LESSON 12
TOPIC: UNITS OF STORAGE IN COMPUTER:
Units of Storage; Bits, Nibble, Byte, Kilobyte, Gigabyte, etc.
OBJECTIVES:
At the end of the lesson, students should be able to:
- State the various units of storage and their values
- Convert from one unit to another
- Differentiate between Kilometer, Kilogram and Kilobyte
- Distinguish between Kilobyte, Megabyte and gigabyte.
THE COMPUTER MEMORY
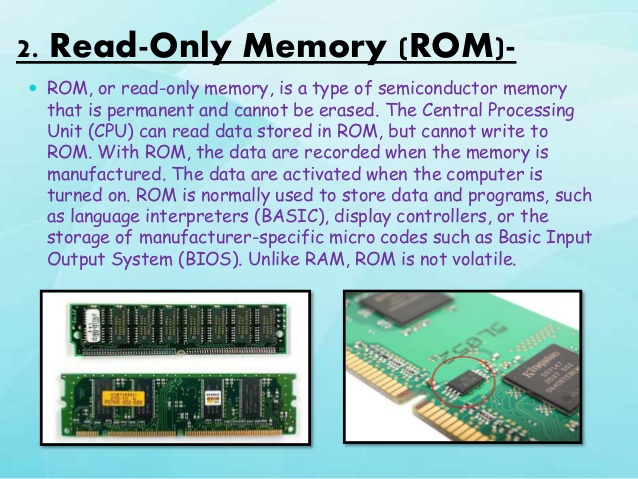
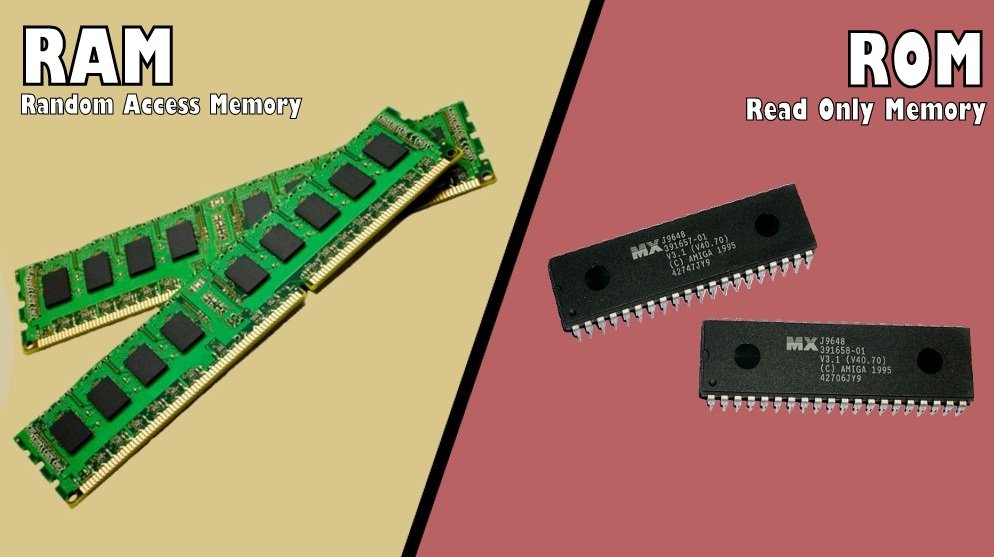
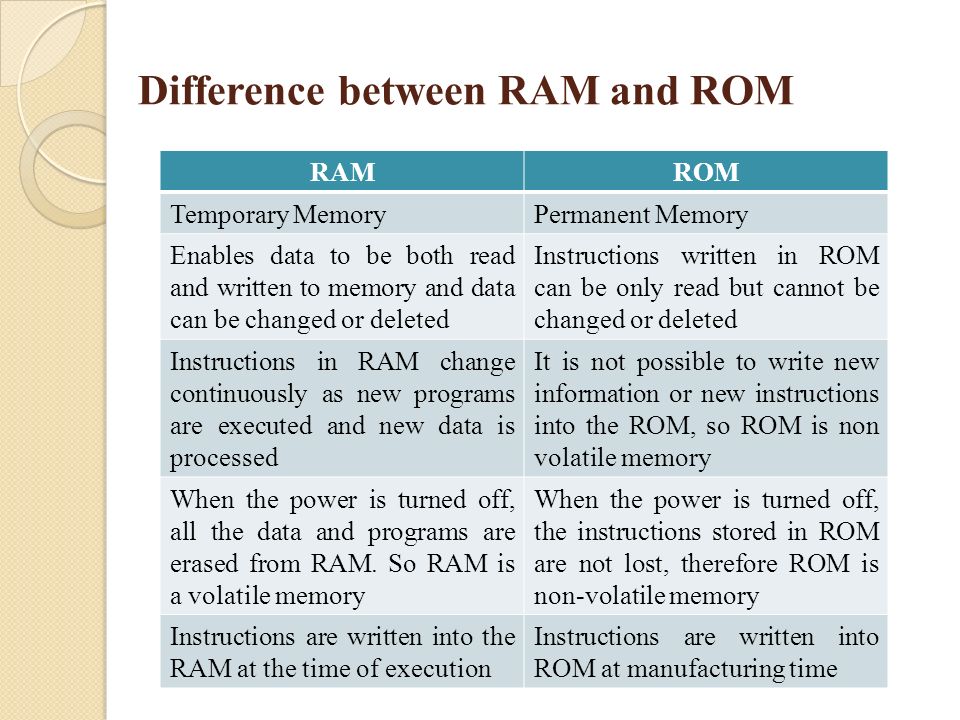
The memory or storage is that part of the computer system that stores data for later use. Computer has types of memory namely; main or internal memory and the auxiliary or external memory. The main memory is referred to as the computer primary storage and resides in the computer casing or system unit. The computer has two kinds of main memory. One is permanently stored and cannot be affected when the machine is turned off and there can be no loss of information. This memory kind is called Read Only Memory (ROM). It is mostly used by the computer manufacturer to store general purpose and permanent instructions on the computer, e.g operating system. The other memory is temporary. The temporary memory is affected when the machine is turned off and there is loss of information. This kind of memory is called Random Access
Memory (RAM), it is the memory that holds data input and the users software while working on them. The amount of RAM varies from one computer to the other.
Auxiliary memory is a secondary storage unit. It is to supplement the main memory. It is also called backing memory or external memory. It is a mass storage unit because it stored large amount of information. Secondary storage is needed due to the volatile nature of RAM and its inability to store large volume of data.
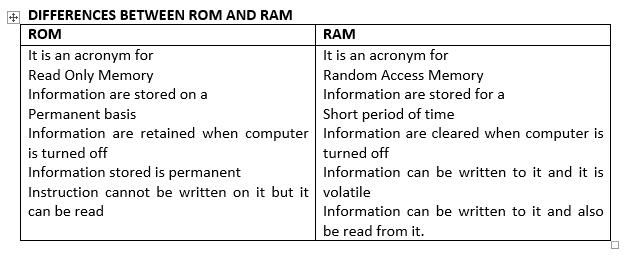
