1ST TERM
Posted: Thu Jun 18, 2015 5:07 pm
NEW SCHEME OF WORK
WEEKS TOPICS
1. Revision of JSS 1 Work
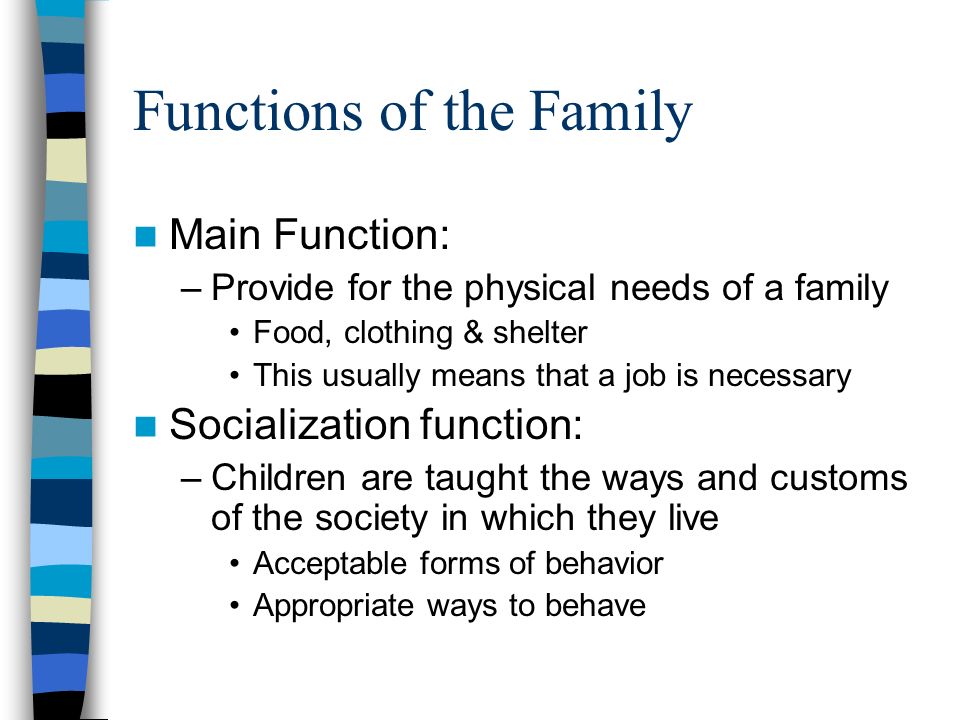
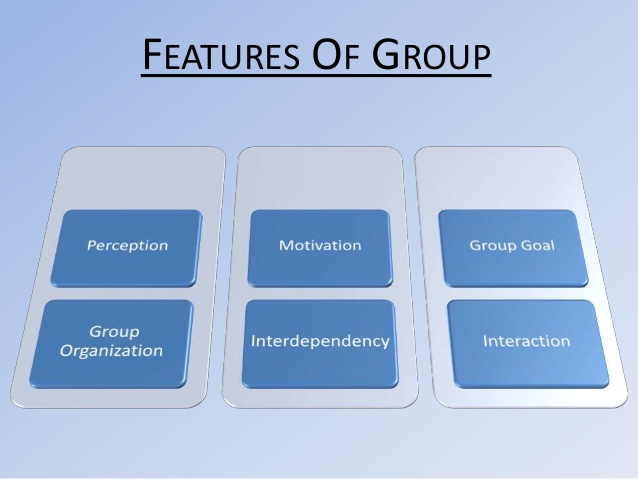
2. Social Groups: (a) Meaning of social groups.(b)Types of social groups e.g. family
(c)Characteristics of primary social groups and secondary social groups.
