1ST TERM
Posted: Thu Jun 18, 2015 6:08 pm
NEW SCHEME OF WORK
WEEKS TOPICS
1. Revision of JSS 2 Work
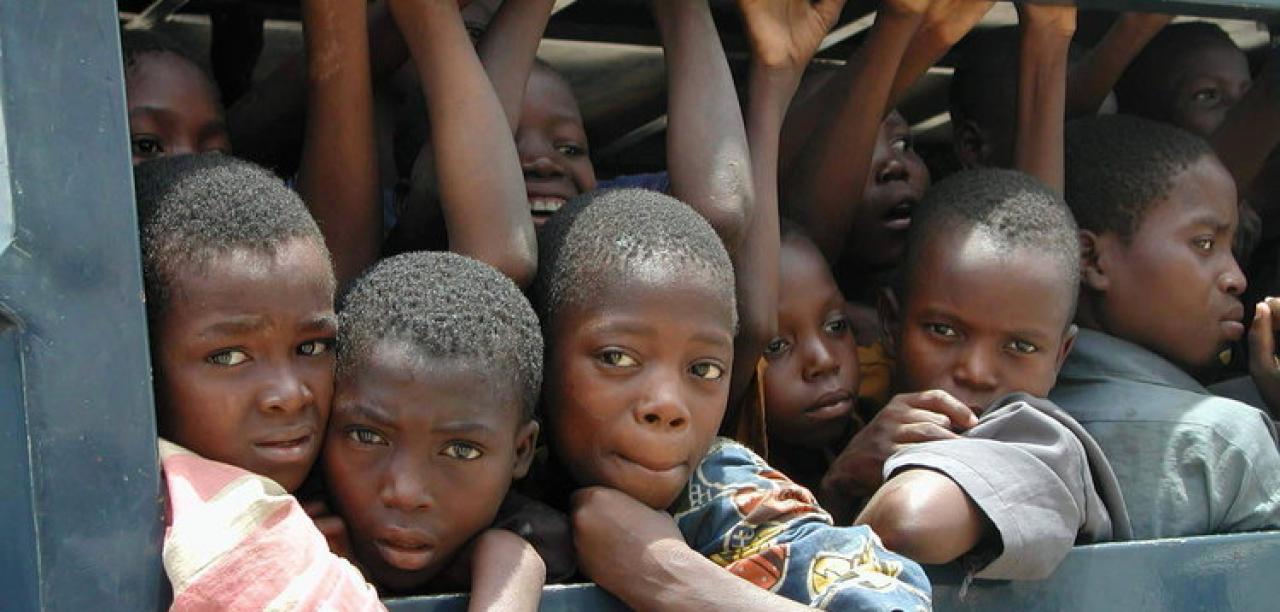
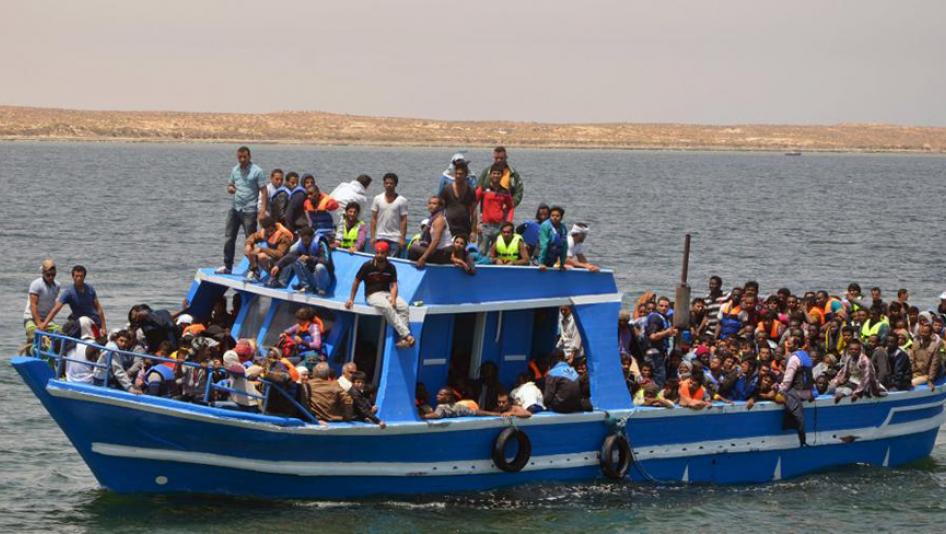
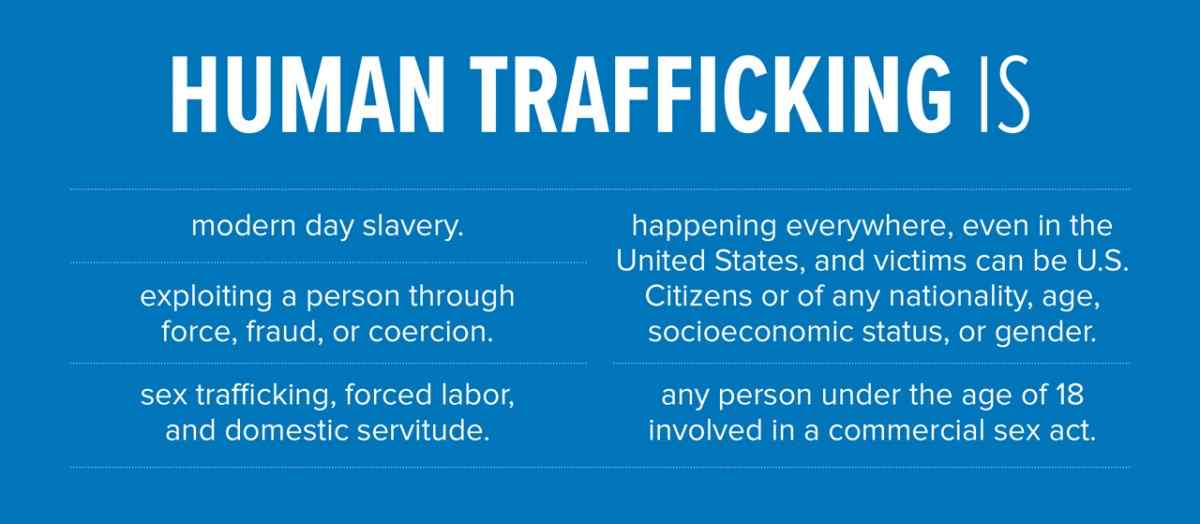
2. Social Value – Trafficking in Children and Women: (a) Meaning of human trafficking. (b) Factors responsible for children and women trafficking.
3. Trafficking in Children and Women: (c) Consequences of human trafficking – Physical, Psychological and Social. (d) Preventive Measures – Public enlightenment, Education, Advocacy and Legislation, etc.
