NEW SCHEME OF WORK:
WEEKS TOPICS
1. Concept of Technology: (a) Definitions and Benefits (b) products of Technology (c) life application of technology(what technology has contributed to human living)
2. Technology and Society: Products of Technology-cutlery, houses, motor cars, computers, lighting system, etc. who should study technology? The need for technological literacy and capability for all as life coping skill.
3. Workshop Safety Rules and Regulation. (a) meaning and causes of workshop accidents (b) accident prevention techniques.
4. Workshop Safety Rules and Regulation (cont’d): safety devices; fire extinguishers, sand buckets, blanket, gloves etc. (d) types of fire: (i) electrical (ii) chemical etc.
5. Properties of materials: (a) Wood – (i) identification by colour, mahogany, afara, obeche, opepe, mansonia, etc. (ii) classification; hardwood and softwood. (iii) Properties e.g. hardwood has broad leaves, seed enclosed in seed cases. Soft wood has needle-like leaves, naked seeds.
6. Properties of materials (cont’d)(b) Metals- (i) identification by their physical properties, e.g. luster, density, sound, malleability, ductility, etc. (ii) classification: ferrous and non-ferrous with examples. Form: e.g. rods, pipes, wires, bars, plates, sheets, etc.
7. Properties of materials (cont’d): (c) ceramics and glass: (i) types: bricks, tiles, bottles, cups, pots, etc. (ii) properties: brittles, heat resistant etc.
8. Drawing Instruments and materials: (a) Definition of technical drawing (b) Drawing Instrument and materials: tee-square, set square, pair of compasses and dividers, the protractor, rulers, templates and stencils, pencils and glass paper block, pencil sharpener, erasers and erasing shields, drawing paper, French curves, drafting tapes, tracing papers, etc. (c) Basic Techniques of handling and Storage of caring for instruments and drawing materials.
9. Revision
OLD SCHEME
WEEKS TOPICS
1. Concepts of Technology (who should study technology)
Definition or meaning of introductory technology, technology and economic development.
2. Workshop Safety Rules and Regulations
For (a) Bench Works and (b) Machine Uses, Accident, Causes and Prevention.
3. Drawing Practice
Drawing Instrument and Materials, Care and Storage of Drawing Instruments and Materials.
4. Freehand sketching - Definition or Meaning and Techniques.
5. Scale Drawing Definition or Meaning and Types of Scale.
6. Board Practices: Definition, Basic techniques: (a) setting the paper on the board (b) using the Tee square in the drawing of lines
(d) drawing of margin lines and positioning of title block.
7. Revision: Practical projects and test.
1ST TERM
WEEK 1
LESSON 1
TOPIC: MEANING OF TECHNOLOGY
OBJECTIVE: At the end of the lesson, the students should be able to
1. Define technology.
2. Define introductory technology.
CONTENT:
TECHNOLOGY
Technology is the process developed by people to provide for their various needs. The common needs of human beings are shelter, security, food, good health, communication, transportation.

Introductory technology is the science of human development. Introductory Technology is now called Basic Technology, the subjects in Introductory Technology include:
1. Technical drawing
2. Auto mechanics
3. Electronic technology
4. Applied electricity
5. Wood work
6. Metal work
7. Building technology

EVALUATION:
Define technology.
Define introductory technology.
Mention the subjects in Basic Technology.
ASSIGNMENT:
Mention 5 olden days equipment and their advanced equipment.
LESSON 2
TOPIC: ECONOMIC IMPORTANCE OF TECHNOLOGY
OBJECTIVE: At the end of the lesson, the students should be able to:
1. State the differences between developed technology and under-developed technology.
2. State the economic importance of technology.
CONTENT:
TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENT
There are two types of technology: the developed technology and the under-developed technology.
1. Under-developed Technology is the technology of the olden days which includes the manual process and the olden day equipment.
2. Developed Technology is the modern day technology that is mechanized technology.

Differences between Developed and Under-developed Technology
Developed Technology.............................................Under-developed Technology
Tractors, harvesters, etc. for farming...........................Hoe, cutlass, baskets for farming.
Sky scrapper, duplex as shelter.......................................Mud houses, hut for shelter.
Aeroplane, ship, cars etc as means of transportation......Trekking, carts, horses, camel as means of transportation.
Phones, E-mail, electronic media as means of communication.......Writing letters, town crying, drums as means of communication.
ECONOMIC IMPORTANCE OF TECHNOLOGY
I. Technology enables a country to maximize the use of its raw materials.
II. A country with well developed technology has reduced problem of security, health, etc.

EVALUATION:
Mention the two types of technology.
State the differences between developed and under-developed technology.
Highlight the economic importance of technological development.
Further Studies 1
TOPIC: MEANING OF TECHNOLOGY
OBJECTIVE: At the end of the lesson, the students should be able to
1. Define technology.
2. Define introductory technology.
CONTENT:
TECHNOLOGY
Technology is the process developed by people to provide for their various needs. The common needs of human beings are shelter, security, food, good health, communication, transportation.

Introductory technology is the science of human development. Introductory Technology is now called Basic Technology, the subjects in Introductory Technology include:
1. Technical drawing
2. Auto mechanics
3. Electronic technology
4. Applied electricity
5. Wood work
6. Metal work
7. Building technology

EVALUATION:
Define technology.
Define introductory technology.
Mention the subjects in Basic Technology.
ASSIGNMENT:
Mention 5 olden days equipment and their advanced equipment.
LESSON 2
TOPIC: ECONOMIC IMPORTANCE OF TECHNOLOGY
OBJECTIVE: At the end of the lesson, the students should be able to:
1. State the differences between developed technology and under-developed technology.
2. State the economic importance of technology.
CONTENT:
TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENT
There are two types of technology: the developed technology and the under-developed technology.
1. Under-developed Technology is the technology of the olden days which includes the manual process and the olden day equipment.
2. Developed Technology is the modern day technology that is mechanized technology.