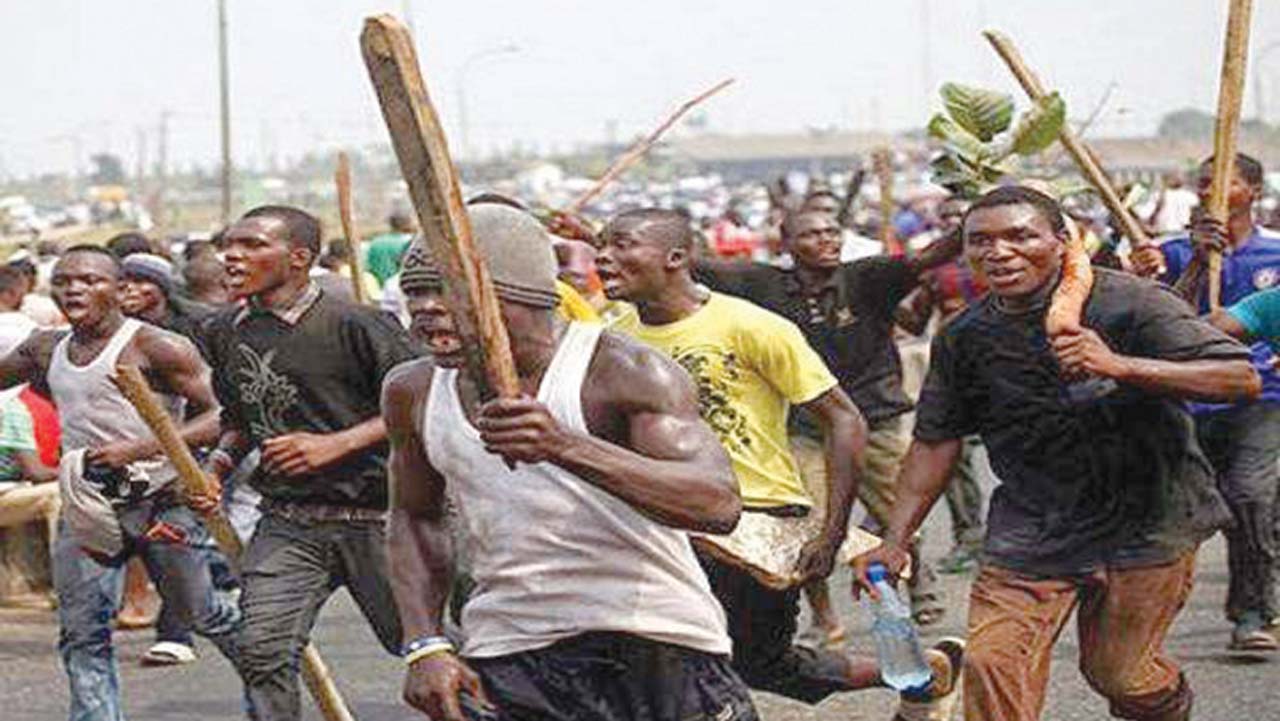
3. Group Behaviour:(a)Types of group behavior-(1)Mass action.
(2)Communal labour.
(b) Characteristics of different types of group behavior (destructive and constructive).
(c) Benefits of group behavior.
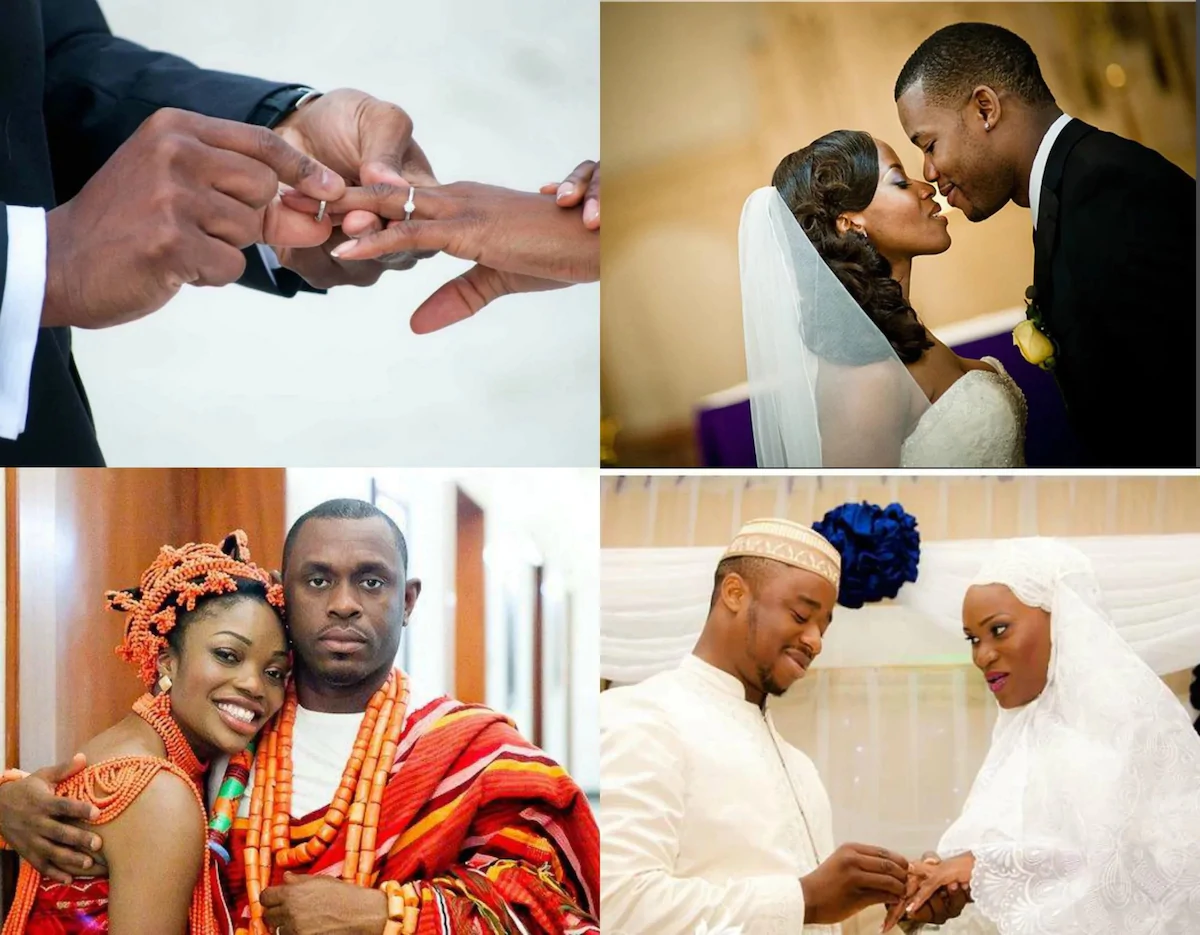
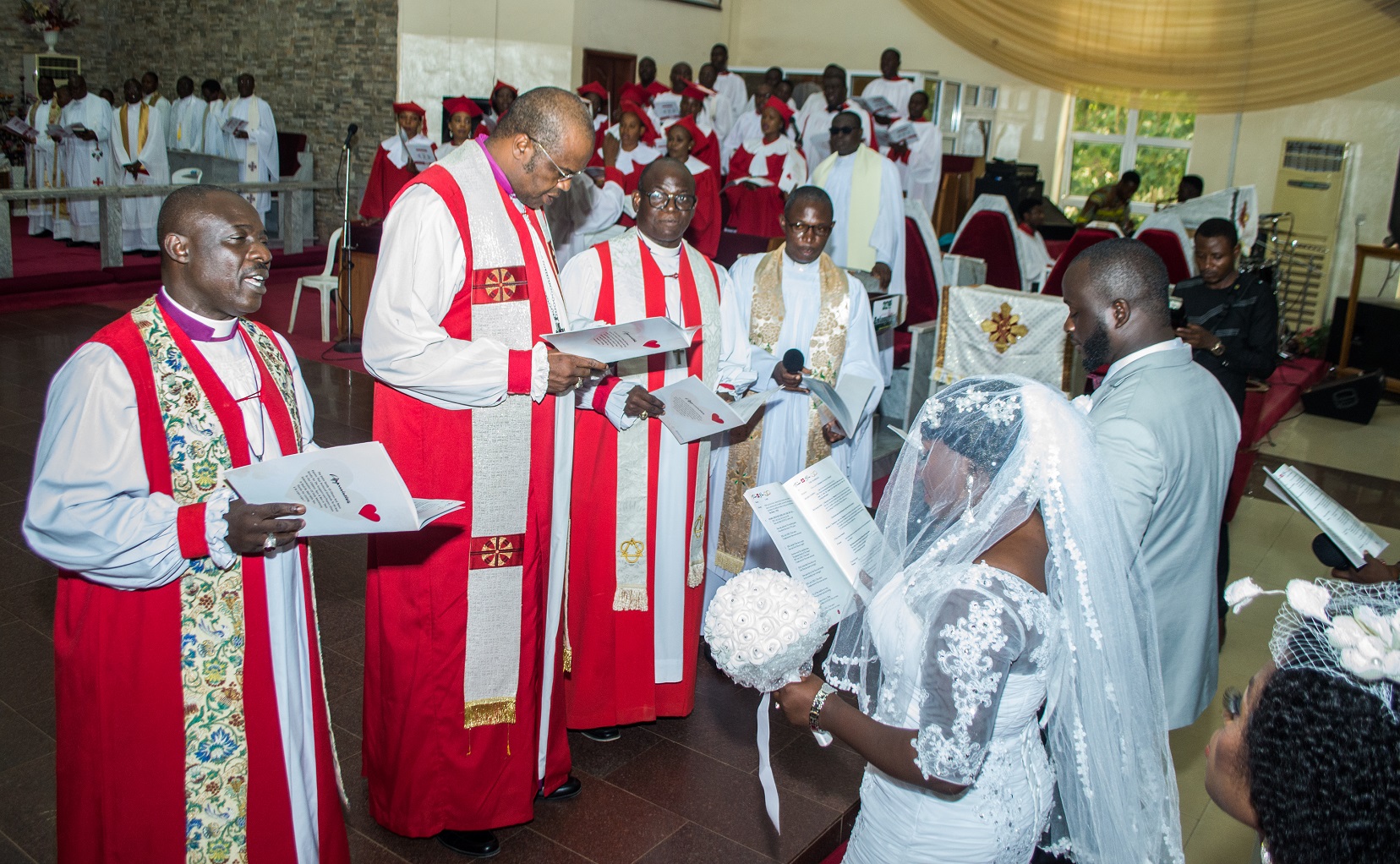
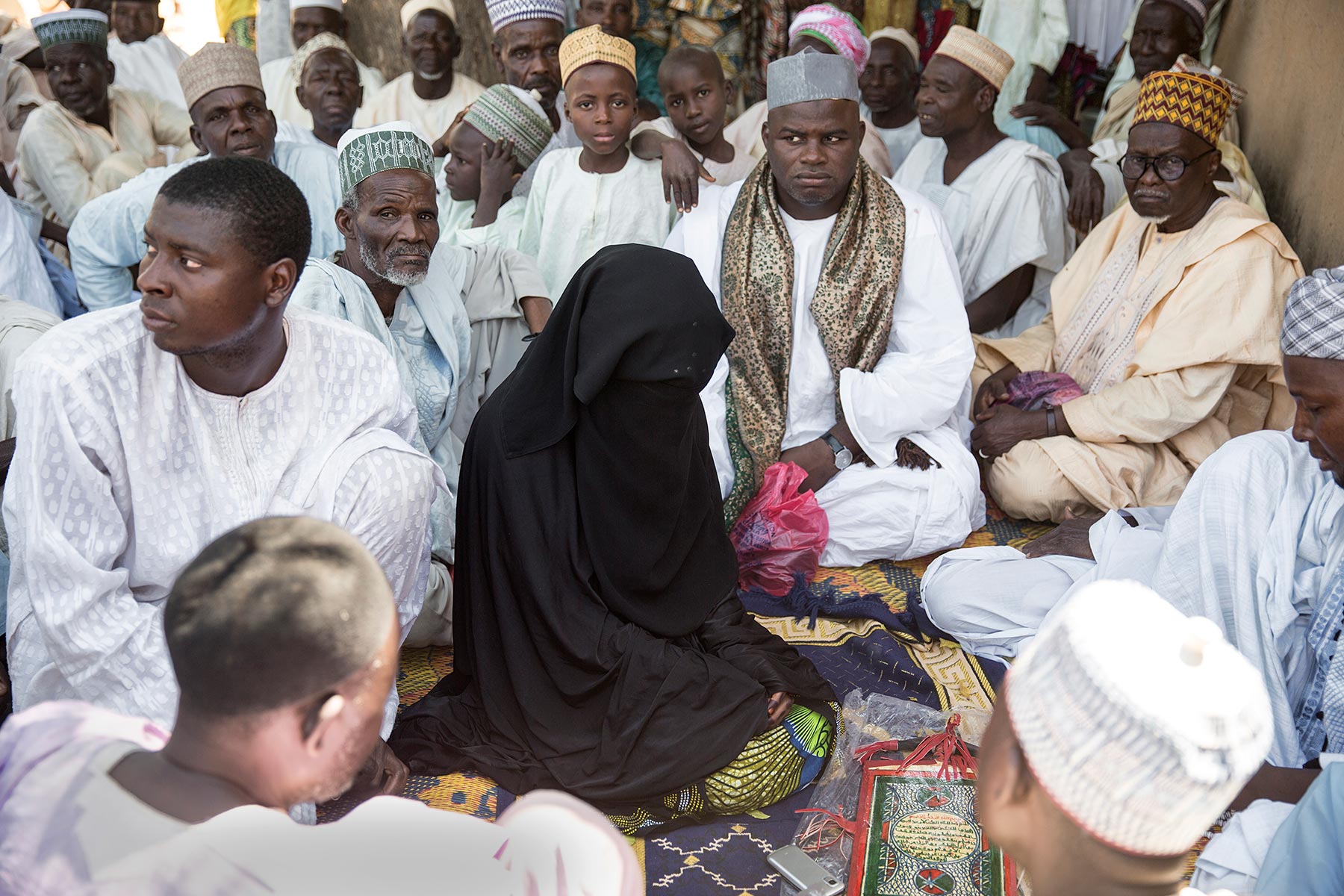
4. Marriage:(a)Meaning of marriage.(b)Types of marriage.
(c)Condition for marriage
(1)Physiological fitness.(2)Psychological fitness.(d)Social stability.(e)Financial readiness.
5. Drug Abuse:(a)Meaning of drug/substance abuse.
(b)Forms of drug abuse. (c) Consequences of drug abuse on the: (1) individual. (2) Community. (3) Nation. (4) international
community. (d) Ways of discouraging drug abuse.
6. Drug Trafficking: (a) Meaning of drug trafficking:
