SCHEME OF WORK
WEEK TOPIC
1. Revision of Second Term work
2. ICT as a Transformational Tool: (a) Meaning of ICT (b) Examples of ICT gadgets
3. ICT as a Transformational tool: (c) Benefits of ICT (d) Disadvantages of ICT
4. ICT Gadgets: (a) The GSM, Fax machine, Telephone et.c, (b) The Differences between GSM, Fax machine and telephone. (c) creating and sending messages using GSM and Fax (d) storing and retrieving information on a GSM handset.
5&6 Internet 1: (a) Definitions (i) Internet (ii)e-mail address (iii) world Wide Web
(b) internet browsers (c)creating an e-mail account (d) samples of e-mail address (e) benefits of the internet (f) Abuses of the internet
7. Internet 2: (a) Internal environment-recognizing and naming the icons in the Internet environment (b) Uses of the Internet (C) Network groups e.g Schoolnet, e-school, et.c.
8. Computer Ethics: (a) Responsible use of the computer and Internet. (b) Areas of misuse of computers
9. Safety Measures: Safety measures in using the computer System. Example (i) The sitting posture (ii) Using the antiglare Protection (iii) Positioning of monitor base (iv) Illuminating the computer room (v) Maintaining a dust free Environment (vi) Keeping liquids away from computers.
10. Revision.
3RD TERM
WEEK 1
LESSON 1
TOPIC: ICT AS A TRANSFORMATION TOOL 1
CONTENTS
1. Meaning of ICT ( information & Communication Technology)
2. Examples of ICT gadgets
MEANING OF ICT ( INFORMATION & COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY)
ICT stands for information and communication technology. The plural form is information and communication technologies (ICTs). They are a diverse set of technological tools and resources used to create process, store, retrieve, communicate, and manage information. ICTs comprise a range of technology products and activities that enable the recording, storage, recording, storage, processing and retrieval, transition, and reception of information.

EXAMPLES OF ICT GADGETS
ICT gadgets include
i. Computers
ii. Telephone (GSM)
iii. Cellular network
iv. Satellite communications
v. Television
vi. The Internet.
EVALUATION:
1. What is the meaning of ICT
2. State 5 examples of modern and traditional ICTs
ASSIGNMENT:
Students are to answer questions 1 and 2 in the revision exercise questions in page 94 of students textbook 2.
TOPIC: ICT AS A TRANSFORMATION TOOL 1
CONTENTS
1. Meaning of ICT ( information & Communication Technology)
2. Examples of ICT gadgets
MEANING OF ICT ( INFORMATION & COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY)
ICT stands for information and communication technology. The plural form is information and communication technologies (ICTs). They are a diverse set of technological tools and resources used to create process, store, retrieve, communicate, and manage information. ICTs comprise a range of technology products and activities that enable the recording, storage, recording, storage, processing and retrieval, transition, and reception of information.

EXAMPLES OF ICT GADGETS
ICT gadgets include
i. Computers
ii. Telephone (GSM)
iii. Cellular network
iv. Satellite communications
v. Television
vi. The Internet.
EVALUATION:
1. What is the meaning of ICT
2. State 5 examples of modern and traditional ICTs
ASSIGNMENT:
Students are to answer questions 1 and 2 in the revision exercise questions in page 94 of students textbook 2.
WEEK 2
LESSON 2
TOPIC: ICT AS A TRANSFORMATION TOOL (2)
CONTENTS
1. Benefits of ICT
2. Disadvantages of ICT
THE BENEFITS OF ICT
The benefits of ICT are numerous which include the following
1. Timely, better and cheaper access to knowledge and information.
2. Speeds up transactions and processes.
3. Provides opportunities for human beings to interact with one another in new ways easily.
4. Makes distance to become irrelevant in business transactions and dealings.
5. ICT has brought about innovative ways of interaction.
6. It provides employment opportunities to people globally
7. It is very useful as a medium of instruction in schools. It also makes people to acquire knowledge especially in ICT.
8. When used in governance, it leads to efficiency. This is called e-administration.
9. It is useful in medicine for medical diagnosis.


DISADVANTAGES OF ICT
Despite the benefits of ICT, it has some disadvantages some of which include the following:
1. It can lead to job loss as a result of computerization of transactions in an office.
2. Youth often abuse the internet by using it mostly for entertainment, watching pornography and using it to commit crime, notably cybercrime.
3. ICT use often leads to a breakdown in social bonds between people. People prefer to send e-mails or call their loved ones on phone rather than visiting them.
4. Extensive use of ICT often leads to some health implications like eye strains, backaches, etc.
5. ICT use can lead to computer addiction, obsessive computing behavior and stress.
6. Advent of ICT has led to infringement of people’s privacy and confidentiality of information today can no longer be guaranteed.


EVALUTION
1. Give four benefits and disadvantages of ICT
ASSIGNMENT:
Students are to answer questions 3 and 4 in the revision exercise questions in page 94 of students textbook 2.
TOPIC: ICT AS A TRANSFORMATION TOOL (2)
CONTENTS
1. Benefits of ICT
2. Disadvantages of ICT
THE BENEFITS OF ICT
The benefits of ICT are numerous which include the following
1. Timely, better and cheaper access to knowledge and information.
2. Speeds up transactions and processes.
3. Provides opportunities for human beings to interact with one another in new ways easily.
4. Makes distance to become irrelevant in business transactions and dealings.
5. ICT has brought about innovative ways of interaction.
6. It provides employment opportunities to people globally
7. It is very useful as a medium of instruction in schools. It also makes people to acquire knowledge especially in ICT.
8. When used in governance, it leads to efficiency. This is called e-administration.
9. It is useful in medicine for medical diagnosis.