Differences between Developed and Under-developed Technology
Developed Technology.............................................Under-developed Technology
Tractors, harvesters, etc. for farming...........................Hoe, cutlass, baskets for farming.
Sky scrapper, duplex as shelter.......................................Mud houses, hut for shelter.
Aeroplane, ship, cars etc as means of transportation......Trekking, carts, horses, camel as means of transportation.
Phones, E-mail, electronic media as means of communication.......Writing letters, town crying, drums as means of communication.
ECONOMIC IMPORTANCE OF TECHNOLOGY
I. Technology enables a country to maximize the use of its raw materials.
II. A country with well developed technology has reduced problem of security, health, etc.

EVALUATION:
Mention the two types of technology.
State the differences between developed and under-developed technology.
Highlight the economic importance of technological development.
Further Studies 1
WEEK 2
LESSON 3
TOPIC: Concept of Technology
SUB-TOPICS: (I) Definition and Introduction to the subject(II) Benefits of Technology
(III) Life Application of Technology
Definition and Introduction to the subject
Technology is the processes (method) and products (materials) that make life easy and stress free. It can also be defined as cultural traditions developed in human communities for developing the physical and biological environment.
Basic Technology comprises of woodwork, metalwork, building technology, automobile technology, electrical/electronics, technical drawing.
Technology has positively affected every area of our life. Therefore, technology makes our work easier, faster, neater, more accurate and more reliable.

Benefits of Technology
1. Technology has improved our transportation system. People can move from one place to another on cars, airplane, trains etc as means of transportation system.
2. Technology has improved communication system. Information beyond our solar system is being gathered through various means such as Telex, radio etc. computer system, internet, e-mail as a means of communication system to make business contact, invitation, alert etc
3. Technology has improved the working environment. The use of machines to produce goods and services has reduced the necessity for human and animals labour.
4. Technology has brought improvement in literacy and educational levels to the society.
5. Technology has improved the development of medical health care delivery
6. Technology has improved quality of goods and increased production as a result for farming , using agricultural equipment eg harvesters, tractors etc

EVALUATION
1. What is Technology?
2. Name three subjects under Basic Technology
3. What are the benefits of technology?
LESSON 4
Life Application of Technology
LIFE APPLICATION OF TECHNOLOGY (What Technology has contributed to human living)

People with inquiring and creative minds will always use technology and right attitude to overcome the limitations of their environment. It was shown that many tasks that are otherwise next to impossible are now possible due to technological innovations. We can now travel fast by air, sea, or land. We can lift heavy loads by use of cranes and can cultivate large areas of land by use of slashers,ploughs, harrowers and tractors. Nowadays, the economic power of a country does not depend on its having a large population or abundant natural resources but rather on technology. There is a chance for everybody to contribute his quota to technological development no matter how small

EVALUATION
Mention some life applications of technology
READING ASSIGNMENT
Read about Concept of Technology
Text: The NERDC Basic Technology for Junior Secondary Schools 1 Chapter 1 Pages 1 - 5
ASSIGNMENT
1. These three subjects are under Basic Technology except (a) Chemistry (b) Woodwork (c) Technical Drawing (d) Automobile Technology.
2. --------------- are benefits of technology expect
(a) Communication system (b) transportation system (c) typing system (d) literacy and educational level
Essay
1. What is technology
2. In your own view, write life application of technology
3. List 4 subjects under Basic Technology
4. Choose 4 out of these – Woodwork, Metalwork, Building Technology, Automobile Technology, Electrical/Electronics, and Technical Drawing.
LESSON 5
Topic: Technology and Society
Sub-Topics:
(I) Products of technology
(II) Who should study technology?
(III) The need for technological literacy and capability for all as life coping skill
Products of technology
Products of technology refer to the materials, machines
and equipment that are used to make life easier which are sometimes called tools.
The modern ways of doing many things today are far easier and faster than they used to be in the past.
The products of technology include the following:

1. Home Appliances: Examples; Refrigerator, Gas cooker, Electric cooker and kettle, Television etc.
2. Agricultural Implements: Examples; tractors, harvesters, seed shellersetc
3. Office Equipment: Examples; Computers, Printers, Scanner etc
4. Sport Equipment: Examples; Rackets, Bats, Internets games etc
5. Communication products: Examples; G.S.M, fixed wireless phone. Internets etc
6. Education Goods: Examples: books, educational software, news paper, magazine etc
7. Power plant: Examples; industrial machines, electrical equipments, power saws, electric motors etc
8. Utility Goods and Equipment: Examples: Calculators, radios, batteries etc
EVALUATION
Name three products of technology and its technological advantage
LESSON 6
Who should study technology?
Everybody living in the society e.g. man, woman, boy or girl should study technology because the need for basic technology literacy is necessary in this modern world.
Technology helps to improve our standard of living in society. It means everybody living in a society should be involved in studying technology.
Under-developed technology involves the use of crude methods and tools to do things while developed technology involves the use of modern methods and equipment to do things.

Under-Developed Technology ...............Developed Technology
Farming.... Use of hoes and cutlasses ....Use of tools and machines
Food preservation.... Drying ....Refrigerators, canning etc
Communication ....Oral message and letter writing ....Telephone, telex, radio message, satellite etc.
PRODUCT OF TECHNOLOGY................. TECHNOLOGY ADVANTAGE
1. Gas cooker ...................Makes cooking easier and faster
2. Aeroplane .........................Makes travelling faster and more comfortable
The need for technological literacy and capability for all as life coping skill.
The technological literacy is the ability for someone to understand and use basic technology for everyday living.
Everybody should be planning to be technologically literate because it:
1. Helps us improve and solve our problems using modern approach.
2. Helps us to acquire practical skills which can be used in our work, home, schools and life generally.
3. Helps us to be capable of doing things which can protect us from dangers.
However, it is necessary for everybody to acquired basic technological literacy and capability which creates jobs to enable every person to have occupational identity.