(b) Reasons for trafficking in drug:
(1)poverty.(2)ignorance.(3)greed.etc. (c)Consequences of drug trafficking-Bad image for the
country, imprisonment for the drug traffickers, Death penalty in some cases, mental and
psychological derangement of the drug addict. (d) Prevention of drug trafficking:
(1) Education/enlightenment, (2) alleviation of poverty, (3) legislation, (4) international
cooperation.
7. Poverty: (a) Meaning of poverty.
(b) Causes of poverty (e.g level of acquired skills, extended
family system, inadequate resources and pattern of distribution, spending habits, level of
literacy, untapped natural resources, etc.). (c) Consequences of poverty: (1) poor quality of
life, (2) inaccessibility to education, (3) violence, (4) prone to drug abuse and other criminal
acts, prostitution and armed robbery. (d) poverty alleviation strategies: (1) Education.
(2) Skills acquisition and development, (3) Hard work.
8. Corruption: (a) Meaning of corruption.
(b) Types of corruption. (c) Causes of corruption –
(1) greed, (2) social attachment to material wealth, (3) Breakdown in societal values and
ethics, (5) Poverty and economic insecurity. (d) Consequences of corruption:(low level of
development, low moral value of the society, result in crime, project bad image of the
country at home and abroad. (e) agencies of corruption prevention in Nigeria and roles of
EFCC, ICPC and code of conduct Bureau, etc. (f) Ways of improving current efforts at
preventing corruption.
9. Revision
OLD SCHEME OF WORK
WEEK TOPIC
1. Revision of last term’s work.
2. Social Issues and Problems
- Meaning types of social issues and problems. Drug abuse - meaning.
- Identify the common ways drugs are abused by people.
- Consequences of drug abuse
- Ways of encouraging drug abuse.
3. Drug Trafficking
- Meaning of drug trafficking
- Reasons for trafficking drugs
- Dangers of drug trafficking
- Ways for preventing drug trafficking.
4. Poverty
- Meaning of poverty
- Causes of poverty
- Consequences of poverty
- Analyse strategies of government and suggest areas of improvement
5. Corruption
- Define Corruption
- Types of corruption
- Causes of corruption
6. Corruption
- Discuss the effects of corruption on individual, the community and the nation.
- Discuss the role of different agencies of government charged with the prevention of corruption.
- Suggest ways of improving current effort by the government at preventing corruption in our society.