DIFFERENCES BETWEEN ROM AND RAM
 TYPES OF SECONDARY MEMORY
TYPES OF SECONDARY MEMORY
There are different types of secondary memory. Some of them are.
(1) Magnetic tapes (2) Magnetic disk (3) Optical disk.
MAGNETIC DISK
Magnetic disk is another form or auxiliary storage device. It is used to write and data on a disk called disk drive.
There are two types of magnetic disks. These are floppy disk and hard disk.
 OPTICAL DISK
OPTICAL DISK
CD ROM is an example of optical disk. It is usually driven by the CD ROM Drive, CD ROM has a larger storage capacity. There are two types of CD ROM. Writable CD and Re-writable CD ROM. Writable CD ROM are used to store data or information which does not require alternations as the contents of the medium cannot be altered while the content of RE- writable CD ROM can be altered and written CD ROM is an acronym for Compact Disk Read Only Memory.
EVALUATION:
1. What is computer memory?
2. Mention two types of computer memory. Give examples.
LESSON 13
DIFFERENCE BETWEEN MAIN MEMORY AND AUXILIARY MEMORY
MAIN MEMORY AUXILIARY MEMORY
1. It is primary storage ..... it is secondary storage
2. It is internal storage ..... it is external storage
3. It acts as main memory .....it acts as backup for main memory
4. It is volatile .....it is non volatile
5. It is expensive ..... it is less expensive
6. It has small memory capacity ..... it has less memory capacity
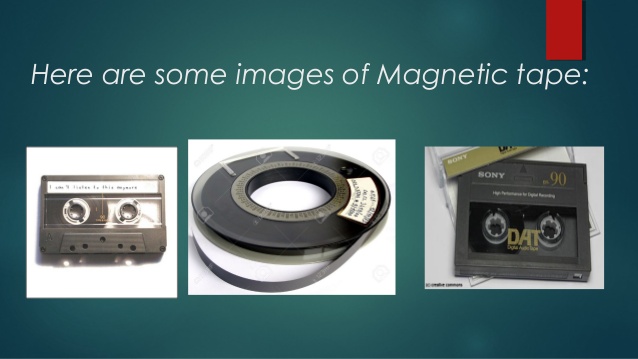
 MAGNETIC TAPE:
MAGNETIC TAPE: This is similar to the tape used in audio tape recorder. Magnetic tapes are made of a long thin film covered with iron oxide. The thin film is wound round a plastic container in a form of a reel. Data can be written from tape to tape and placed into the main memory. It performs the function of an input and output devices. It is a sequential access storage device.