EVALUATION
Discuss who should study Technology
READING ASSIGNMENT
Read about Technology and Society
Text: The NERDC Basic Technology for Junior Secondary Schools 1 Chapter 1 Pages 1 - 5
ASSIGNMENT
1. ………………………… are products of technology except
(a) Home appliances (b) Office Equipment (c)typing appliances
(d) Communication products
2. The following are true of under-developed technology except
(a) The use of hooks for fishing
(b) The provision of artificial raw materials
(c) The use of horse-drawn carts
(d) The use of gong for communication
3. A country with an under-developed technology use
(a) Telephone for communication
(b) Fertilizer for farming
(c) Refrigerator for preserving food
(d) Drying for preserving food
Theory
1. Technology is the processes and products that make life easy and stress-free OR
Technology is a cultural traditions developed in human communities for developing the physical and biological environment. Discuss
Economic Activity Under Developed Developed
Transportation (a) _____________ Use of motor complex
(b) _____________ Use of hooks and nets Use of sophisticated and fast-moving fishing vessel
Food preservation Drying (c) _______________
TOPIC: Concept of Technology
SUB-TOPICS: (I) Definition and Introduction to the subject(II) Benefits of Technology
(III) Life Application of Technology
Definition and Introduction to the subject
Technology is the processes (method) and products (materials) that make life easy and stress free. It can also be defined as cultural traditions developed in human communities for developing the physical and biological environment.
Basic Technology comprises of woodwork, metalwork, building technology, automobile technology, electrical/electronics, technical drawing.
Technology has positively affected every area of our life. Therefore, technology makes our work easier, faster, neater, more accurate and more reliable.

Benefits of Technology
1. Technology has improved our transportation system. People can move from one place to another on cars, airplane, trains etc as means of transportation system.
2. Technology has improved communication system. Information beyond our solar system is being gathered through various means such as Telex, radio etc. computer system, internet, e-mail as a means of communication system to make business contact, invitation, alert etc
3. Technology has improved the working environment. The use of machines to produce goods and services has reduced the necessity for human and animals labour.
4. Technology has brought improvement in literacy and educational levels to the society.
5. Technology has improved the development of medical health care delivery
6. Technology has improved quality of goods and increased production as a result for farming , using agricultural equipment eg harvesters, tractors etc

EVALUATION
1. What is Technology?
2. Name three subjects under Basic Technology
3. What are the benefits of technology?
LESSON 4
Life Application of Technology
LIFE APPLICATION OF TECHNOLOGY (What Technology has contributed to human living)

People with inquiring and creative minds will always use technology and right attitude to overcome the limitations of their environment. It was shown that many tasks that are otherwise next to impossible are now possible due to technological innovations. We can now travel fast by air, sea, or land. We can lift heavy loads by use of cranes and can cultivate large areas of land by use of slashers,ploughs, harrowers and tractors. Nowadays, the economic power of a country does not depend on its having a large population or abundant natural resources but rather on technology. There is a chance for everybody to contribute his quota to technological development no matter how small

EVALUATION
Mention some life applications of technology
READING ASSIGNMENT
Read about Concept of Technology
Text: The NERDC Basic Technology for Junior Secondary Schools 1 Chapter 1 Pages 1 - 5
ASSIGNMENT
1. These three subjects are under Basic Technology except (a) Chemistry (b) Woodwork (c) Technical Drawing (d) Automobile Technology.
2. --------------- are benefits of technology expect
(a) Communication system (b) transportation system (c) typing system (d) literacy and educational level
Essay
1. What is technology
2. In your own view, write life application of technology
3. List 4 subjects under Basic Technology
4. Choose 4 out of these – Woodwork, Metalwork, Building Technology, Automobile Technology, Electrical/Electronics, and Technical Drawing.
LESSON 5
Topic: Technology and Society
Sub-Topics:
(I) Products of technology
(II) Who should study technology?
(III) The need for technological literacy and capability for all as life coping skill
Products of technology
Products of technology refer to the materials, machines
and equipment that are used to make life easier which are sometimes called tools.
The modern ways of doing many things today are far easier and faster than they used to be in the past.
The products of technology include the following:
1. Home Appliances: Examples; Refrigerator, Gas cooker, Electric cooker and kettle, Television etc.
2. Agricultural Implements: Examples; tractors, harvesters, seed shellersetc
3. Office Equipment: Examples; Computers, Printers, Scanner etc
4. Sport Equipment: Examples; Rackets, Bats, Internets games etc
5. Communication products: Examples; G.S.M, fixed wireless phone. Internets etc
6. Education Goods: Examples: books, educational software, news paper, magazine etc
7. Power plant: Examples; industrial machines, electrical equipments, power saws, electric motors etc
8. Utility Goods and Equipment: Examples: Calculators, radios, batteries etc
EVALUATION
Name three products of technology and its technological advantage
LESSON 6
Who should study technology?
Everybody living in the society e.g. man, woman, boy or girl should study technology because the need for basic technology literacy is necessary in this modern world.
Technology helps to improve our standard of living in society. It means everybody living in a society should be involved in studying technology.
Under-developed technology involves the use of crude methods and tools to do things while developed technology involves the use of modern methods and equipment to do things.

Under-Developed Technology ...............Developed Technology
Farming.... Use of hoes and cutlasses ....Use of tools and machines
Food preservation.... Drying ....Refrigerators, canning etc
Communication ....Oral message and letter writing ....Telephone, telex, radio message, satellite etc.
PRODUCT OF TECHNOLOGY................. TECHNOLOGY ADVANTAGE
1. Gas cooker ...................Makes cooking easier and faster
2. Aeroplane .........................Makes travelling faster and more comfortable
The need for technological literacy and capability for all as life coping skill.
The technological literacy is the ability for someone to understand and use basic technology for everyday living.
Everybody should be planning to be technologically literate because it:
1. Helps us improve and solve our problems using modern approach.
2. Helps us to acquire practical skills which can be used in our work, home, schools and life generally.
3. Helps us to be capable of doing things which can protect us from dangers.
However, it is necessary for everybody to acquired basic technological literacy and capability which creates jobs to enable every person to have occupational identity.

