
(2) A break in the skin or damage to mucous membrane is ….... (a) Dislocation (b) Cramps (c)Wound (d) Fracture
(3) The displacement one or more bones at a joint is ……… (a) Dislocation (b) Wound (c) Shock (d) Fracture
(4) The twisting or over stretching of the joint is …………… (a) Strain (b) Sprain (c) Fracture (d) Cramps
Essay Test:
(1) Mention six types of wound.
(2) Differentiate between a sprain and a strain.
(3) Explain the following
(a) Impacted fracture
(b) Depressed fracture
(c) Greenstick fracture
(4) Itemize six types of fractures
WEEK 6
LESSON 9
Topic: FAMILY LIFE EDUCATION
CONTENT: (a) Meaning and types of family.
(b) Duties of members of the family
(c) Puberty in boys and girls
(d) Pre-marital sex and its health consequences.
(e) Assertiveness and communicable skill.
MEANING AND TYPE OF FAMILY
What is family? The family is a basic unit of the society that is responsible for supporting, caring for and preparing children for adulthood.
It is a group of people that are related to one another by blood, marriage or law. The family is usually the first environment of every child, the personality development of the child is highly influenced by the family. The family is the primary environment in which the child grows.

Types of family
There are two types of family:
• Nuclear family
• Extended family
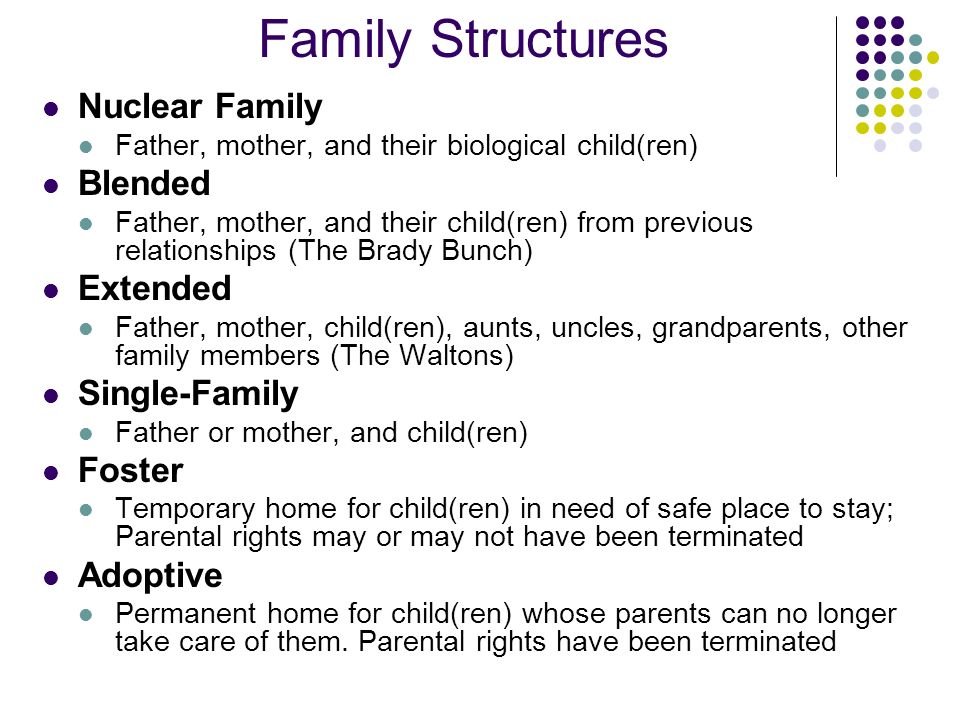
Other types of modern day family
• Foster family
• Adopted family
The nuclear family is made up of the husband, wife and their children.