DISADVANTAGES OF ICT
Despite the benefits of ICT, it has some disadvantages some of which include the following:
1. It can lead to job loss as a result of computerization of transactions in an office.
2. Youth often abuse the internet by using it mostly for entertainment, watching pornography and using it to commit crime, notably cybercrime.
3. ICT use often leads to a breakdown in social bonds between people. People prefer to send e-mails or call their loved ones on phone rather than visiting them.
4. Extensive use of ICT often leads to some health implications like eye strains, backaches, etc.
5. ICT use can lead to computer addiction, obsessive computing behavior and stress.
6. Advent of ICT has led to infringement of people’s privacy and confidentiality of information today can no longer be guaranteed.


EVALUTION
1. Give four benefits and disadvantages of ICT
ASSIGNMENT:
Students are to answer questions 3 and 4 in the revision exercise questions in page 94 of students textbook 2.
WEEK 3
LESSON 3
TOPIC: ICT GADGETS
CONTENTS
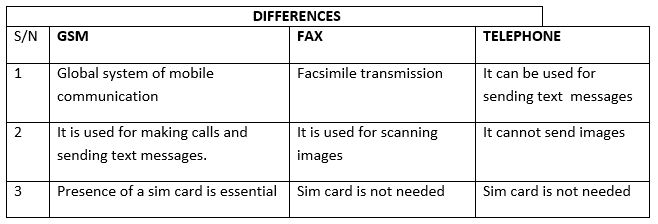
1. GSM (Global System for Mobile Communication)
2. The differences between GSM, Fax machine and telephone
3. Creating and sending messages using GSM and Fax
4. Storing and retrieving information on a GSM
GSM (GLOBAL SYSTEM FOR MOBILE COMMUNICATION)
The Global System for Mobile Communication (GSM; original from Group Special Mobile)is the most popular standard for mobile phones in the world.GSM service is used by over 2 billion people across more than 212 countries and territories. The ubiquity of the GSM standard makes international roaming very common between mobile phone operators, enabling subscribers to use their phones in many part of the world.GSM differs significantly from its predecessors in that it is considered a second generation(2G)mobile phone system.
From the point of view of GSM users, the key advantage of GSM systems has been higher digital voice quality and low cost alternatives to making calls such as text messaging. Also, like other cellar standards, GSM allows network operators to offer roaming services which means subscribers can use their phones all over the world.
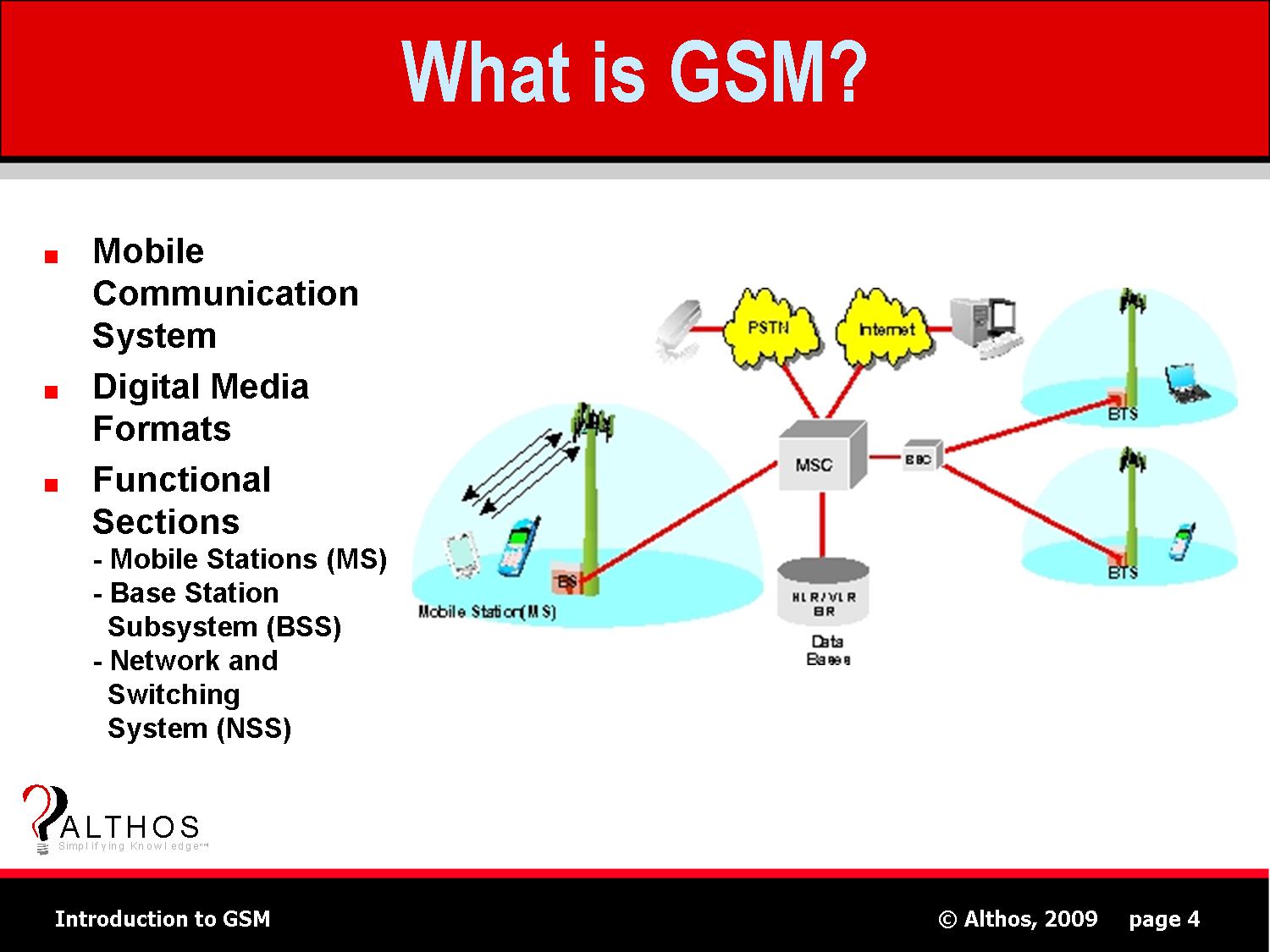
Subscriber Identity Module (SIM)
One of the key features of GSM is the subscriber identity module (SIM), commonly known as a SIM card. The SIM is detachable smart card containing the user’s subscription information and phonebook. This allows the user to retain his or her information after switching off the handsets. Alternatively, the user can also change operators while retaining the handset simply by changing the SIM, some operators will block this by allowing the phone to use only a single SIM or only a SIM issued by them; this practice is known as SIM locking, and is illegal in some countries.
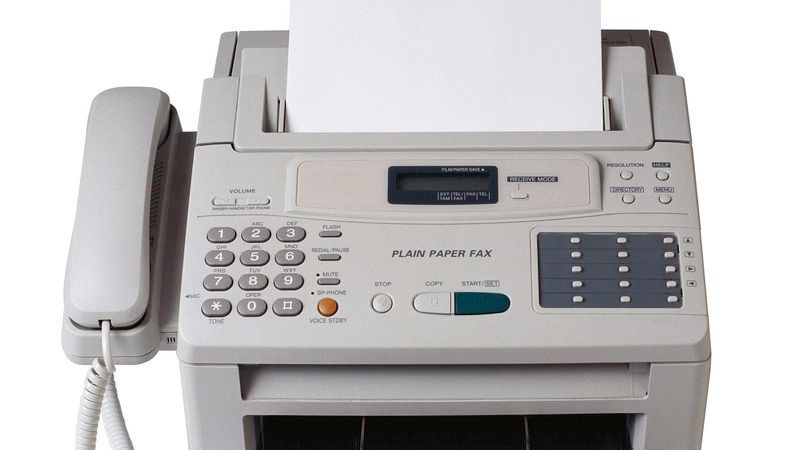
Fax Machine
Fax (short for facsimile, i.e. “make a copy”) is a telecommunications technology used to transfer copies (facsimiles) of documents, especially using affordable devices operating over the telephone network. The word telefax, short for telefacsimile, for “make a copy at a distance”, is also used as a synonym.
A fax machine is essentially an image scanner, a modem, and a computer printer combined into a highly specialised package. The scanner converts the content of a physical document into a digital image, the modem sends the image data over a phone line, and the printer at the other end, makes a duplicate of the original document.
Fax machines with additional electronic features can connect to computers; can be used to scan documents into a computer, and to print documents from the computer. Such high-end devices are called multifunction printers and cost more than fax machines.