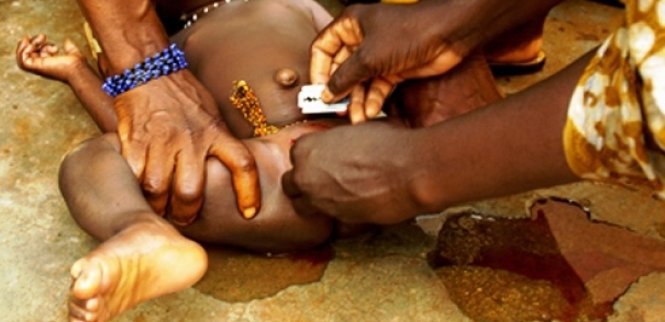
4. Harmful Traditional Practices: (a) Meaning of human traditional practices. (b) Examples of harmful traditional practices. (c) Consequences – Social Economic 1, Psychological. (d) Measure of harmful traditional practices- Public.
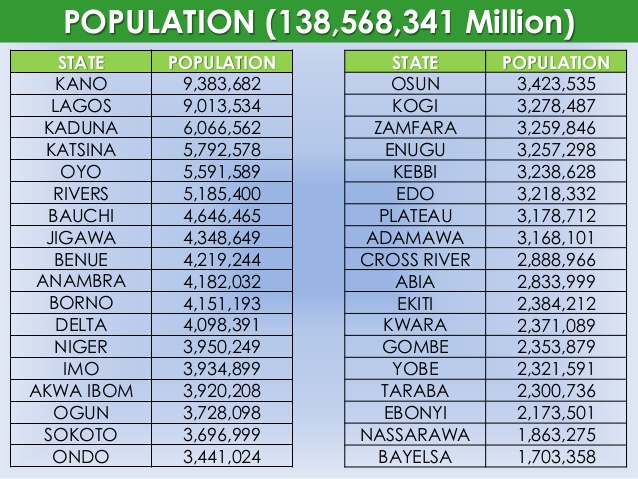
5. Population: (a) Meaning of population. (b) Basic unit of population – Family, Community. (c) Factors in securing population growth. (d) Population control.
