LESSON 21
TOPIC: WORK, ENERGY AND POWER
CONTENT:
1. Concept of work, energy and power.
2. Meaning of potential and kinetic energy.
3. Calculations involving work-done.
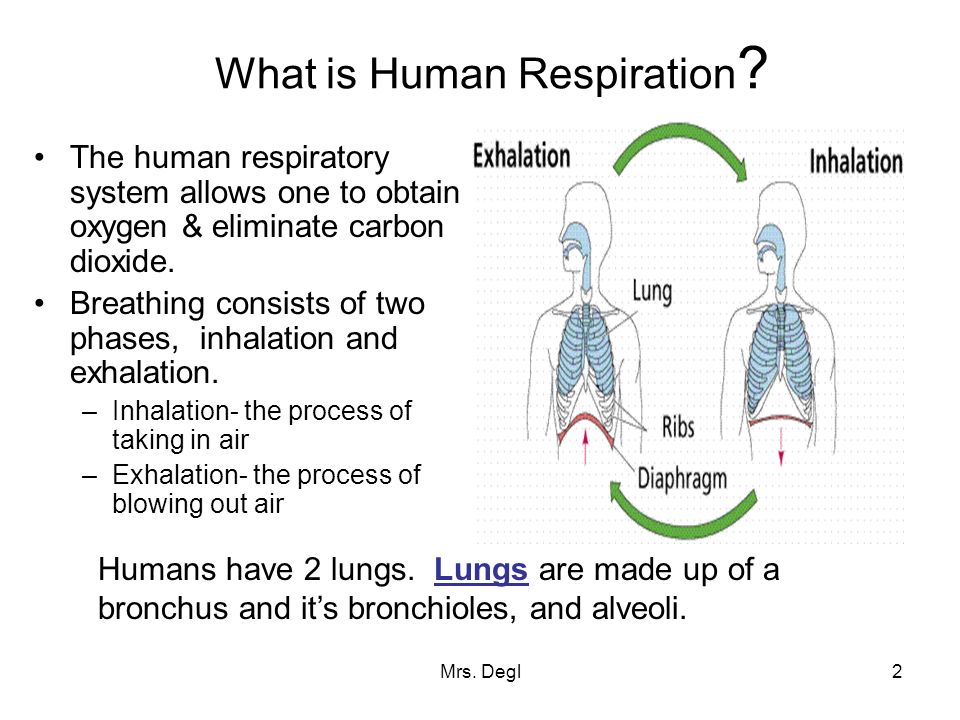
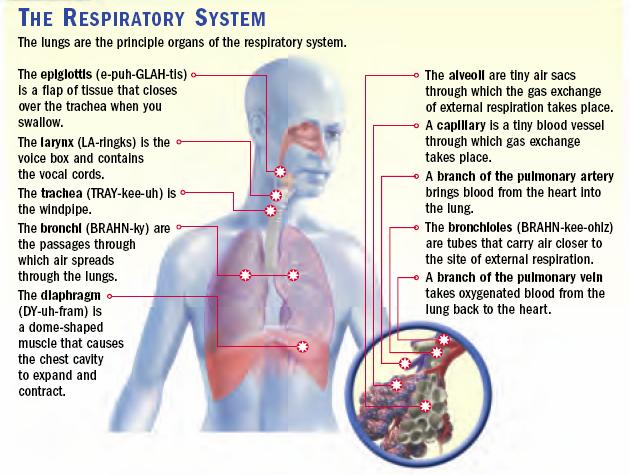
CONCEPT OF WORK, ENERGY AND POWER
WORK
Work is said to be done whenever a force or load moves through a distance. i.e. work=force x distance moved in the direction of the force(fxd).

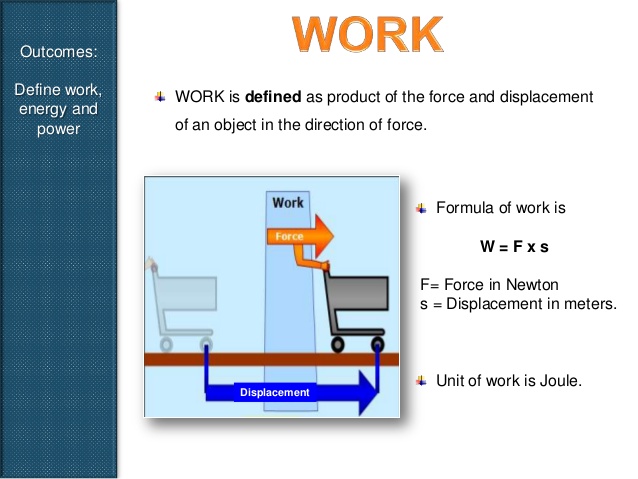
Mathematically
W(d)=fxd
The unit of work is joules with symbol J.