The telephone
The telephone is a telecommunication device which is used to transmit and receive sound (most commonly voice and speech) across distance. Most telephones operate through transmission of electric signals over a complex telephone network which allows almost any phone user to communicate with almost any other. Thus, a telephone is an electric tool. Using a telephone, two people who are in different places can talk.
Computer can use a machine called a modem to talk to other computer over a telephone line. This allows a computer to connect to other computer networks including the internet.

Mobile telephones
Early telephones needed to be connected with wires. Now telephone calls can be sent with radio. This is also called wireless. While the term “wireless” in this context means radio and can refer to any telephone that uses radio waves, it is primarily used for cellular mobile phones.

LESSON 4
THE DIFFERENCES BETWEEN GSM, FAX MACHINE AND TELEPHONE
STEPS IN CREATING AND SENDING MESSAGES USING GSM
The following steps are involved
i. Using any handset irrespective of the network
ii. Look for an icon that indicate message
iii. Click on the icon
iv. Sub menu pops up under it
v. Scroll down and look for icon label create a message
vi. Click on create a message
vii. Type the message and the phone number of the recipient
viii. Click the given green button on the handset to send the message.
STORING AND RETRIEVING INFORMATION ON A GSM
To store information using GSM
1. Type in the message
2. Click save
To retrieve information using GSM
1. Look for message icon
2. Click on it
3. Scroll down to look for saved items
4. Click on the icon
5. It pops up the information
Practical:
i. Creating and sending messages using GSM
ii. Storing and retrieving information on a GSM handset
EVALUATION:
1. Mention two uses of:
(a) GSM phone (b) Fax machine (c) Telephone.
2. Describe how a telephone works.
TOPIC: ICT GADGETS
CONTENTS
1. GSM (Global System for Mobile Communication)
2. The differences between GSM, Fax machine and telephone
3. Creating and sending messages using GSM and Fax
4. Storing and retrieving information on a GSM
GSM (GLOBAL SYSTEM FOR MOBILE COMMUNICATION)
The Global System for Mobile Communication (GSM; original from Group Special Mobile)is the most popular standard for mobile phones in the world.GSM service is used by over 2 billion people across more than 212 countries and territories. The ubiquity of the GSM standard makes international roaming very common between mobile phone operators, enabling subscribers to use their phones in many part of the world.GSM differs significantly from its predecessors in that it is considered a second generation(2G)mobile phone system.
From the point of view of GSM users, the key advantage of GSM systems has been higher digital voice quality and low cost alternatives to making calls such as text messaging. Also, like other cellar standards, GSM allows network operators to offer roaming services which means subscribers can use their phones all over the world.