6. Family Life Education: (a) Meaning of family life education. (b) Population and resources available, customs, value, beliefs and traditional gender issues and core messages (family size & family welfare). (c) Family size and consequences. (c) Census problems in Nigeria.
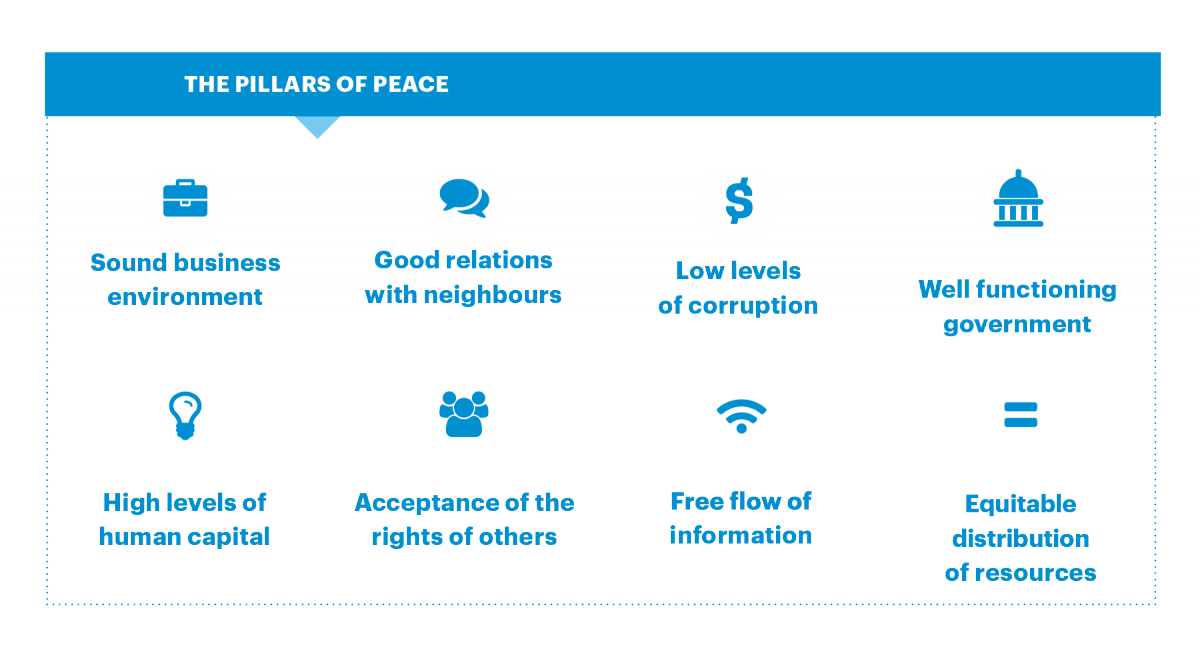
7. Peace: (a) Meaning of peace. (b) Types: positive peace, Negative /uneasy peace. (b) Importance of peace. (d) Ways of promoting peace – tolerance, social justice, human rights, etc.
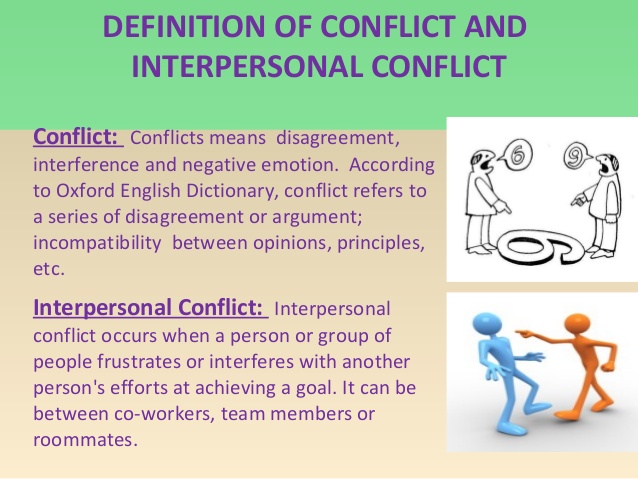
8. Conflicts: (a) Meaning of conflict. (b) Types of conflict- non violent, violent. (c) Examples of conflict- (i) interpersonal misunderstanding, (ii)intra-national/inter-ethnic conflicts e.g. Urhobo/ Itsekiri/Izon, Kataf/ Hausa, Yoruba/Hausa,etc. conflicts. (iii) Communal /intra-ethnic conflicts e.g. Ife/Modakeke, Aguleri/Umuleri.