7. Cultism
- Define cultism
- Causes of cultism
- Solutions to the problems of cultism in Nigeria.
8. Accidents in the School
- Types of accident in the school
- Ways of preventing accidents in the school.
- Steps to take when accidents occur in the school.
9. People and their Environment
- Social group
- Define social groups
- Types of social groups
- Characteristics of social groups
10. Group Behaviour
- Types of group behavior
- Distinguish between the different types
- Benefits of group behavior
11. Revision.
WEEKS TOPICS
1. Revision of JSS 1 Work
2. Social Groups: (a) Meaning of social groups.(b)Types of social groups e.g. family
(c)Characteristics of primary social groups and secondary social groups.
3. Group Behaviour:(a)Types of group behavior-(1)Mass action.
(2)Communal labour.
(b) Characteristics of different types of group behavior (destructive and constructive).
(c) Benefits of group behavior.
4. Marriage:(a)Meaning of marriage.(b)Types of marriage.
(c)Condition for marriage
(1)Physiological fitness.(2)Psychological fitness.(d)Social stability.(e)Financial readiness.
5. Drug Abuse:(a)Meaning of drug/substance abuse.
(b)Forms of drug abuse. (c) Consequences of drug abuse on the: (1) individual. (2) Community. (3) Nation. (4) international
community. (d) Ways of discouraging drug abuse.
6. Drug Trafficking: (a) Meaning of drug trafficking:
(b) Reasons for trafficking in drug:
(1)poverty.(2)ignorance.(3)greed.etc. (c)Consequences of drug trafficking-Bad image for the
country, imprisonment for the drug traffickers, Death penalty in some cases, mental and
psychological derangement of the drug addict. (d) Prevention of drug trafficking:
(1) Education/enlightenment, (2) alleviation of poverty, (3) legislation, (4) international
cooperation.
7. Poverty: (a) Meaning of poverty.
(b) Causes of poverty (e.g level of acquired skills, extended
family system, inadequate resources and pattern of distribution, spending habits, level of
literacy, untapped natural resources, etc.). (c) Consequences of poverty: (1) poor quality of
life, (2) inaccessibility to education, (3) violence, (4) prone to drug abuse and other criminal
acts, prostitution and armed robbery. (d) poverty alleviation strategies: (1) Education.
(2) Skills acquisition and development, (3) Hard work.
8. Corruption: (a) Meaning of corruption.
(b) Types of corruption. (c) Causes of corruption –
(1) greed, (2) social attachment to material wealth, (3) Breakdown in societal values and
ethics, (5) Poverty and economic insecurity. (d) Consequences of corruption:(low level of
development, low moral value of the society, result in crime, project bad image of the
country at home and abroad. (e) agencies of corruption prevention in Nigeria and roles of
EFCC, ICPC and code of conduct Bureau, etc. (f) Ways of improving current efforts at
preventing corruption.
9. Revision
OLD SCHEME OF WORK
WEEK TOPIC
1. Revision of last term’s work.
2. Social Issues and Problems
- Meaning types of social issues and problems. Drug abuse - meaning.
- Identify the common ways drugs are abused by people.
- Consequences of drug abuse
- Ways of encouraging drug abuse.
3. Drug Trafficking
- Meaning of drug trafficking
- Reasons for trafficking drugs
- Dangers of drug trafficking
- Ways for preventing drug trafficking.
4. Poverty
- Meaning of poverty
- Causes of poverty
- Consequences of poverty
- Analyse strategies of government and suggest areas of improvement
5. Corruption
- Define Corruption
- Types of corruption
- Causes of corruption
6. Corruption
- Discuss the effects of corruption on individual, the community and the nation.
- Discuss the role of different agencies of government charged with the prevention of corruption.
- Suggest ways of improving current effort by the government at preventing corruption in our society.
7. Cultism
- Define cultism
- Causes of cultism
- Solutions to the problems of cultism in Nigeria.
8. Accidents in the School
- Types of accident in the school
- Ways of preventing accidents in the school.
- Steps to take when accidents occur in the school.
9. People and their Environment
- Social group
- Define social groups
- Types of social groups
- Characteristics of social groups
10. Group Behaviour
- Types of group behavior
- Distinguish between the different types
- Benefits of group behavior
11. Revision.