The extended family consists of the husband, wife or wives, their children, grandparent’s aunts, uncle and cousins. If it is a polygamous family, it will include co-wives and their children. This type of family provides care and social support for dependent relatives and interdependency among all members of the family unit.
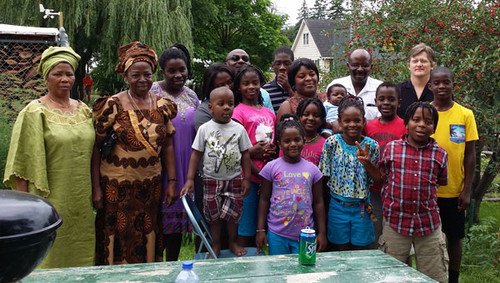
The foster family is made up of adults acting as parents to children who may or may not be related to them, compensations are awarded to the parents
Adopted family: Children whose biological parents are unable to cater for are given out to another family by legal action. In adopted family, children are given rights of a child born into the family. The parents receive no compensations but are expected to exercise all the duties of natural parents.
ROLE AND RESPONSIBILITIES OF EACH MEMBER
Every member has a role to play within the family. The parent is to provide love, food, clothes, shelter and guidance. The role of the child is to be obedient assist with household chores and childcare, perform well in school and prepare for a meaningful adult life.
Responsibilities of the family
• It is the responsibility of the family to raise children
• To care for the child from childhood till he is old enough to care for himself
• It is responsible for the education of the child
• It is responsible for the transmission of societal norms and culture to the child
• It is the responsibility of the family to provide emotional, psychological, moral and material support to the child
• It is responsible for the provision of physical security such as food, clothing shelter and other needs.
Roles of the father
• Provision of food, shelter, and money for the family
• Making important decisions

Roles of the mother
• Preparation of food
• Keeping the house in order
• Nurturing and raising children
• Teaching the children morals and values
Note: Many of the above should be in conjunction with the father.

Roles of the children
• Obeying their parents.
• Assisting in performing household chores such as laundry, washing the car, cooking and gardening
• performing well in school
• Living up to family expectations.

PUBERTY
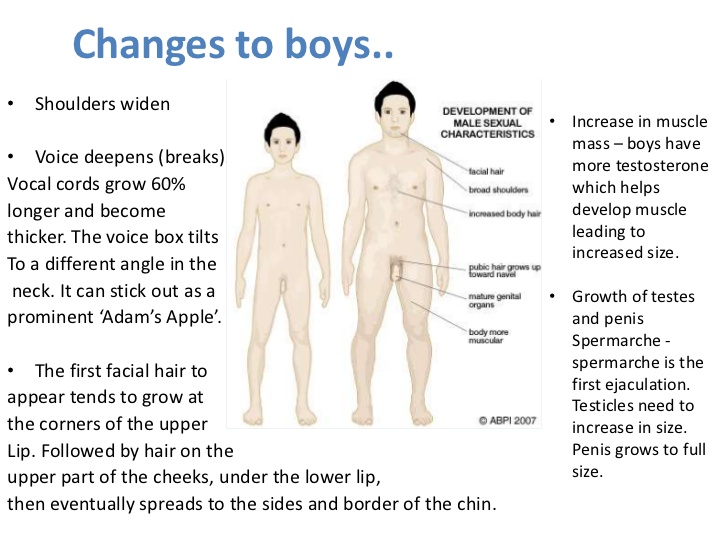
What is Puberty? Puberty is the time in your life when your body starts changing from that of child to an adult. While there is no right time for puberty to begin, girls usually start a little earlier than boys – usually between 8and 13 years of age. Puberty for boys usually starts at about 10 to 14 years of age.