9. Conflicts: (d) Causes and consequences of Conflicts. (e) Conflict management and Resolution e.g. dialogue, compromise, etc.
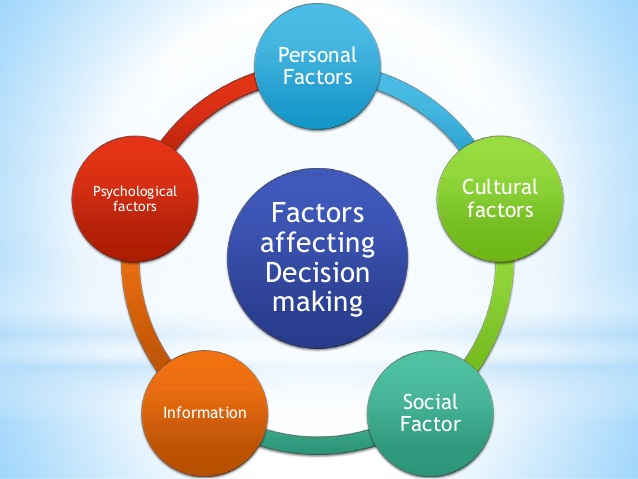
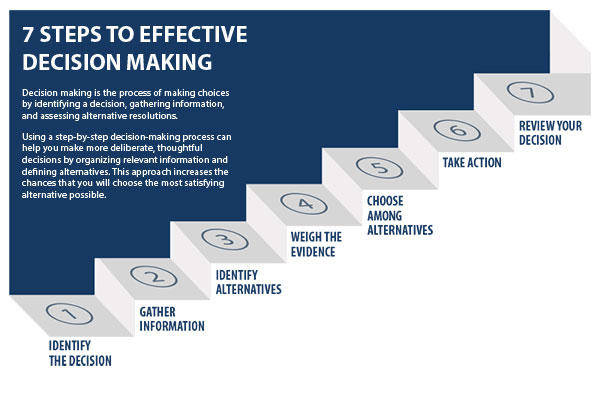
Decision Making
- Meaning of decision making.
- Situations that require decision making.
- Importance of decision making.
- Factors that influence decision making.
10. Introduction to the Origin of Man.
- Myths and Legends, Religious Beliefs, Scientific Version
11. Revision.
WEEKS TOPICS
1. Revision of JSS 2 Work
2. Social Value – Trafficking in Children and Women: (a) Meaning of human trafficking. (b) Factors responsible for children and women trafficking.
3. Trafficking in Children and Women: (c) Consequences of human trafficking – Physical, Psychological and Social. (d) Preventive Measures – Public enlightenment, Education, Advocacy and Legislation, etc.
4. Harmful Traditional Practices: (a) Meaning of human traditional practices. (b) Examples of harmful traditional practices. (c) Consequences – Social Economic 1, Psychological. (d) Measure of harmful traditional practices- Public.
5. Population: (a) Meaning of population. (b) Basic unit of population – Family, Community. (c) Factors in securing population growth. (d) Population control.
6. Family Life Education: (a) Meaning of family life education. (b) Population and resources available, customs, value, beliefs and traditional gender issues and core messages (family size & family welfare). (c) Family size and consequences. (c) Census problems in Nigeria.
7. Peace: (a) Meaning of peace. (b) Types: positive peace, Negative /uneasy peace. (b) Importance of peace. (d) Ways of promoting peace – tolerance, social justice, human rights, etc.
8. Conflicts: (a) Meaning of conflict. (b) Types of conflict- non violent, violent. (c) Examples of conflict- (i) interpersonal misunderstanding, (ii)intra-national/inter-ethnic conflicts e.g. Urhobo/ Itsekiri/Izon, Kataf/ Hausa, Yoruba/Hausa,etc. conflicts. (iii) Communal /intra-ethnic conflicts e.g. Ife/Modakeke, Aguleri/Umuleri.
9. Conflicts: (d) Causes and consequences of Conflicts. (e) Conflict management and Resolution e.g. dialogue, compromise, etc.
Decision Making
- Meaning of decision making.
- Situations that require decision making.
- Importance of decision making.
- Factors that influence decision making.
10. Introduction to the Origin of Man.
- Myths and Legends, Religious Beliefs, Scientific Version
11. Revision.