 BIT:
BIT: This is a binary digit i.e. binary digit i.e. 0 and 1
BYTE: byte is a bit of eight digit i.e. 01011101, 11110110, 01010110 etc
NIBBLE: This is half of a byte (i.e. 4 bits 0101, 1110, 0101, 1101, 1001 etc) it is also called a group of two words.
WORD: A word is a group of fixed numbers of bits in a given computer. It is also described as a group of two.
BYTES:
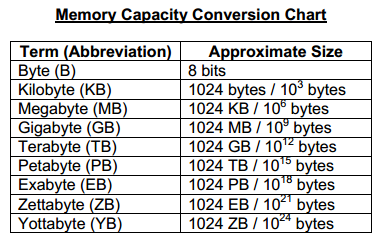
KILOBYTE: This is equivalent of 210 =1024
MEGABYTE: A megabyte is equivalent to 210x 210 1024 kilobyte= I MB.
GIGABYTE: A gigabyte is equivalent to 210x 210x 210 megabytes
TERABYTE: A terabyte is 240 =1,099,511,628,000, thus 240=1,099,511,628,000 bytes
WORKING EXAMPLES
A byte = 8 bit
1 kilobyte (KB)=210=1024
1 megabyte (MB) = 210 x210 x210=220=1,048,576 bytes
I gigabyte (GB) = 210 x 210x 210=1,073,741,824 bytes
I terabyte (TB)= 210x210x210x210=240 thus 240=1,099,511,628,000 bytes
FURTHER WORKINGS
Bit = 0 or 1
4 bits = I nibble
2 nibbles = 8 bit and 8 bit = 1 byte
3 nibbles = (3 x4) bits = 12bit
4 nibbles = (4x4) bits = 16 bit
5 nibbles = (5 x4) bits = 20 bits
Conversion of bytes to bits
1 bytes = 8 bits
2 bytes = 16 bits
3 bytes = 24 bits
5 bytes = 40 bits
Unlike the metric system where I kilometer (km) is equal to 1000 meter the sub-units of byte are converted as follows.
EXAMPLES 1
Converts 2 kilobytes to byte
1 KM = 1024bytes = 2048 bytes
2 KM = 2(1024) bytes = 2048 bytes.
Convert 4KM to Byte
Note IKB = 1024 bytes
4KB = 4(1024) bytes
4096 bytes
EXAMPLES 3
Convert 2048 bytes to kilobytes
Recall 1024 bytes = IKB
2048 bytes = 2048bytes
1024bytes = 2 kilobyte.
EXAMPLES 4
Change 3 megabytes to byte
IMB = 1048, 576 bytes
3 MB = 3(1048, 576 bytes) =3,145,728 bytes
3 145, 728 bytes = 3 MB
1048 576 bytes
Convert words to bytes
Recall I word = group of 2 bytes
1 word = 2 bytes
2 bytes = 16bytes
2 word = 2(2bytes = 2x 16bits)
= 32 bits
4 word = 4(2 bytes)
= 8bytes
8 bytes = 64 bits
Change 3, 145, 728 Byte to MB
Solution: To change 3, 145, 728 to MB
1, 048,576B = 1MB
3, 145,728 = 3,145, 728
1,048,576
3MB
EVALUATION;
I. Explain the following terms
(a) Nibble (b) Word (c) Double words (d) word nipple (e) Byte (f) Kilobyte (g) Megabyte (h) Gigabyte
2. Convert, (i) 3 bytes to bits (ii) 5 nibbles to bit (c) 2word to byte
3. Convert the followings: (i) megabyte to kilobyte (ii) kilobyte to byte (iii) 6bytes to nibble.
READING ASSIGNMENT:
Read to revise this lesson again, and be prepared for questions on it.
ASSIGNMENT:
1. A type of memory that supplements the main memory is called______
(a)Main memory (b) Auxiliary memory (c) Active memory (d)
None
2. A type of memory that cannot be affected by power failure is called______
(a) RAM (b) ROM (c) Optical disk (d) Magnetic disk
3. A group of fixed numbers of bits in a given computer is called_____
(a) Word (b) Nibble (c) Bit (d) Bytes
4. 4 kilobytes is equivalent to ____ bytes
(a) 3096 (b) 4096 (c) 9069 (d) 1000
5. Which of the following storage device is used to store data or information that does not require alteration
(a)Writable CD-ROM (b) RE-Writable CD-ROM(c) Optical disk
(d)Magnetic disk