EVALUATION
Discuss who should study Technology
READING ASSIGNMENT
Read about Technology and Society
Text: The NERDC Basic Technology for Junior Secondary Schools 1 Chapter 1 Pages 1 - 5
ASSIGNMENT
1. ………………………… are products of technology except
(a) Home appliances (b) Office Equipment (c)typing appliances
(d) Communication products
2. The following are true of under-developed technology except
(a) The use of hooks for fishing
(b) The provision of artificial raw materials
(c) The use of horse-drawn carts
(d) The use of gong for communication
3. A country with an under-developed technology use
(a) Telephone for communication
(b) Fertilizer for farming
(c) Refrigerator for preserving food
(d) Drying for preserving food
Theory
1. Technology is the processes and products that make life easy and stress-free OR
Technology is a cultural traditions developed in human communities for developing the physical and biological environment. Discuss
Economic Activity Under Developed Developed
Transportation (a) _____________ Use of motor complex
(b) _____________ Use of hooks and nets Use of sophisticated and fast-moving fishing vessel
Food preservation Drying (c) _______________
WEEK 3
LESSON 7
TOPIC: Workshop Safety Rules and Regulation
SUB-TOPICS:
(i) Safety Rules for Bench workers
(ii) Safety Rules for machine users
(iii) Accidents, Causes and Prevention
Safety Rules for Bench Workers
Safety rules/precautions are the rules and regulations guiding the movement and behavior of individual in the workshop to avoid vital accident. The following are the safety rules for bench workers:
(1) If chips are likely to fly, wear goggle.
(2) Always hold the work piece securely in the vice.
(3) Never use a chisel which has developed a mushroomed head.
(4) If a workplace is hot, mark it in some ways to indicate the facts to others.
(5) Always use a brush to remove chippings or filings. Do not use your hands to blow.

Safety Rules for Machine Users
1. Never indulge in horse play in a machinery workshop or in the metal workshop in general.
2. Never operate a machine unless you have been properly instructed in its use.
3. Always ensure you are properly dressed for the job in hand. Always wear some type of eye protection when using machines especially grinding machines.
4. It is very important to read the maker’s instructions on all packed goods before opening or unscrewing stoppers on new machines even if you think you know the procedure. It is possible that the makers have amended their instructions since your last reading.
5. Never clean the machine when it is on motion.

Evaluation
What is safety precaution?
State two safety rules for bench workers and machine users.
LESSON 8
Sub-Topic 3: Accidents: Cause and Prevention
An accident is a negative experience that happens to somebody when he does not expect it. Accident is an unforeseen cause of events. Accidents are caused by people and equipment.
Causes of Accidents
Accidents in the workshop are caused when:
(1) Students do not follow the manufacturer’s or teacher’s instructions on how to use the machine in the workshop.
(2) Students are not careful enough in the workshop while handling the machines.
(3) Students engage in horse play in the workshop.
(4) The machines being used are not in good form.
(5) The worn out parts of machines are not replaced on time.
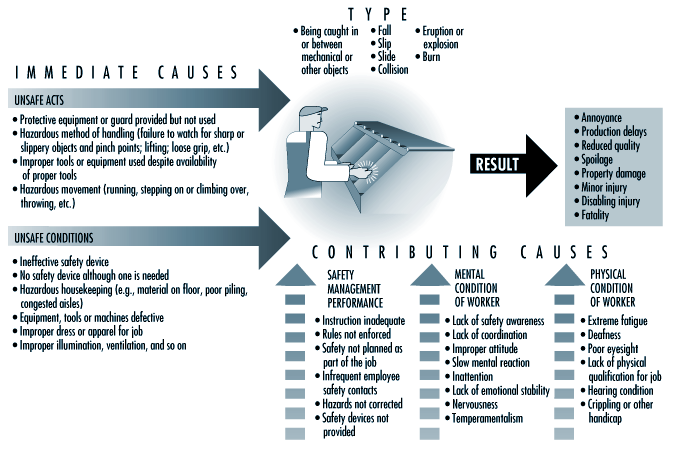
Accident Prevention Techniques
Steps to take in preventing accidents are:
(i) Routine Checking – This involves checking all machines to ensure that they are in good condition before setting them up for use.
(ii) Routine Servicing - It involves servicing all machines and changing the worn out parts regularly so that they can work effectively.
(iii) Students’ Comportment – Students should avoid noise-making and talkativeness in the workshop because this can make them lose concentration on the work they are doing.
(iv) Preventive Measures – Electronic equipment should be used with voltage stabilizers in order to prevent electrical fire as a result of power surge.
(v) Teachers’ supervision – To prevent workshop accidents, every workshop lesson or practical session should be supervised by the teacher. Students should not be left alone in the workshop.
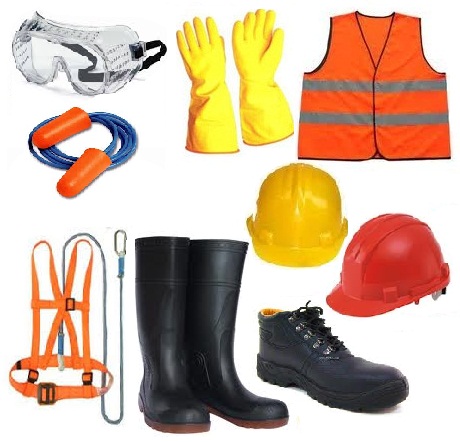
It is wiser to prevent an accident from happening than to cure the harm done after the accident. The protective safety devices include gloves to protect the palms and the fingers, the shield or goggle to protect the eyes, boots to protect the legs, the feet and toes, the helmet to protect the head and the overall to protect the chest.
EVALUATION
1. What is safety precaution?
2. Define an accident
3. Explain two steps of preventing accident.
4. State two safety rules for bench worker.
5. Name two protective safety devices.
READING ASSIGNMENT – Workshop Safety Rules and Regulation
Text: NERDC Basic Technology for Junior Secondary Schools 1 Chapter 2 pages 6 – 16
ASSIGNMENT:
Theory:
1) What are safety precautions?
2) State four causes of accidents
Objectives:
1) A negative experience that happens to somebody when he does not expect it is -----
a) Prevention b) Accident c) Technique d) Unwanted
2) To prevent accident, somebody needs to do the following except------
a) Follows the makers guide i.e. code of practice
b) Wears suitable working materials
c) Runs around inside the workshop
d) Keeps tools in a cupboard after use
3) A machine user should never operate a machine unless he had been properly instructed in its use; true or false
4) The following are the causes of accident except
a) Throwing sharp tools at each other in the workshop
b) Engaging in horse play in the workshop
c) Using a faulty machine and equipments
d) Concentrating on the work at hand
5) When a tool or equipment is faulty, or the working environment constitutes a danger to the users, then the workman would do these except:
a) The workman should continue working
b) The workman should report the case to an expert
c) The workman should stop using or operating in that workshop
d) The workman should find a corrective measure
MODEL ANSWERS:
Theory:
1. Safety precautions are the rules and regulation guiding the movement and behavior of individual in the workshop to avoid vital accident (4 marks)
2. Accidents occur when –
(i) Students engage in horse play in the workshop
(ii) The machine being used are not in good form
(iii) The worn out parts of machines are not replaced on time.
(iv) Students are not careful enough in the workshop while handling the machines.
(v) Students do not follow the manufacturer’s or teacher’s instructions on how to use the machine in the workshop (4 marks each)
Students should state four (all over 20 marks)
TOPIC: Workshop Safety Rules and Regulation
SUB-TOPICS:
(i) Safety Rules for Bench workers
(ii) Safety Rules for machine users
(iii) Accidents, Causes and Prevention
Safety Rules for Bench Workers
Safety rules/precautions are the rules and regulations guiding the movement and behavior of individual in the workshop to avoid vital accident. The following are the safety rules for bench workers:
(1) If chips are likely to fly, wear goggle.
(2) Always hold the work piece securely in the vice.
(3) Never use a chisel which has developed a mushroomed head.
(4) If a workplace is hot, mark it in some ways to indicate the facts to others.
(5) Always use a brush to remove chippings or filings. Do not use your hands to blow.