Physical changes that take place in boys
• A boy’s voice gets deeper
• His muscle develop
• His chest gets broader
• Hair starts to grow under his arms, on his legs and face
• During this time his penis and testicles will also grow bigger and longer
Hair, often called public hair, will also start to grow at the base of his penis. He will start to have erections and he may have wet dreams.
Physical changes that take place in girls during puberty
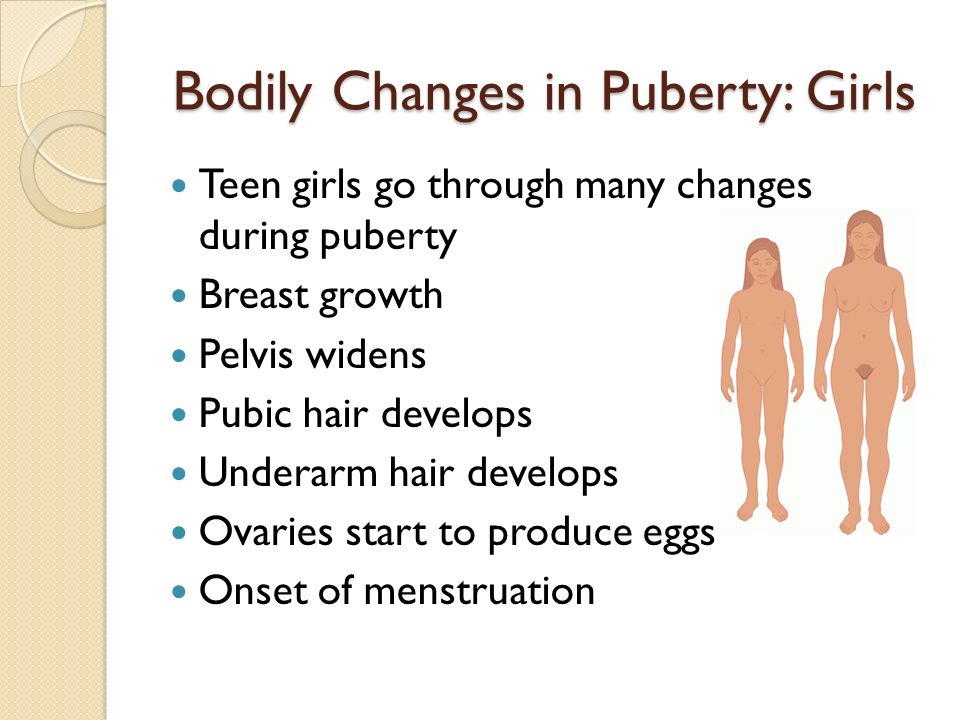
• A girl breasts will start to grow
• Her hips get rounder
• Hair will start to grow under her arms. Hair, often called public hair, will also grow between her legs. She will also start to have periods.
PREMARITAL-SEX
Sex: The sexual urge or instinct as it manifests itself in behavior.
Premarital-sex is the sexual intercourse between parties not married to each other.
Adultery: sexual intercourse between a married person and one other than the lawful spouse.
HEALTH CONSEQUENCES OF PREMARITAL SEX
• Unwanted pregnancies
• Unwanted child
• Life- long emotional effects
• Sexually transmitted diseases


Evaluation:
(1) What is family?
(2) Explain types of families.
(3) List and explain duties of each member in the family
READING ASSIGNMENT: Bounty Upper Basic PHE for Js 3 pg 41-45
Assignment:
Objective Test:
(1) A basic unit of the society that is responsible for supporting, caring and preparing children for adulthood is……………….. (a) Age (b) family (c) Status (d) Call
(2) How many types of family do we have? ............. (a) 3 (b) 2 (c) 4 (d) 5
(3) The type of family that consists of father, mother and their children is …………. (a) Nuclear family (b) Extended family (c) monogamous family (d) Casual family
(4) The following are physical changes in boys except……… (a) Testicular enlargement (b) Boy voice gets deeper (c) Muscles develop (d) Vagina develops
Essay Test:
(1) Differentiate between puberty in boys and girls
(2) List four consequences of pre-marital sex.
Topic: FAMILY LIFE EDUCATION
CONTENT: (a) Meaning and types of family.
(b) Duties of members of the family
(c) Puberty in boys and girls
(d) Pre-marital sex and its health consequences.
(e) Assertiveness and communicable skill.
MEANING AND TYPE OF FAMILY
What is family? The family is a basic unit of the society that is responsible for supporting, caring for and preparing children for adulthood.
It is a group of people that are related to one another by blood, marriage or law. The family is usually the first environment of every child, the personality development of the child is highly influenced by the family. The family is the primary environment in which the child grows.

Types of family
There are two types of family:
• Nuclear family
• Extended family

Other types of modern day family
• Foster family
• Adopted family
The nuclear family is made up of the husband, wife and their children.