Force
Force is that which changes a body’s state of rest or uniform motion in a straight line. It can as well be expressed as:
Force = mass x acceleration
i.e. F = m x a
where: F = force, M=mass and A=acceleration
The unit of force is Newton(N).
If force = mass x acceleration
Work can be given as: Work = Mass x acceleration x distance.
This is a simple formula that can be used to calculate work done especially against gravity.
 ENERGY
ENERGY
Energy is the capacity for doing work or the ability to do work. Energy has the same unit as work, that is, energy is measured in joules.
PRINCIPLE OF CONSERVATION OF ENERGY
It states: Energy cannot be created or destroyed but can be converted from one form to another.
 FORMS OF ENERGY
FORMS OF ENERGY
Mechanical energy
Light energy
Sound energy
Electrical energy
Heat energy
Nuclear energy
Magnetic energy
Chemical energy
Solar energy
These forms of energy are very useful to us in our daily activities. We derive comfort or pleasure from electrical and sound energy produced from the oxidation of food in our body tissues and it is utilized in doing work.
POWER
Power is defined as the rate at which work is done or the rate of transfer of energy or the rate of doing work. i.e. work done divided by time
Power = (workdone or energy transferred)/(time taken)
The S.I unit of power is watt (w).The larger units are kilowatt (KW) Such as electric bulb used in our homes are usually rated at 40w or 60w.
![Image]()
2.
KINETIC ENERGY: This is the energy possessed by reason of motion. Moving objects possess kinetic energy. The stored potential energy in the springs of clock and wristwatches gradually changes to kinetic energy as it winds.
The amount of kinetic energy possessed by a body is dependent on its mass and the velocity with which it is moving. To this end, the kinetic energy of a moving object with mass “M” traveling with a velocity ‘v’ is written by the formula given below

kinetic energy (k.e)= 1/2mv2
where,
m=mass of an object
v=velocity of an object
EVALUATION
1.Explain these words with appropriate examples.
(a)Potential energy
(b)Kinetic energy
LESSON 23
CALCULATIONS INVOLVING WORK-DONE
What work is done when a mass of 5.00kg is raised through a vertical height of 2.5m (acceleration due to gravity is 10m/sec)?
Solution
Work-done = mass acceleration × distance
Since force = mass × acceleration
W(d) =mass accel. distance
=5.00kg 10m/s2 2.5m
=125joules
2. Calculate the work-done by a body of weight 200N which, moves through a distance of 12N
Solution
Force=200N
Distance moved=12m
Work-done=force distance moved
=(200 12)joules
=2400joules
ENERGY TRANSFER WHEN WORK IS DONE
1. As the watch ticks working by moving the hands, the stored energy called potential energy has been converted to kinetic energy.
2. The chemical energy in petrol is converted into heat in the engine, which makes the car moves.
3. Torch light store chemical energy which is converted to electrical energy, then to heat and light which provides us light to see at night.
4. In riding a bicycle, the rider provides chemical energy which changes to mechanical energy as the .rider pedals the bicycle and the pedaling gives rise to a forward movement (kinetic energy) therefore work has taken place.
 Force and Motion
Force and Motion
Force makes things move. When you ride a bicycle, the force of pushing the pedal causes the bicycle to go in motion.
 LESSON 24
LESSON 24
SPECIFIC TOPIC: Renewable and non-renewable energy