Subscriber Identity Module (SIM)
One of the key features of GSM is the subscriber identity module (SIM), commonly known as a SIM card. The SIM is detachable smart card containing the user’s subscription information and phonebook. This allows the user to retain his or her information after switching off the handsets. Alternatively, the user can also change operators while retaining the handset simply by changing the SIM, some operators will block this by allowing the phone to use only a single SIM or only a SIM issued by them; this practice is known as SIM locking, and is illegal in some countries.

Fax Machine
Fax (short for facsimile, i.e. “make a copy”) is a telecommunications technology used to transfer copies (facsimiles) of documents, especially using affordable devices operating over the telephone network. The word telefax, short for telefacsimile, for “make a copy at a distance”, is also used as a synonym.
A fax machine is essentially an image scanner, a modem, and a computer printer combined into a highly specialised package. The scanner converts the content of a physical document into a digital image, the modem sends the image data over a phone line, and the printer at the other end, makes a duplicate of the original document.
Fax machines with additional electronic features can connect to computers; can be used to scan documents into a computer, and to print documents from the computer. Such high-end devices are called multifunction printers and cost more than fax machines.

The telephone
The telephone is a telecommunication device which is used to transmit and receive sound (most commonly voice and speech) across distance. Most telephones operate through transmission of electric signals over a complex telephone network which allows almost any phone user to communicate with almost any other. Thus, a telephone is an electric tool. Using a telephone, two people who are in different places can talk.
Computer can use a machine called a modem to talk to other computer over a telephone line. This allows a computer to connect to other computer networks including the internet.

Mobile telephones
Early telephones needed to be connected with wires. Now telephone calls can be sent with radio. This is also called wireless. While the term “wireless” in this context means radio and can refer to any telephone that uses radio waves, it is primarily used for cellular mobile phones.

LESSON 4
THE DIFFERENCES BETWEEN GSM, FAX MACHINE AND TELEPHONE

STEPS IN CREATING AND SENDING MESSAGES USING GSM
The following steps are involved
i. Using any handset irrespective of the network
ii. Look for an icon that indicate message
iii. Click on the icon
iv. Sub menu pops up under it
v. Scroll down and look for icon label create a message
vi. Click on create a message
vii. Type the message and the phone number of the recipient
viii. Click the given green button on the handset to send the message.

STORING AND RETRIEVING INFORMATION ON A GSM
To store information using GSM
1. Type in the message
2. Click save
To retrieve information using GSM
1. Look for message icon
2. Click on it
3. Scroll down to look for saved items
4. Click on the icon
5. It pops up the information

Practical:
i. Creating and sending messages using GSM
ii. Storing and retrieving information on a GSM handset
EVALUATION:
1. Mention two uses of:
(a) GSM phone (b) Fax machine (c) Telephone.
2. Describe how a telephone works.
WEEK 4
LESSON 5
TOPIC: THE INTERNET(1)
CONTENTS
1. Definition of internet
2. Internet browser
3. Creating e-mail address
WHAT IS THE INTERNET?
The Internet is a collection of computers, all linked together, to share information worldwide. It is the largest computer network in the world.
We can search for information, read newspapers or listen to the news, send and receive mails (e-mail) and do many other things on the internet.
Some of the specific resources which the internet provides include, but not limited to the following:

ELECTRONIC MAIL (E-MAIL): This allows a message to be sent from one person to another, or to many others, via computer. Internet has its own e-mail standards that have also become the means of interconnecting most of the world’s e-mail systems. Internet e-mail addresses usually have a form such as “editor @encarta.microsoft.com” –where ‘editor ‘is the e-mail account name and Encarta.microsoft.com is the domain identity of the computer hosting the account. E-mail Addresses The e-mail address is the address used to send and receive e-mails. Every e-mail user has his or her own unique address. Examples of an e-mail address are;
AdeUche@yahoo.com, palchigo@yahoo.com, penwriteonline@yahoo.com
An e-mail address is generally made up of four parts;
i. The username
ii. The @ (at) symbol
iii. The name of the mail server or organisation where the user’s mailbox is located.
iv. The kind of organisation operating the e-mail.
Thus: from the e-mail address- penwriteonline@yahoo.com, “penwriteonline” is the “username”, ‘yahoo” is the name of the organisation. “.com” is the type of the organisation.
The e-mail address is pronounced as 'penwriteonline at yahoo dot com’. The organisation is a Commercial organisation that is why the e-mail address ends with “.com’

THE WORLD WIDE WEB (WWW): This allows the seamless creation and use of elegant point-and –click hypermedia presentations, linked across the internet in a way that creates a vast open knowledge repository, through which users can easily browse.
File Transfer Protocol (FTP): Is a set of conventions allowing the easy transfer of files between host computers. This remains the biggest use of the internet, especially for software distribution, and many public distribution sites exist.
USERNET: Allows automatic global distribution of news messages among thousands of user group, called newsgroups.
TELNET:This is the system that allows a user to “log in” to a remote computer, and make use of it.