The extended family consists of the husband, wife or wives, their children, grandparent’s aunts, uncle and cousins. If it is a polygamous family, it will include co-wives and their children. This type of family provides care and social support for dependent relatives and interdependency among all members of the family unit.
The foster family is made up of adults acting as parents to children who may or may not be related to them, compensations are awarded to the parents
Adopted family: Children whose biological parents are unable to cater for are given out to another family by legal action. In adopted family, children are given rights of a child born into the family. The parents receive no compensations but are expected to exercise all the duties of natural parents.
ROLE AND RESPONSIBILITIES OF EACH MEMBER
Every member has a role to play within the family. The parent is to provide love, food, clothes, shelter and guidance. The role of the child is to be obedient assist with household chores and childcare, perform well in school and prepare for a meaningful adult life.
Responsibilities of the family
• It is the responsibility of the family to raise children
• To care for the child from childhood till he is old enough to care for himself
• It is responsible for the education of the child
• It is responsible for the transmission of societal norms and culture to the child
• It is the responsibility of the family to provide emotional, psychological, moral and material support to the child
• It is responsible for the provision of physical security such as food, clothing shelter and other needs.
Roles of the father
• Provision of food, shelter, and money for the family
• Making important decisions

Roles of the mother
• Preparation of food
• Keeping the house in order
• Nurturing and raising children
• Teaching the children morals and values
Note: Many of the above should be in conjunction with the father.

Roles of the children
• Obeying their parents.
• Assisting in performing household chores such as laundry, washing the car, cooking and gardening
• performing well in school
• Living up to family expectations.

PUBERTY
What is Puberty? Puberty is the time in your life when your body starts changing from that of child to an adult. While there is no right time for puberty to begin, girls usually start a little earlier than boys – usually between 8and 13 years of age. Puberty for boys usually starts at about 10 to 14 years of age.

Physical changes that take place in boys
• A boy’s voice gets deeper
• His muscle develop
• His chest gets broader
• Hair starts to grow under his arms, on his legs and face
• During this time his penis and testicles will also grow bigger and longer
Hair, often called public hair, will also start to grow at the base of his penis. He will start to have erections and he may have wet dreams.

Physical changes that take place in girls during puberty
• A girl breasts will start to grow
• Her hips get rounder
• Hair will start to grow under her arms. Hair, often called public hair, will also grow between her legs. She will also start to have periods.

PREMARITAL-SEX
Sex: The sexual urge or instinct as it manifests itself in behavior.
Premarital-sex is the sexual intercourse between parties not married to each other.
Adultery: sexual intercourse between a married person and one other than the lawful spouse.
HEALTH CONSEQUENCES OF PREMARITAL SEX
• Unwanted pregnancies
• Unwanted child
• Life- long emotional effects
• Sexually transmitted diseases


Evaluation:
(1) What is family?
(2) Explain types of families.
(3) List and explain duties of each member in the family
READING ASSIGNMENT: Bounty Upper Basic PHE for Js 3 pg 41-45
Assignment:
Objective Test:
(1) A basic unit of the society that is responsible for supporting, caring and preparing children for adulthood is……………….. (a) Age (b) family (c) Status (d) Call
(2) How many types of family do we have? ............. (a) 3 (b) 2 (c) 4 (d) 5
(3) The type of family that consists of father, mother and their children is …………. (a) Nuclear family (b) Extended family (c) monogamous family (d) Casual family
(4) The following are physical changes in boys except……… (a) Testicular enlargement (b) Boy voice gets deeper (c) Muscles develop (d) Vagina develops
Essay Test:
(1) Differentiate between puberty in boys and girls
(2) List four consequences of pre-marital sex.
WEEK 7
LESSON 10
Topic: Physical Education, Health Education, Agency and Career Opportunity:
(a)Sport promotion agency and body in Nigeria
(i) Sport Association
(ii) NAPHER
(iii) Nigeria Institute of Sport
(b) Agency and Organization that promote Health Education in Nigeria
(i) NSHA
(ii) NAHET
(iii) Ministry of Health
(iv) NDLEA
(v) Road Safety Corps
(vi) NAFDAC
(vii) UNIESCO
(viii) USAID
(ix) WHO
(x) IICA
(xi) UNWEF
(c) Career Opportunity in Health Education.
NEEDS FOR PROMOTION OF SPORTS IN OUR SOCIETY
• Apart from the life-enriching and fulfilling role of sport
• It is also part of man’s common culture in that it responds to an inherent human physical and mental desire.
• As well as being a way of responding to the inherent desire in human to move their bodies
• It fosters stamina and physical strength
• Relieves mental stress
• Helps to prevent the habitual lifestyle diseases
• It enhances the nation’s interest in sport.
• Makes a deep emotional impression.
• It fosters sense of personal responsibility
• And self-control and a spirit of fair-play
• Sport also fosters in the young communication ability.
• A sound education for children and youths
• Promotion of a new sense of cohesion in our regional communities.
• Create employment opportunities
• Contributes to the economic development of our country
• Is one element of the world’s cultural heritage
• Contributory element in fostering international friendship.
SPORT PROMOTION AGENCIES AND BODIES IN NIGERIA
• Nigeria sports association
• Nigeria association of physical health education and recreation (NAPHER)
• Nigeria institute of sports.