REFERENCE BOOK: Nigerian Basic Science Project Pupils textbook1 by STAN
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVE: At the end of the lesson the students should be able to:
a. Explain renewable and non-renewable energy
b. Mention examples of renewable and non-renewable energy
CONTENT: Renewable energy
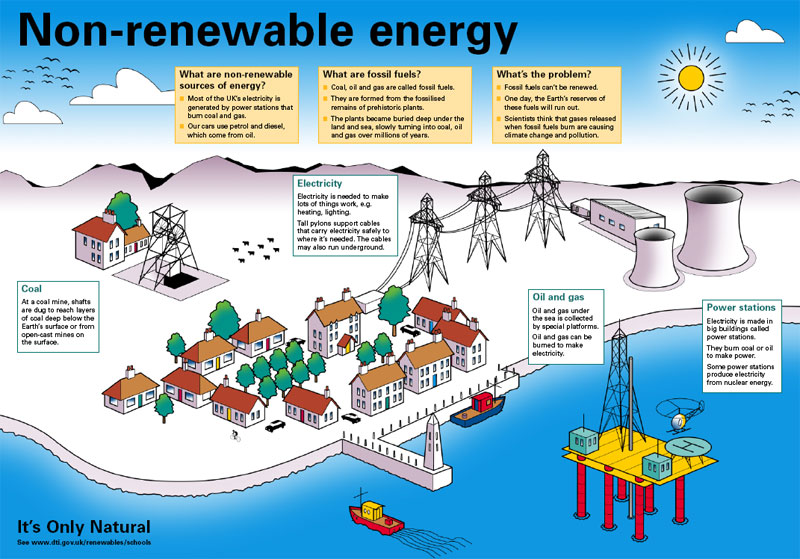
Renewable energy are the types of energy that last for a life time. Renewable energy are clean and does not cause pollution. Renewable energy is cheap once it is installed. Examples of renewable energy are: wind energy, water i.e. Hydro-electric dam
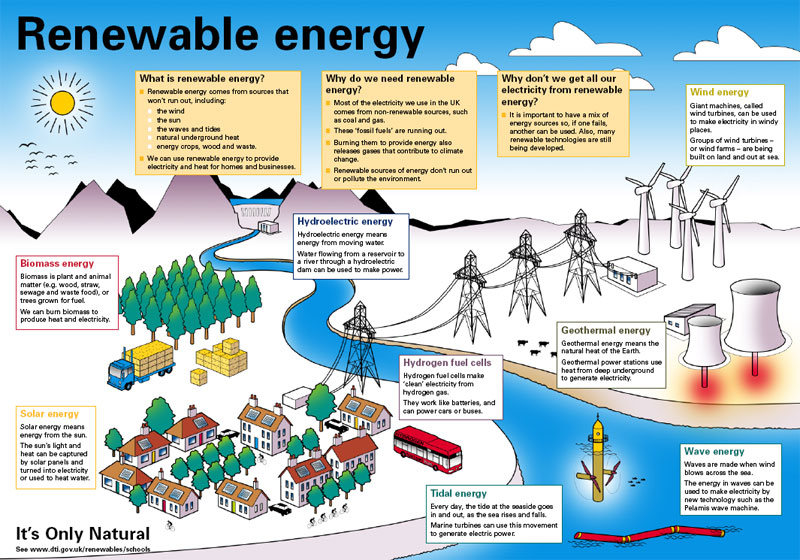
Non-renewable energy: is the type of energy that cannot last for. It forever causes pollution and is expensive. Examples are crude oil, coal firewood etc
EVALUATION
a. Explain renewable and non-renewable energy
b. Give examples of renewable and non-renewable energy
further studies
http://www.eia.gov/kids/
http://www.childrensuniversity.manchest ... renewable/
http://www.ecofriendlykids.co.uk/renewa ... urces.html
practice test
http://www.darvill.clara.net/altenerg/mainquiz.htm
http://www.proprofs.com/quiz-school/sto ... -resources
http://www.quia.com/quiz/106563.html?AP_rand=278326452
LESSON 25
MAIN TOPIC: Wildlife conservation
SPECIFIC TOPIC: Man's activities affecting wildlife
REFERENCE BOOK: Integrated science for JSCE by Adebayo Begun
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVE: At the end of the lesson the students should be able to:
a. Enumerate man's activities affecting wildlife
b. Mention game reserves in Nigeria.
CONTENT: Games reserves national park and 2003 in Nigeria
Name...................State..................Status
Kainji lake............Niger..................National park
Old Oyo...............Oyo....................National park
Yankari................Bauchi................National park
Okpara................Oyo....................Game reserves
Kogin kano............Kano..................Game reserves
Orle river.............Edo....................Game reserves
Obudu ...............Cross River.............Cattle ranch
Ikogosi ...............Ekiti ..................Warm Spring
U.I zoo................Oyo....................Zoo
Jos wildlife park...Plateau..............National park
Man's activities, affecting wildlife
1. Uncontrolled and indiscriminate hunting for meat
2. Sport hunting of wildlife and fish
3. Burning of bush
4. Industrialization projects
5. Pollution through air
 GAME RESERVES IN NIGERIA
GAME RESERVES IN NIGERIA
Nigeria has eight national parks and game reserves spread throughout the country. The parks make up about 3 percent of Nigeria's total land area. Collectively they contain an abundant diversity of fauna like buffaloes, roan antelopes, chimpanzees, crocodiles, hippopotamuses, hyenas, giant forest hogs, lions and leopards, as well as flora.
Chad Basin
Established in 1991, Chad Basin is located in the Borno and Yobe States. The park includes the Sambisa game reserve and parts of the Hadejia-Nguru wetlands. It is an important sanctuary for migratory birds and a total of 377 species of birds have been recorded.
Cross River
The largest rain forest in Nigeria and the oldest surviving one in Africa is located in Cross River National Park. Sharing its name with the state, Cross River also was established in 1991 and has the highest tropical biodiversity in Africa. Twenty percent of the world’s total known species of butterflies reside in Cross River.