LESSON 6
INTERNET BROWSER
An Internet browser is a program that locates website on the World Wide Web. It allows people to move around (browse) the World Wide Web and view web pages.
Examples of Internet browsers are
i. Internet Explorers
ii. Netscape Navigator
iii. Mozilla fire fox.
iv. Opera
v. Safari

E-MAIL:
E-Mail is a system for sending and receiving messages electronically over the internet e-mail allows messages to be sent between computers just like the traditional postal system allows letters to be sent between postal addresses. Each e-mail user has an electronic mailbox that is stored on special computer known as a mail server.
Common endings for e-mail addresses are:
.com or co (commercial organisation)
.edu (educational institution)
.mil (military)
.net (a network or non-commercial organisation)
.ac (academic institution)
Some e-mail addresses have a fifth part made up of an additional two letters known as the country code. This shows the country where the organisation or mail server is located. Examples are;
Adu.Uche@ui.edu.ng
J.C.Brown@acme.co.za
In the examples above,”ng” represents Nigeria while ‘za’ stands for South Africa. Other country codes are;
.gh ¬– Ghana
.bw – Botswana
.uk – United Kingdom
.in – India
.cn – China

CREATING AN E-MAIL ACCOUNT
An e-mail user must have an e-mail account in order to send or receive e-mails
Some e-mail services such as Yahoo! Mail, MSN, and Hotmail are provided for free to internet users. Others require a user to sign up with an ISP or be a member of an organisation or institution. To create a free account with Yahoo! Mail for example:
1. Open internet explorer and type mail.yahoo.com in the address bar.
2. On the Yahoo! Mail Webpage, click on Sign up to create new account. A new page will load.
3. Fill out the form on the new page and follow the instructions for creating a new account that are outlined on the page.
Note that you will be asked to choose a unique e-mail address (one that is not already being used by someone else), also you should choose a password that is easy for you to remember but difficult for others to guess.
SAMPLES OF E-MAIL ADDRESS
i. musa@hotmail.com
ii. emeka@yahoo.com
iii. kola@onebox.com, etc.
EVALUATION
1. Explain these terms
a. World wide web
b. E-mail
c. Usernet
2. How can you create an e-mail address?
TOPIC: THE INTERNET(1)
CONTENTS
1. Definition of internet
2. Internet browser
3. Creating e-mail address
WHAT IS THE INTERNET?
The Internet is a collection of computers, all linked together, to share information worldwide. It is the largest computer network in the world.
We can search for information, read newspapers or listen to the news, send and receive mails (e-mail) and do many other things on the internet.
Some of the specific resources which the internet provides include, but not limited to the following:

ELECTRONIC MAIL (E-MAIL): This allows a message to be sent from one person to another, or to many others, via computer. Internet has its own e-mail standards that have also become the means of interconnecting most of the world’s e-mail systems. Internet e-mail addresses usually have a form such as “editor @encarta.microsoft.com” –where ‘editor ‘is the e-mail account name and Encarta.microsoft.com is the domain identity of the computer hosting the account. E-mail Addresses The e-mail address is the address used to send and receive e-mails. Every e-mail user has his or her own unique address. Examples of an e-mail address are;
AdeUche@yahoo.com, palchigo@yahoo.com, penwriteonline@yahoo.com
An e-mail address is generally made up of four parts;
i. The username
ii. The @ (at) symbol
iii. The name of the mail server or organisation where the user’s mailbox is located.
iv. The kind of organisation operating the e-mail.
Thus: from the e-mail address- penwriteonline@yahoo.com, “penwriteonline” is the “username”, ‘yahoo” is the name of the organisation. “.com” is the type of the organisation.
The e-mail address is pronounced as 'penwriteonline at yahoo dot com’. The organisation is a Commercial organisation that is why the e-mail address ends with “.com’

THE WORLD WIDE WEB (WWW): This allows the seamless creation and use of elegant point-and –click hypermedia presentations, linked across the internet in a way that creates a vast open knowledge repository, through which users can easily browse.
File Transfer Protocol (FTP): Is a set of conventions allowing the easy transfer of files between host computers. This remains the biggest use of the internet, especially for software distribution, and many public distribution sites exist.
USERNET: Allows automatic global distribution of news messages among thousands of user group, called newsgroups.
TELNET:This is the system that allows a user to “log in” to a remote computer, and make use of it.