AGENCIES/ ORGANIZATION PROMOTING HEALTH EDUCATION IN NIGERIA
• Ministry of health
• Nigeria drug law enforcement agencies (NDLEA)
• Road safety corps
• National agency for food, drug administration and control (NAFDAC)
• United nations educational, scientific and cultural organization(UNESCO)
• United states agency for international development (USAID)
• World health organization.(WHO)
• Japan international cooperation agency (JICA)
• The united nations children’s funds(UNICEF)

CAREER OPPORTUNITY IN PHYSICAL EDUCATION
• Coaching
• Training
• Sport journalism
• Teaching
• Editing/publishing
CAREER OPPORTUNITY IN HEALTH EDUCATION
• Teaching
• Health journalism
• Editing/ publishing of health materials
• Social work
• Community development
Evaluation
(1) List three agencies promoting Health Education in Nigeria
(2) List two career opportunities in physical Education
READING ASSIGNMENT: Bounty Upper Basic PHE for Js 3 pg 47-49
Assignment
(1) Mention three agencies promoting sports in Nigeria
Topic: Physical Education, Health Education, Agency and Career Opportunity:
(a)Sport promotion agency and body in Nigeria
(i) Sport Association
(ii) NAPHER
(iii) Nigeria Institute of Sport
(b) Agency and Organization that promote Health Education in Nigeria
(i) NSHA
(ii) NAHET
(iii) Ministry of Health
(iv) NDLEA
(v) Road Safety Corps
(vi) NAFDAC
(vii) UNIESCO
(viii) USAID
(ix) WHO
(x) IICA
(xi) UNWEF
(c) Career Opportunity in Health Education.
NEEDS FOR PROMOTION OF SPORTS IN OUR SOCIETY
• Apart from the life-enriching and fulfilling role of sport
• It is also part of man’s common culture in that it responds to an inherent human physical and mental desire.
• As well as being a way of responding to the inherent desire in human to move their bodies
• It fosters stamina and physical strength
• Relieves mental stress
• Helps to prevent the habitual lifestyle diseases
• It enhances the nation’s interest in sport.
• Makes a deep emotional impression.
• It fosters sense of personal responsibility
• And self-control and a spirit of fair-play
• Sport also fosters in the young communication ability.
• A sound education for children and youths
• Promotion of a new sense of cohesion in our regional communities.
• Create employment opportunities
• Contributes to the economic development of our country
• Is one element of the world’s cultural heritage
• Contributory element in fostering international friendship.
SPORT PROMOTION AGENCIES AND BODIES IN NIGERIA
• Nigeria sports association
• Nigeria association of physical health education and recreation (NAPHER)
• Nigeria institute of sports.

AGENCIES/ ORGANIZATION PROMOTING HEALTH EDUCATION IN NIGERIA
• Ministry of health
• Nigeria drug law enforcement agencies (NDLEA)
• Road safety corps
• National agency for food, drug administration and control (NAFDAC)
• United nations educational, scientific and cultural organization(UNESCO)
• United states agency for international development (USAID)
• World health organization.(WHO)
• Japan international cooperation agency (JICA)
• The united nations children’s funds(UNICEF)

