LESSON 5
TOPIC:
THE HAIR AND EYES
CONTENT: 1. Structure, functions, care and grooming of the hair.
2. Structure, functions, care and grooming of the eye.
Structure, functions, Care and grooming of the hair:
Human hair is mostly found on the head. It is one of the beautiful assets on a human body; it makes an individual attractive when it is well cared for.
The structure of the hair:
Hair grows from a hair pit/narrow tube inside the skin called follicles. Each follicle has at its side tiny oil glands, which produces oil. The oil helps to lubricate the hair and keep the skin around it soft and smooth.
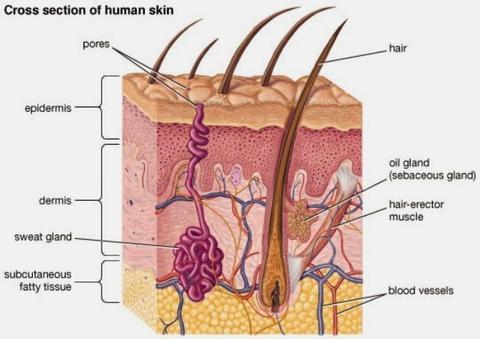 Types of Hair:
Types of Hair:
Hair comes in different colours, textures, shades, and length depending on race, food, health condition, ageing and care.
We shall however discuss the types of hair under:
a.
Dry Hair: it is usually dry, dull, and unattractive, Causes could include insufficient production of oil, illness, poor food etc, from the oil gland.
b.
Greasy or oily Hair: caused by over active oil gland, which produces more than is needed.
c.
Soft Hair: usually very light and silky when touched and can be blown by wind.
d.
Tough/Coarse Hair: usually very thick and difficult to comb or manage.
e.
Short Hair: this is hair, which is cut and kept short. It is easier to care for than long hair.
f.
Long Hair: it can result from heredity, good food, care etc.
Hair type can also be artificial if it has been changed using hair chemicals, or when another thing is attached to the hair .For example wig and attachment.
 Functions of the hair
Functions of the hair
1. It protects the head.
2. It keeps the head warm in cold weather.
3. It improves personal appearance and adds beauty to a person.
 Care and grooming of the Hair
Care and grooming of the Hair
Whatever the type of hair, it is necessary to keep the hair clean and tidy. The following should be done to achieve beautiful hair.
1. Brush or comb your hair daily. It stimulates the flow of blood and helps to remove dandruff.
2. Hair should be washed frequently with shampoo at least once a week and preferably during the day.
3. Long hairs should be well drained after washing before tying it up.
4. Hair should be oiled regularly to stimulate the scalp except for persons with greasy or oily hair.
5. Plait, style or pack your hair neatly.
Simple and complex hair care equipment and materials include: combs, brushes, mirrors, plaiting threads, towels, hair dryer, hair sprays, pins, clips etc


Activities
Students should divide the hair equipment into simple and complicated.
Identify 3 people in your class and the type of the hair they have.
Evaluation
1. Describe the hair structure.
2. ------- under the follicle produces oil for the hair.
3. List 5 types of hair.
4. Mention 5 ways of caring for the hair.
5. State 5 materials and 2 equipments for hair care.
Reading assignment
Popoola o.o. Home Economics for JSS Book 1pages 20-22
LESSON 6
Structure, functions, care and grooming of the eye.
This week as a continuation on the study of the human body, we shall discuss on the structure, function and care of the eyes:
 The Structure of the Eyes
The Structure of the Eyes