LESSON 6
INTERNET BROWSER
An Internet browser is a program that locates website on the World Wide Web. It allows people to move around (browse) the World Wide Web and view web pages.
Examples of Internet browsers are
i. Internet Explorers
ii. Netscape Navigator
iii. Mozilla fire fox.
iv. Opera
v. Safari
E-MAIL:
E-Mail is a system for sending and receiving messages electronically over the internet e-mail allows messages to be sent between computers just like the traditional postal system allows letters to be sent between postal addresses. Each e-mail user has an electronic mailbox that is stored on special computer known as a mail server.
Common endings for e-mail addresses are:
.com or co (commercial organisation)
.edu (educational institution)
.mil (military)
.net (a network or non-commercial organisation)
.ac (academic institution)
Some e-mail addresses have a fifth part made up of an additional two letters known as the country code. This shows the country where the organisation or mail server is located. Examples are;
Adu.Uche@ui.edu.ng
J.C.Brown@acme.co.za
In the examples above,”ng” represents Nigeria while ‘za’ stands for South Africa. Other country codes are;
.gh ¬– Ghana
.bw – Botswana
.uk – United Kingdom
.in – India
.cn – China

CREATING AN E-MAIL ACCOUNT
An e-mail user must have an e-mail account in order to send or receive e-mails
Some e-mail services such as Yahoo! Mail, MSN, and Hotmail are provided for free to internet users. Others require a user to sign up with an ISP or be a member of an organisation or institution. To create a free account with Yahoo! Mail for example:
1. Open internet explorer and type mail.yahoo.com in the address bar.
2. On the Yahoo! Mail Webpage, click on Sign up to create new account. A new page will load.
3. Fill out the form on the new page and follow the instructions for creating a new account that are outlined on the page.
Note that you will be asked to choose a unique e-mail address (one that is not already being used by someone else), also you should choose a password that is easy for you to remember but difficult for others to guess.

SAMPLES OF E-MAIL ADDRESS
i. musa@hotmail.com
ii. emeka@yahoo.com
iii. kola@onebox.com, etc.

EVALUATION
1. Explain these terms
a. World wide web
b. E-mail
c. Usernet
2. How can you create an e-mail address?
WEEK 5
LESSON 7
TOPIC: INTERNET- THE INTERNET Environment
CONTENTS
1. Using a Browser
2. Sending an e-mail
3. Network groups
Using a web browser
A web browser is a type of software that allows you to find and view websites on the Internet. Even if you didn't know it, you're using a web browser right now to read this page! There are many different web browsers, but some of the most common ones include Google Chrome, Internet Explorer, Safari, Microsoft Edge, and Mozilla Firefox.
No matter which web browser you use, you'll want to learn the basics of browsing the Web. In this lesson, we'll talk about navigating to different websites, using tabbed browsing, creating bookmarks, and more.
https://youtu.be/FxirRVJWUTs
Sending an e-mail
There are some special software called mailers for sending and receiving e-mails services over the internet. Some mailers are provided with free e-mail services over the internet.
Examples are: Yahoo! Mail, MSN, and Hotmail. Other mailers use special software that requires users to pay regular fees to ISP or organization that provides the e-mails account.
An e-mail message is made up of two parts: the header and the body.
1. Sending and receiving e-mail
The header is made up of:
1. The e-mail address of the receiver (to:)
2. The subject or title of sender message
3. The e-mail address of the sender(from: )
Some other information such as date may also be included in the header. The body of e-mail is in the content of the message.

TO SEND AN E-MAIL MESSAGE
1. Open the mailer software (e.g mail.yahoo.com).
2. Log in with your e-mail address and password.
3. Type in the address of the receiver into the: box
4. Type a title for your message in the subject: box
5. Type your message in the body of the e-mail.
6. After typing the message, click on the send button to send it to the receiver.
You can also attach files to e-mail message, to send pictures sounds document videos and other type of files with your e-mail. The mail server has a mailbox for each e-mail user. The mailbox contains folders where incoming mails and outgoing mails are stored. Incoming mails are stored in the inbox and outgoing mails are stored in the outbox .Some mailbox also have folders where deleted e-mails are stored. This folder is called either trash or deleted items.
CHATTING ON THE INTERNET:
Instant messaging software such as Yahoo! Messenger and MSN Messenger. Allows users to contact friends and other people through the internet and communicate or chat with them in real time.
When two or more people communicate in real time it means that they are all online at the same time so they can send message to each other and reply instantly.
Users have to have the instant messaging software and create an account on it.
The software can be downloaded for free from the internet. The user also creates a list of contacts (people he chats with) that is stored by the software. When the user is online, the software will notify him whenever any of his contacts are online and a contact is available. Instant messaging allows you to chat, send messages and files only with people that you choose.

NETWORK GROUPS
Network groups are a means for groups of people with common interest to connect with each other via internet. There are two major types of network groups namely; Mailing lists and Newsgroups.
Mailing lists: a mailing list (also called a listserve) is a discussion list which allows communications via e-mail among a group of people who are interested in a common topic. A person has to sign up to become a member of a list. To join a list, a person sends an e-mail message to a special e-mail address known as list server. The server adds the person’s e-mail address to mailing list. List can be local, national or international. They can have a few or many thousands of members. Lists are used for wide range of purposes including informal discussion, disseminating information, surveys and questionnaires, and locating people with similar interest. By joining a list, a user will receive all mails sent to the list members. While many lists are public and open for anyone to join, others are private and closed.
Newsgroups: Newsgroups are also called Usenet. Unlike mailing lists, newsgroups are like electronic bulletin boards. Messages to a group (known as postings) are stored on a computer server and users have to access this computer in order to read them. Group participants can use the group to make announcements, ask for answers to problems, air opinions and so on. Many newsgroups are international and have hundreds of postings everyday. A special piece of software called a newsreader is required in order to send message to, or read messages on the server.
Examples of news groups for students are
http://www.schoolnet.org
http://www.stow.net