Safety Rules for Machine Users
1. Never indulge in horse play in a machinery workshop or in the metal workshop in general.
2. Never operate a machine unless you have been properly instructed in its use.
3. Always ensure you are properly dressed for the job in hand. Always wear some type of eye protection when using machines especially grinding machines.
4. It is very important to read the maker’s instructions on all packed goods before opening or unscrewing stoppers on new machines even if you think you know the procedure. It is possible that the makers have amended their instructions since your last reading.
5. Never clean the machine when it is on motion.

Evaluation
What is safety precaution?
State two safety rules for bench workers and machine users.
LESSON 8
Sub-Topic 3: Accidents: Cause and Prevention
An accident is a negative experience that happens to somebody when he does not expect it. Accident is an unforeseen cause of events. Accidents are caused by people and equipment.
Causes of Accidents
Accidents in the workshop are caused when:
(1) Students do not follow the manufacturer’s or teacher’s instructions on how to use the machine in the workshop.
(2) Students are not careful enough in the workshop while handling the machines.
(3) Students engage in horse play in the workshop.
(4) The machines being used are not in good form.
(5) The worn out parts of machines are not replaced on time.

Accident Prevention Techniques
Steps to take in preventing accidents are:
(i) Routine Checking – This involves checking all machines to ensure that they are in good condition before setting them up for use.
(ii) Routine Servicing - It involves servicing all machines and changing the worn out parts regularly so that they can work effectively.
(iii) Students’ Comportment – Students should avoid noise-making and talkativeness in the workshop because this can make them lose concentration on the work they are doing.
(iv) Preventive Measures – Electronic equipment should be used with voltage stabilizers in order to prevent electrical fire as a result of power surge.
(v) Teachers’ supervision – To prevent workshop accidents, every workshop lesson or practical session should be supervised by the teacher. Students should not be left alone in the workshop.
It is wiser to prevent an accident from happening than to cure the harm done after the accident. The protective safety devices include gloves to protect the palms and the fingers, the shield or goggle to protect the eyes, boots to protect the legs, the feet and toes, the helmet to protect the head and the overall to protect the chest.
EVALUATION
1. What is safety precaution?
2. Define an accident
3. Explain two steps of preventing accident.
4. State two safety rules for bench worker.
5. Name two protective safety devices.
READING ASSIGNMENT – Workshop Safety Rules and Regulation
Text: NERDC Basic Technology for Junior Secondary Schools 1 Chapter 2 pages 6 – 16
ASSIGNMENT:
Theory:
1) What are safety precautions?
2) State four causes of accidents
Objectives:
1) A negative experience that happens to somebody when he does not expect it is -----
a) Prevention b) Accident c) Technique d) Unwanted
2) To prevent accident, somebody needs to do the following except------
a) Follows the makers guide i.e. code of practice
b) Wears suitable working materials
c) Runs around inside the workshop
d) Keeps tools in a cupboard after use
3) A machine user should never operate a machine unless he had been properly instructed in its use; true or false
4) The following are the causes of accident except
a) Throwing sharp tools at each other in the workshop
b) Engaging in horse play in the workshop
c) Using a faulty machine and equipments
d) Concentrating on the work at hand
5) When a tool or equipment is faulty, or the working environment constitutes a danger to the users, then the workman would do these except:
a) The workman should continue working
b) The workman should report the case to an expert
c) The workman should stop using or operating in that workshop
d) The workman should find a corrective measure
MODEL ANSWERS:
Theory:
1. Safety precautions are the rules and regulation guiding the movement and behavior of individual in the workshop to avoid vital accident (4 marks)
2. Accidents occur when –
(i) Students engage in horse play in the workshop
(ii) The machine being used are not in good form
(iii) The worn out parts of machines are not replaced on time.
(iv) Students are not careful enough in the workshop while handling the machines.
(v) Students do not follow the manufacturer’s or teacher’s instructions on how to use the machine in the workshop (4 marks each)
Students should state four (all over 20 marks)
WEEK 4
LESSON 9
TOPIC: RULES AND REGULATION FOR BENCH WORKERS
OBJECTIVES: At the end of the lesson, the students should be able to:
1. List workshop safety rules and regulation.
2. Define accident.
CONTENT:
MEANING AND CAUSES OF WORKSHOP ACCIDENTS
Accidents are defined as events occurring by chance which results in injury to people or damage to property. All accidents in the workshop are to be reported to the teacher immediately so that you will get first aid treatment.