CAREER OPPORTUNITY IN PHYSICAL EDUCATION
• Coaching
• Training
• Sport journalism
• Teaching
• Editing/publishing
CAREER OPPORTUNITY IN HEALTH EDUCATION
• Teaching
• Health journalism
• Editing/ publishing of health materials
• Social work
• Community development
Evaluation
(1) List three agencies promoting Health Education in Nigeria
(2) List two career opportunities in physical Education
READING ASSIGNMENT: Bounty Upper Basic PHE for Js 3 pg 47-49
Assignment
(1) Mention three agencies promoting sports in Nigeria
WEEK 8
LESSON 11
TOPIC: AGEING AND DEATH EDUCATION
CONTENT: (a) Description of Ageing and Death
(b) Life exchanging measure against ageing: Exercise, Nutrition, Rest and Sleep
(c) Supporting a dying people
(d) Supporting a grieving and ageing person
DESCRIPTION OF AGEING AND DEATH
Ageing is the process of growing old reaching the end of useful life. It is also a time in life where one becomes obsolescent.
Death is the termination of the biological functions that define living organisms. Death begins when the heart stops beating. Death is a process rather than events.

LIFE ENHANCING MEASURE AGAINST AGEING
• Rest and sleep
• Exercise
• Nutrition
• Greater participation in activities
• Having more close friends
• Visiting with family
• Addressing basic needs
• Promotes healthy behaviors

SUPPORTING DYING PEOPLE
• Be there consistently, as often as the patient wants, and as frequently as the time schedule permits.
• Maintain contact on a regular basis, over a period of time, so the dying person will feel comfortable with sharing thoughts, fears, feelings, wishes, dreams and hopes
• Listen more than talk. Follow the dying person’s agenda as time is spent with them.
• Let them also know who is in the room ;tell him or her who is touching an arm or patting a shoulder
• Remind them of the time and date.
• It is very important, especially during the hours and minutes immediately preceding death, that arrangements be made for the patient and family members, friends, spouse, and partners to have time alone with the patient to hold, to touch, to say things one last time before they part

SUPPORTING A GRIEVING AND AGEING PERSON
• Social support
• Good self-care
• The passage of time
• Contact a counselor
• Contact bereavement support group for help.
Evaluation:
(1) What is ageing?
(2) Write short note on death.
READING ASSIGNMENT: Bounty Upper Basic PHE for Js 3 pg 51-57
Assignment
(1) State three steps to support dying person.
(2) List four life enhancing measure against ageing
TOPIC: AGEING AND DEATH EDUCATION
CONTENT: (a) Description of Ageing and Death
(b) Life exchanging measure against ageing: Exercise, Nutrition, Rest and Sleep
(c) Supporting a dying people
(d) Supporting a grieving and ageing person
DESCRIPTION OF AGEING AND DEATH
Ageing is the process of growing old reaching the end of useful life. It is also a time in life where one becomes obsolescent.

Death is the termination of the biological functions that define living organisms. Death begins when the heart stops beating. Death is a process rather than events.

LIFE ENHANCING MEASURE AGAINST AGEING
• Rest and sleep
• Exercise
• Nutrition
• Greater participation in activities
• Having more close friends
• Visiting with family
• Addressing basic needs
• Promotes healthy behaviors

SUPPORTING DYING PEOPLE
• Be there consistently, as often as the patient wants, and as frequently as the time schedule permits.
• Maintain contact on a regular basis, over a period of time, so the dying person will feel comfortable with sharing thoughts, fears, feelings, wishes, dreams and hopes
• Listen more than talk. Follow the dying person’s agenda as time is spent with them.
• Let them also know who is in the room ;tell him or her who is touching an arm or patting a shoulder
• Remind them of the time and date.
• It is very important, especially during the hours and minutes immediately preceding death, that arrangements be made for the patient and family members, friends, spouse, and partners to have time alone with the patient to hold, to touch, to say things one last time before they part

SUPPORTING A GRIEVING AND AGEING PERSON
• Social support
• Good self-care
• The passage of time
• Contact a counselor
• Contact bereavement support group for help.
Evaluation:
(1) What is ageing?
(2) Write short note on death.
READING ASSIGNMENT: Bounty Upper Basic PHE for Js 3 pg 51-57
Assignment
(1) State three steps to support dying person.
(2) List four life enhancing measure against ageing