Gashaka Gumti
The largest national park in Nigeria, established in 1991, is located in the Taraba and Adamawa states and along the Cameroon border. It contains grasslands as well as the country's highest peak, Chappal Waddii known as the “Mountain of Death,” with an elevation of 7,936 feet.
Kainji
Establish in 1979, Kainji is the oldest national park. The second largest park can be found in the Niger and Kwara states. Inside the park, visitors will find the Kainji Lake, the Borgu and Zugurma game reserves.
Kamuku
Founded in 1999, Kamuku is in the Kaduna State, the park is easily accessible thanks to the Kaduna International Airport situated close by. The vegetation is a savannah woodland populated with a large variety of birds, as well as elephants, roan antelopes, mountain reedbucks, side stripped hyenas and jackals.
Okomu
This small park, totaling only 44,726 acres, is part of the larger Okomu forest reserve. It is the second largest rain forest in Nigeria and a great place for bird and primate watching as it is largely undisturbed. Okomu is located in the state Edo and was established in 1999.
Old Oyo
Found in the states Oyo and Kwara, Old Oyo was established in 1991. The largest collection of archaeological and cultural sites of Nigeria are located in Old Oyo including the royal cemeteries and the walls that surrounded the former ancient capital city.
Yankari
Situated in the state of Bauchi, Yankari is the premier game reserve, which first opened to the public in 1962. It boasts the largest population of elephants in West Africa as well as several endangered species like the leopard.
EVALUATION:
a. State man's activities that affects wildlife
b. Mention game reserves, parts and zoos in Nigeria
LESSON 26
MAIN TOPIC: Balance in Nature
SPECIFIC TOPIC: COMMUNITY
REFERENCE BOOK: Integrated Science for Junior Secondary Schools Bk2 by Evans
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVE: At the end of the lesson the students should be able to:
a. Define community
b. Explain balance in nature
c. Sate the primary source of energy to the community
 CONTENT: Community
CONTENT: Community
Community is a group of different organisms living in a given area. This includes plants, human beings and other animals in that area.

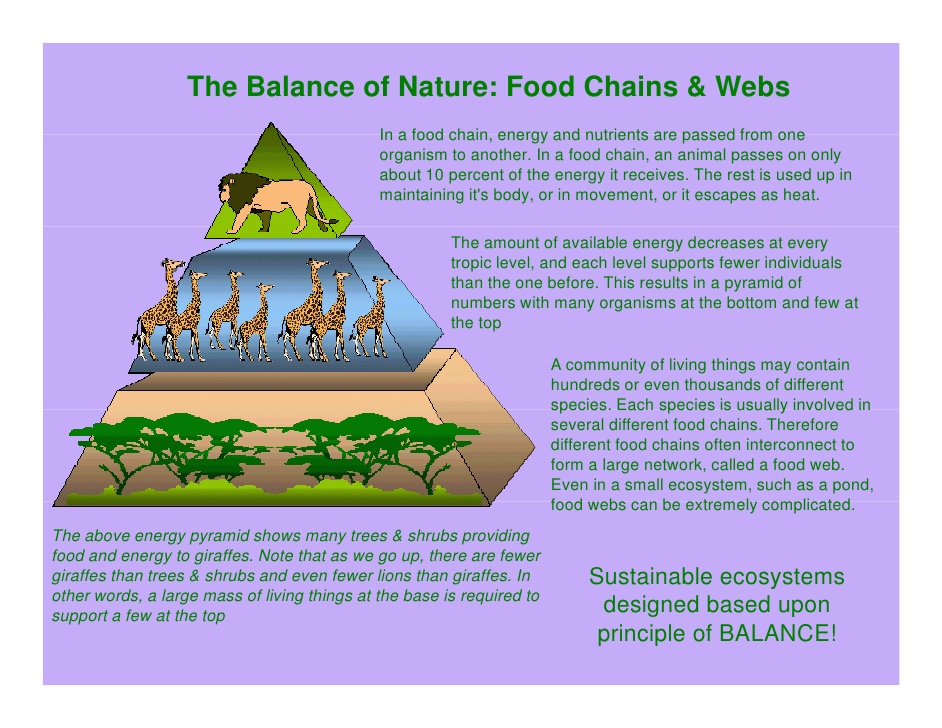
Balance in Nature
For a balanced community. The biotic and abiotic factors in the environment have to be kept stable.

Energy is absorbed by plants from the sun which is the primary source of energy to the community is taken by the primary consumers, secondary and tertiary consumers. The decomposers feed on the dead remains of the plants and animals to liberate energy. Other ways of balancing the environment are through carbon cycle, nitrogen cycle and water cycle.
EVALUATION:
a. Define community
b. Explain balance in nature
c. What is the primary source of energy to the community
further studies
http://www.thewaterpage.com/water-conservation.htm
http://environment.nationalgeographic.c ... t-threats/