CAUSES OF ACCIDENTS
There are two major groups of cause of accidents in the workshop:
1. Unsafe actions
2. Unsafe conditions
Unsafe actions are
(a) Failure to use safety devices.
(b) Entering the workshop in a disorderly manner.
Unsafe conditions
(a) Slippery or wet floors
(b) Absence of safety devices etc.
SAFETY RULES AND REGULATIONS IN THE WORKSHOP
1. Students should walk gently and quietly in orderly manner to the workshop.
2. Students must not touch any tools or machines displayed in the workshop unless they are told to do so.
3. Appropriate safety device like helmet, eye goggle or shield, hand gloves must be used when necessary.
EVALUATION:
Define accident.
State the causes of accident.
Enumerate the rules and regulations to be obeyed in the workshop.
further studies
http://www.technologystudent.com/health1/safetyr1.htm
LESSON 10
TOPIC: WORKSHOP SAFETY
OBJECTIVE: At the end of the lesson, the students should be able to:
1. Mention the safety devices.
2. State ways of preventing accidents in the workshop.
CONTENT:
HOW TO PREVENT ACCIDENTS IN A WORKSHOP
Accidents in a workshop happen or occur as a result of carelessness, ignorance and when rules and regulations in the workshop are not obeyed.
To prevent accidents students must be careful and obey simple rules and regulations, with the use of correct tools for any job. It is important for you to note that:
i. Students are responsible for their safety.
ii. Students are also responsible for the safety of other people and equipment in the workshop.
SAFETY DEVICES
Safety devices are used to protect human body and also to protect materials in the workshop.
The common safety devices are:
1. Overall or apron
2. Goggles or visors
3. Gloves
4. Workshop shoes
5. Fire extinguishers
6. Water-hoses and water
7. Fire alarm
8. Sand bucket and sand

EVALUATION:
State ways of preventing accident.
Mention safety devises.
ASSIGNMENT:
Mention and draw 5 more safety devices.
further studies
http://www.cornbeltcarving.org/Safety.htm
practice test
http://www.gotoquiz.com/workshop_safety
LESSON 11
TOPIC: Workshop Safety Rules and Regulations (cont’d)
Contents of the Topic
(i) Safety Devices
(ii) Types of Fire
Safety Devices
Safety Devices are used to protect human beings and material things such as buildings, machines etc. The following safety devices are seen in the workshop:
1) Fire Alarm: This is an equipment which make noises whenever it senses the occurrence of accident. Fire alarms are used for preventing accidents from occurring.
2) Goggles and Visors: They protect the eyes against metallic objects, dust and high intensity light.
3) Gloves: They protect hand against corrosive metals, burns, cuts, electric shock etc. They must not be worn around a rotating machine to prevent them from being caught by the machine parts.
4) Fire Extinguishers, Sand Buckets and Sand: They are used to fight and control fire anytime fire occurs. They are kept at important positions in the workshop or buildings.
5) Shoes: Special workshop shoes made up of thick soles and metal caps are used for foot protection.
6) Aprons and Overalls: They are strong and long clothes tied properly at the back to protect inner clothes from dirt.
7) Water Hoses: They are pipes used to provide water for cooling and putting off fire.
8) Blanket: This is a material which is used to cover and put off fire. This material can be a solid or gas such as Carbondioxide etc.

Evaluation
1) List three types of fire fighting materials and equipment
2) Why should sleeves be rolled up above the elbows when in the workshop?
3) How can you keep long hair from getting caught in a machine?
LESSON 12
Types of Fire
Two basic types of fire occur in the workshop:
1) Electric Fire: Electric fire can be caused by the following:
i) Sparks due to partial contact of electrical parts or short circuit
ii) Wrong electrical connections
iii) Poor wiring
iv) Overloading

Electrical fire can be controlled by:
i) Switching off the control switch of all electrical applicants
ii) Setting up the fire alarm to notify every worker in the workshop
2) Chemical Fire: Chemical Fire is caused by chemical substances such as oil, grease and gas etc in the workshop. Chemical Fire can be controlled by using dry sand or a fire extinguisher containing foam or gas. Never use a fire extinguisher containing water to put off chemical Fire.
Evaluation:
1) List the basic types of fire that you know
2) How can electrical fire be caused and controlled?
Reading Assignment
NERDC Basic Technology for Junior Secondary Schools 1 Chapter 2 Pages 13-16
Assignment
1) Accidents may occur as a result of --------------------------- and -------------------------------------------
2) Goggles and visors protect the ------------------------------------------- against injury
3) Aprons and overalls protect the ------------------------------- from ---------------------------------------------
4) Gloves protect the -------------------------------------------- against ---------------------------------------------, -----------------------------------, ------------------------------------ and --------------------------------.
5) We use --------------------------------, ------------------------------- and --------------------------- to put out fire in the workshop
TOPIC: RULES AND REGULATION FOR BENCH WORKERS
OBJECTIVES: At the end of the lesson, the students should be able to:
1. List workshop safety rules and regulation.
2. Define accident.
CONTENT:
MEANING AND CAUSES OF WORKSHOP ACCIDENTS
Accidents are defined as events occurring by chance which results in injury to people or damage to property. All accidents in the workshop are to be reported to the teacher immediately so that you will get first aid treatment.