The eye is made up of different parts. Each part performs different roles in helping us to see. The parts of the eyes are: Iris, Cornea, Lens, Retina, Optic nerve, Pupil, Tear gland, the eye ball, Eyebrow, Eyelashes, Aqueous and Vitreous humors.
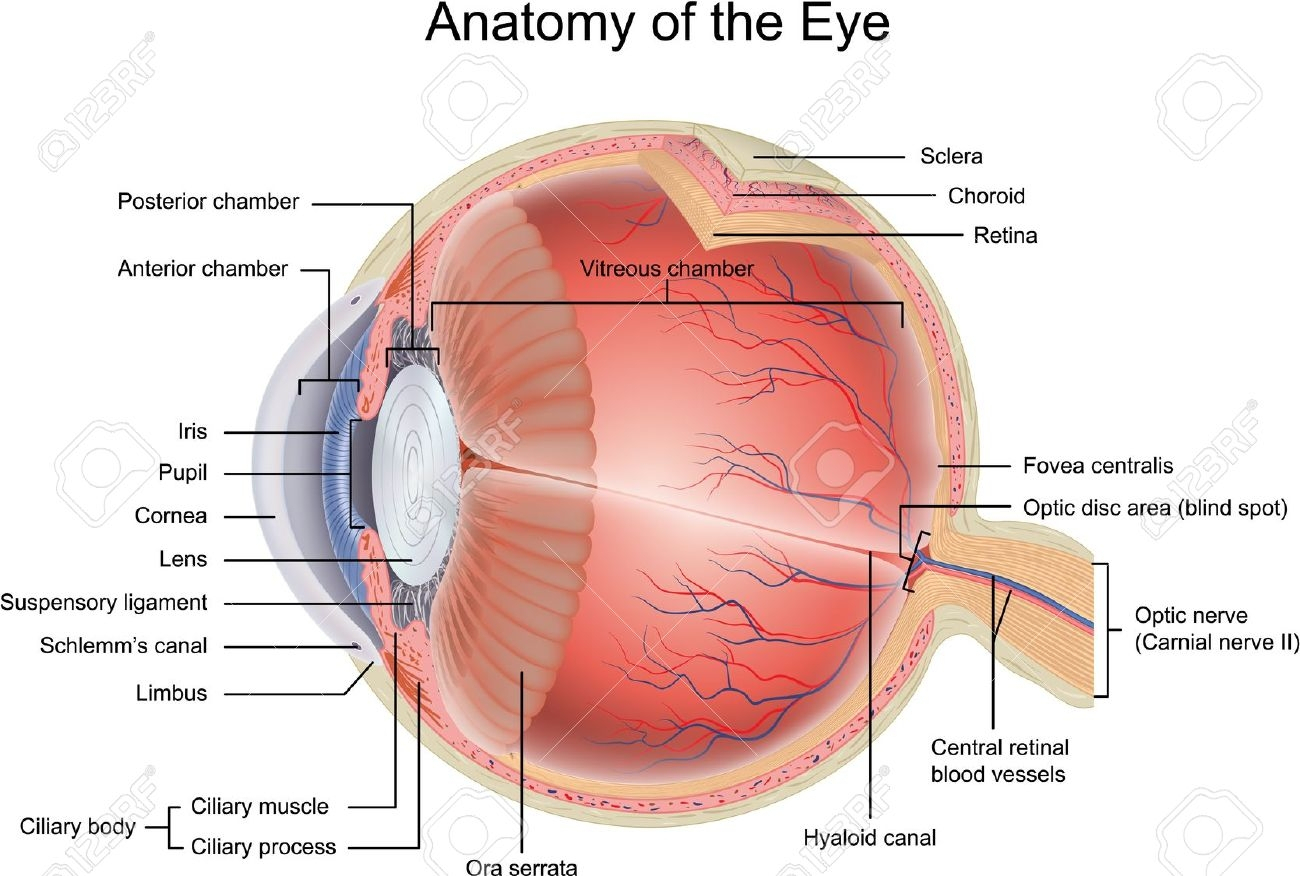
PARTS OF THE EYES FUNCTIONS
The Iris ---- This is the coloured part of the eye. It surrounds the pupils and helps it to regulate the pupils to darken or brighten.
Cornea- ----The cornea is a protective layer. It helps to keep dirt and dust away from the pupils.
Lens ----- This is the glass-like part of the eyes. It helps the eyes to see things that are so far or nearby changing their size.
Pupils- ----This is the hole in front of the eyeball through which light enters the eyes.
Optic nerve ----- This part of the eye is a sensory nerve, which links the eyeball to the brain.
Retina ----- This is a sensitive spot in the eye where images are formed.
Tear gland- ---- This gland helps to pour out tear over the front of the eye. The tears poured out, helps to wash away dusts, which enters the eyes.
Eyes lashes- ---- These are the hair at the lid. They help to protect the eye from dirt and dust.
The eye balls- ---- These are the organs of sight connected to the brain through the optic nerve.
Eye lid ----- This is the skin covering the eyeball. It can be closed to prevent foreign objects from entering the eyes.
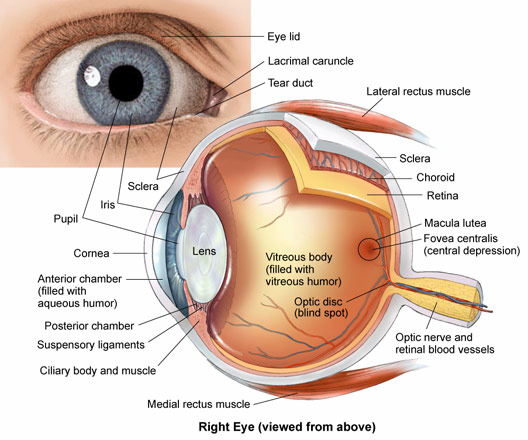
Generally, the eye helps us to see.
Care and grooming of the eye.
To care for the eyes we should;
I. Use good light when reading or sewing to avoid straining the eyes.
II. Eat foods rich in Vitamin A, such as green vegetables, palm oil etc.
III. Avoid looking directly at very bright light e.g. light from electricity, welders, sunlight etc.
IV. Avoid washing our eyes with disinfectants except at the prescription of an optician/ophthalmologist.
V. Avoid reading small prints for long period; doing this strains the eyes.
VI. Avoid rubbing the eye when there is something in it. It is better to remove the object dipping the eye in a clean bowl of water with frequent blinking.
VII. Relax the eyes by looking up from time to time when watching TV, reading books, writing or sewing.
VIII. Avoid holding a book or work too near to the face as doing that may strain the eyes.
IX. Wear glasses if you are so directed by the optician and make sure your glasses are always kept clean.
X. See an optician in case you have sore watering eyes when reading

Lack of care for the eye could lead to:
(1) Poor eye sight.
(2) Wearing of glasses.
(3) Blindness.
(4) Eye infection.
(5) Short sightedness / myopia (inability to see objects that are far away).
(6) Long sightedness / hypermetropia (inability to see objects that are near).
Conjunctivitis (a contagious disease that causes a lot of itching in the eye).
Evaluation
1. List 7 parts of the eye and state their functions.
2. The eyes is the organ of…….
3. Mention four problems of the eye due to lack of proper care.
4. State five ways to care for the eyes.
5. Is it proper to use another person’s face towel?
6. Name one contagious disease of the eye
Reading assignment
Popoola o.o. Home Economics for JSS Book 1pages 23-24
Assignment
Popoola O.O. Workbook on Home Economics New Concepts for JSS Book 1 Unit 3 Pages 4-6.