EVALUATION
1. Describe the following internet resources
(i) News groups
(ii) Chatting
(iii) Mailing lists
(iv) Electronic mailing
2. List the steps involved in sending an e-mail message.
TOPIC: INTERNET- THE INTERNET Environment
CONTENTS
1. Using a Browser
2. Sending an e-mail
3. Network groups
Using a web browser
A web browser is a type of software that allows you to find and view websites on the Internet. Even if you didn't know it, you're using a web browser right now to read this page! There are many different web browsers, but some of the most common ones include Google Chrome, Internet Explorer, Safari, Microsoft Edge, and Mozilla Firefox.
No matter which web browser you use, you'll want to learn the basics of browsing the Web. In this lesson, we'll talk about navigating to different websites, using tabbed browsing, creating bookmarks, and more.
https://youtu.be/FxirRVJWUTs
Sending an e-mail
There are some special software called mailers for sending and receiving e-mails services over the internet. Some mailers are provided with free e-mail services over the internet.
Examples are: Yahoo! Mail, MSN, and Hotmail. Other mailers use special software that requires users to pay regular fees to ISP or organization that provides the e-mails account.
An e-mail message is made up of two parts: the header and the body.
1. Sending and receiving e-mail
The header is made up of:
1. The e-mail address of the receiver (to:)
2. The subject or title of sender message
3. The e-mail address of the sender(from: )
Some other information such as date may also be included in the header. The body of e-mail is in the content of the message.

TO SEND AN E-MAIL MESSAGE
1. Open the mailer software (e.g mail.yahoo.com).
2. Log in with your e-mail address and password.
3. Type in the address of the receiver into the: box
4. Type a title for your message in the subject: box
5. Type your message in the body of the e-mail.
6. After typing the message, click on the send button to send it to the receiver.
You can also attach files to e-mail message, to send pictures sounds document videos and other type of files with your e-mail. The mail server has a mailbox for each e-mail user. The mailbox contains folders where incoming mails and outgoing mails are stored. Incoming mails are stored in the inbox and outgoing mails are stored in the outbox .Some mailbox also have folders where deleted e-mails are stored. This folder is called either trash or deleted items.

CHATTING ON THE INTERNET:
Instant messaging software such as Yahoo! Messenger and MSN Messenger. Allows users to contact friends and other people through the internet and communicate or chat with them in real time.
When two or more people communicate in real time it means that they are all online at the same time so they can send message to each other and reply instantly.
Users have to have the instant messaging software and create an account on it.
The software can be downloaded for free from the internet. The user also creates a list of contacts (people he chats with) that is stored by the software. When the user is online, the software will notify him whenever any of his contacts are online and a contact is available. Instant messaging allows you to chat, send messages and files only with people that you choose.

NETWORK GROUPS
Network groups are a means for groups of people with common interest to connect with each other via internet. There are two major types of network groups namely; Mailing lists and Newsgroups.
Mailing lists: a mailing list (also called a listserve) is a discussion list which allows communications via e-mail among a group of people who are interested in a common topic. A person has to sign up to become a member of a list. To join a list, a person sends an e-mail message to a special e-mail address known as list server. The server adds the person’s e-mail address to mailing list. List can be local, national or international. They can have a few or many thousands of members. Lists are used for wide range of purposes including informal discussion, disseminating information, surveys and questionnaires, and locating people with similar interest. By joining a list, a user will receive all mails sent to the list members. While many lists are public and open for anyone to join, others are private and closed.

Newsgroups: Newsgroups are also called Usenet. Unlike mailing lists, newsgroups are like electronic bulletin boards. Messages to a group (known as postings) are stored on a computer server and users have to access this computer in order to read them. Group participants can use the group to make announcements, ask for answers to problems, air opinions and so on. Many newsgroups are international and have hundreds of postings everyday. A special piece of software called a newsreader is required in order to send message to, or read messages on the server.
Examples of news groups for students are
http://www.schoolnet.org
http://www.stow.net

EVALUATION
1. Describe the following internet resources
(i) News groups
(ii) Chatting
(iii) Mailing lists
(iv) Electronic mailing
2. List the steps involved in sending an e-mail message.
WEEK 7 & 8
LESSON 8
TOPIC: COMPUTER ETHICS
CONTENTS
1. Responsible use of the computer
2. Areas of misuse of computers
RESPONSIBLE USE OF COMPUTERS
In order to get the maximum performance from a computer, the computer system must be used responsibly. This means that a user should observe the following rules:
1: Avoid dropping food or liquids on the system.
2: Cover the computer and all peripherals with dust covers when not in use.
3: The system should be protected from power surges by using either a voltage stabilizer or a surge protector.
4: In places where power outages are common, the system should be connected to an uninterruptible power supply unit (UPS) to protect the system from shutting down abruptly and avoid damage to the computer’s memory.
5: The system should be unplugged from the power source when it is not going to be used for a long time.

Responsible use of the Internet
1: Check your e-mail regularly.
2: Answer mail promptly and politely
3: The subject of e-mails should be short, meaningful and truthful.
4: Be aware that the internet is a public medium and the content of any e-mail may end up in unexpected places so write thoughtfully.
5: Check your spellings.
6: Be careful about the sites you visit on the WWW, a lot of innocent looking Sites contain pornographic and other offensive materials.
7. Do not open file attachments from unknown sources, they Can contain Viruses.
8. Be careful about giving personal information about yourself to anyone you meet over the internet.