CAUSES OF ACCIDENTS
There are two major groups of cause of accidents in the workshop:
1. Unsafe actions
2. Unsafe conditions
Unsafe actions are
(a) Failure to use safety devices.
(b) Entering the workshop in a disorderly manner.
Unsafe conditions
(a) Slippery or wet floors
(b) Absence of safety devices etc.
SAFETY RULES AND REGULATIONS IN THE WORKSHOP
1. Students should walk gently and quietly in orderly manner to the workshop.
2. Students must not touch any tools or machines displayed in the workshop unless they are told to do so.
3. Appropriate safety device like helmet, eye goggle or shield, hand gloves must be used when necessary.
EVALUATION:
Define accident.
State the causes of accident.
Enumerate the rules and regulations to be obeyed in the workshop.
further studies
http://www.technologystudent.com/health1/safetyr1.htm
LESSON 10
TOPIC: WORKSHOP SAFETY
OBJECTIVE: At the end of the lesson, the students should be able to:
1. Mention the safety devices.
2. State ways of preventing accidents in the workshop.
CONTENT:
HOW TO PREVENT ACCIDENTS IN A WORKSHOP
Accidents in a workshop happen or occur as a result of carelessness, ignorance and when rules and regulations in the workshop are not obeyed.
To prevent accidents students must be careful and obey simple rules and regulations, with the use of correct tools for any job. It is important for you to note that:
i. Students are responsible for their safety.
ii. Students are also responsible for the safety of other people and equipment in the workshop.
SAFETY DEVICES
Safety devices are used to protect human body and also to protect materials in the workshop.
The common safety devices are:
1. Overall or apron
2. Goggles or visors
3. Gloves
4. Workshop shoes
5. Fire extinguishers
6. Water-hoses and water
7. Fire alarm
8. Sand bucket and sand

EVALUATION:
State ways of preventing accident.
Mention safety devises.
ASSIGNMENT:
Mention and draw 5 more safety devices.
further studies
http://www.cornbeltcarving.org/Safety.htm
practice test
http://www.gotoquiz.com/workshop_safety
LESSON 11
TOPIC: Workshop Safety Rules and Regulations (cont’d)
Contents of the Topic
(i) Safety Devices
(ii) Types of Fire
Safety Devices
Safety Devices are used to protect human beings and material things such as buildings, machines etc. The following safety devices are seen in the workshop:
1) Fire Alarm: This is an equipment which make noises whenever it senses the occurrence of accident. Fire alarms are used for preventing accidents from occurring.
2) Goggles and Visors: They protect the eyes against metallic objects, dust and high intensity light.
3) Gloves: They protect hand against corrosive metals, burns, cuts, electric shock etc. They must not be worn around a rotating machine to prevent them from being caught by the machine parts.
4) Fire Extinguishers, Sand Buckets and Sand: They are used to fight and control fire anytime fire occurs. They are kept at important positions in the workshop or buildings.
5) Shoes: Special workshop shoes made up of thick soles and metal caps are used for foot protection.
6) Aprons and Overalls: They are strong and long clothes tied properly at the back to protect inner clothes from dirt.
7) Water Hoses: They are pipes used to provide water for cooling and putting off fire.
8) Blanket: This is a material which is used to cover and put off fire. This material can be a solid or gas such as Carbondioxide etc.

Evaluation
1) List three types of fire fighting materials and equipment
2) Why should sleeves be rolled up above the elbows when in the workshop?
3) How can you keep long hair from getting caught in a machine?
LESSON 12
Types of Fire
Two basic types of fire occur in the workshop:
1) Electric Fire: Electric fire can be caused by the following:
i) Sparks due to partial contact of electrical parts or short circuit
ii) Wrong electrical connections
iii) Poor wiring
iv) Overloading

Electrical fire can be controlled by:
i) Switching off the control switch of all electrical applicants
ii) Setting up the fire alarm to notify every worker in the workshop
2) Chemical Fire: Chemical Fire is caused by chemical substances such as oil, grease and gas etc in the workshop. Chemical Fire can be controlled by using dry sand or a fire extinguisher containing foam or gas. Never use a fire extinguisher containing water to put off chemical Fire.
Evaluation:
1) List the basic types of fire that you know
2) How can electrical fire be caused and controlled?
Reading Assignment
NERDC Basic Technology for Junior Secondary Schools 1 Chapter 2 Pages 13-16
Assignment
1) Accidents may occur as a result of --------------------------- and -------------------------------------------
2) Goggles and visors protect the ------------------------------------------- against injury
3) Aprons and overalls protect the ------------------------------- from ---------------------------------------------
4) Gloves protect the -------------------------------------------- against ---------------------------------------------, -----------------------------------, ------------------------------------ and --------------------------------.
5) We use --------------------------------, ------------------------------- and --------------------------- to put out fire in the workshop
WEEK 5
LESSON 13
TOPIC: Properties of Materials - Wood
SUB-TOPICS:
(i) Properties of Materials and Identification of wood, timber, structure of wood
(ii) Five main parts of tree, cross section, classes and properties
Properties of Materials and Identification of wood, timber, structure of wood
Felling of trees can be done in two places: Free Areas and Forest Reserve.
Free area is one that is owned by individual. Trees can be cut down thereafter consulting the owner, but the contractor will pay certain amount of money through forest guard to the government, this is called ‘Tariff’.
A forest reserve is a very large area of land owned by the government. The wood can only be cut down there when getting approval from the government.
The company usually bought tree from forest reserve. The timber contractor pays for the total volume of timber taken out. The money paid is known as O.T.V i.e. Out Turn Volume.
The Growth of Timber and Wood Structure
The tree need food to grow, this food is absorbed by the roots in the soil. It passes through the sapwood to the leaves where chemical reaction takes place through the sunlight. The food will now be transferred to the tree through the blast.