MISUSE OF COMPUTER AND THE INTERNET
People misuse computers and the internet in several ways including:
1. INVASION OF PRIVACY: In a network environment people can use a computer in the network to gain illegal access to files and other information. Such unauthorized access is known as hacking. Hackers can also access computers to collect private information about individuals or delete important information.
2. COMPUTER VIRUS: people can introduce a virus into a computer system or network via fictitious e-mails, infected diskettes, etc.
3. FRAUD: false data and information are sent through e-mails and mailings lists to fraudulently collect money and other items from unsuspecting victims.
4. PORNOGRAPHY: unscrupulous people use the internet to promote and distribute pornographic materials.
5. PIRACY: many people use CD or DVD writers in computers to make illegal copies of software and other materials such music, films, etc.
6. PLAGIARISM: Plagiarism is the act of copying another person’s intellectual work such as a book, music, etc and presenting it is as one’s own. It is a serious crime and many institutions of higher learning have dismissed students and staff as a result of plagiarism. Computers and the internet have made it easy to get access to, and copy other people’ works.

EVALUATION:
1. Mention and explain four ways to use computers and the internet responsibly.
2. Mention and explain five ways in which computers and the internet can be misused.
ASSIGNMENT: Students are to read page 140-143 of textbook.
TOPIC: COMPUTER ETHICS
CONTENTS
1. Responsible use of the computer
2. Areas of misuse of computers
RESPONSIBLE USE OF COMPUTERS
In order to get the maximum performance from a computer, the computer system must be used responsibly. This means that a user should observe the following rules:
1: Avoid dropping food or liquids on the system.
2: Cover the computer and all peripherals with dust covers when not in use.
3: The system should be protected from power surges by using either a voltage stabilizer or a surge protector.
4: In places where power outages are common, the system should be connected to an uninterruptible power supply unit (UPS) to protect the system from shutting down abruptly and avoid damage to the computer’s memory.
5: The system should be unplugged from the power source when it is not going to be used for a long time.

Responsible use of the Internet
1: Check your e-mail regularly.
2: Answer mail promptly and politely
3: The subject of e-mails should be short, meaningful and truthful.
4: Be aware that the internet is a public medium and the content of any e-mail may end up in unexpected places so write thoughtfully.
5: Check your spellings.
6: Be careful about the sites you visit on the WWW, a lot of innocent looking Sites contain pornographic and other offensive materials.
7. Do not open file attachments from unknown sources, they Can contain Viruses.
8. Be careful about giving personal information about yourself to anyone you meet over the internet.


MISUSE OF COMPUTER AND THE INTERNET
People misuse computers and the internet in several ways including:
1. INVASION OF PRIVACY: In a network environment people can use a computer in the network to gain illegal access to files and other information. Such unauthorized access is known as hacking. Hackers can also access computers to collect private information about individuals or delete important information.
2. COMPUTER VIRUS: people can introduce a virus into a computer system or network via fictitious e-mails, infected diskettes, etc.
3. FRAUD: false data and information are sent through e-mails and mailings lists to fraudulently collect money and other items from unsuspecting victims.
4. PORNOGRAPHY: unscrupulous people use the internet to promote and distribute pornographic materials.
5. PIRACY: many people use CD or DVD writers in computers to make illegal copies of software and other materials such music, films, etc.
6. PLAGIARISM: Plagiarism is the act of copying another person’s intellectual work such as a book, music, etc and presenting it is as one’s own. It is a serious crime and many institutions of higher learning have dismissed students and staff as a result of plagiarism. Computers and the internet have made it easy to get access to, and copy other people’ works.

EVALUATION:
1. Mention and explain four ways to use computers and the internet responsibly.
2. Mention and explain five ways in which computers and the internet can be misused.
ASSIGNMENT: Students are to read page 140-143 of textbook.
WEEK 9
LESSON 9
TOPIC: SAFETY MEASURES
SAFETY MEASURES
When using computers, safety measures must be taken to protect both the computer system and the
People that are using it, by doing this, the computer’s life span can be prolonged.
The following points summaries the safety measures every computer user is expected to take in the
Process of using the computer systems:
1. Good sitting habit must be exercised.
2. Using antiglare protection should be recommended.
3. Monitor base must be positioned correctly.
4. Dust free environment must be maintained.
5. Keep liquid away from the computer. Students are not expected to eat or drink beside the computer.
6. A computer room must be adequately illuminated.
7. A computer laboratory or where computer is placed should be well ventilated. This can be done by using air conditioner to keep the surrounding cool.

EVALUATION:
State four measures that need to be taken when using a computer
…………………………………………………………….
…………………………………………………………….
…………………………………………………………….
…………………………………………………………….
TOPIC: SAFETY MEASURES
SAFETY MEASURES
When using computers, safety measures must be taken to protect both the computer system and the
People that are using it, by doing this, the computer’s life span can be prolonged.
The following points summaries the safety measures every computer user is expected to take in the
Process of using the computer systems:
1. Good sitting habit must be exercised.
2. Using antiglare protection should be recommended.
3. Monitor base must be positioned correctly.
4. Dust free environment must be maintained.
5. Keep liquid away from the computer. Students are not expected to eat or drink beside the computer.
6. A computer room must be adequately illuminated.
7. A computer laboratory or where computer is placed should be well ventilated. This can be done by using air conditioner to keep the surrounding cool.

EVALUATION:
State four measures that need to be taken when using a computer
…………………………………………………………….
…………………………………………………………….
…………………………………………………………….
…………………………………………………………….