EVALUATION
1. Mention two places where felling of wood can be done.
2. What is the full meaning of O.T.V?
LESSON 14
Five main parts cross section, classes and properties.[/b]
The five main parts of tree are:
1. Root: It searches for various mineral salts in the moist ground. They also hold the tree firmly in the ground.
2. Trunk or Stem: is part that acts as a support for the branches which rises as high as possible towards the light. It is from the trunk that we get our timber.
3. Branches: develop at leaves.
4. Leaves: These manufacture food for the tree through the action of sunlight and air.
5. Bark: protects the growing part of the tree from the weather, animals and any other injuries.

The features of the cross-section of a tree when felled are:
(i) The Cambium Layer is actual living part.
(ii) Sapwood is active part of tree.
(iii) Heartwood is the mature part of the tree.
(iv) Pith: The Central core of the trunk
(v) Medullar Rays are food storage cells.
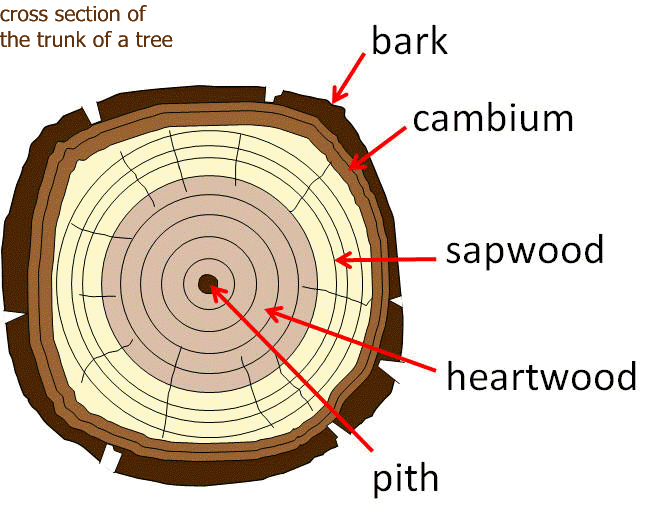
The Structure of Wood
Wood is made up of a number of tiny tube- like units called ‘cells’. These cells are called fibres or tracheids. Wood is composed of cellulose (60%) lignin (28%) and other minor materials.
Wood can be classified into two namely:
1. Hardwood or Deciduous trees
2. Softwood or Coniferous trees or simply conifers
Hardwood or Deciduous Tree: These trees have broad leaves.
(a) Their seeds are enclosed in cases.
(b) The trees shed their leaves at least every year
(c) It produce the timbers used for our furniture and in construction (d) It grows in the temperate and tropical regions of the world.
Examples of Nigerian broad leaved trees are: Iroko, Afara, Mahogany, Opepe, Omo etc.

Softwood or Coniferous Trees or Simply Conifers
These trees have needle-like leaves.
(a) They bear naked seeds which are in cones that are why it is referred to as conifers.
(b) They do not shed their leaves.
(c) They are said to be evergreen because their branches always bear green leaves.
(d) It produces the commercial softwoods.


EVALUATION
1. How many classes of wood do we have?
2. Name three examples of Hardwood tree.
3. Mention two features of Softwood.
READING ASSIGNMENT: Read about Wood
TEXT: NERDC Basic Technology for Junior Secondary Schools 1 Chapter 3 pages 18-21
ASSIGNMENT
1. How many classes of wood do we have? (a) 6 (b) 4 (c) 2 (d) 10
2. ______ can also be called deciduous tree. (a) pawpaw tree (b) hardwood (c) softwood (d) water leaf
3. The central core of the truck is called _____ (a) medullar raw (b) pith (c) sapwood (d) heartwood
4. The money to be paid in Free Area is called ______ (a) O.T.V (b) coins (c) Tariff (d) naira
5. _________ protects the growing part of the tree from the weather, animal and other injuries. (a) Root (b) trunk (c) leaves (d) bark.
THEORY
1. State two differences between softwood and hardwood.
2. Draw and name five main parts of tree.
Marking Scheme
1. C
2. B
3. B
4. C
5. D
THEORY
1a. Hardwood has broad leaves while softwood has needlelike leaves.
b. The seeds of hardwood is enclosed in cases while softwood beans naked seed etc
2. (diagram of a tree labeled)
LESSON 15
TOPIC: IDENTIFICATION OF MATERIALS (WOOD)
OBJECTIVE: At the end of the lesson, the students should be able to:
1. Mention the classes of wood.
2. Differentiate between the two groups of wood.
CONTENT:
Materials are substances from which other things can be made. The common engineering materials are: (a) wood (b) metal (c) rubber (d) plastic (e) ceramic
Identification of Wood
One of the materials that is supplied by nature is wood. Wood is commonly used in some engineering work because it is light, strong and can be marked upon easily. Wood is obtained from tree. Mature trees can be found and felled in two places.
(a) Forest reserve area
(b) Free zone
It can be identified with their colour, appearance, weight, hardness, leaves and seed of trees. There are two types of wood:
(a) Softwood from coniferous tree.
(b) Hardwood from deciduous trees.
Wood is a hard, tough substance that forms the trunks of trees and that has been used for thousands of years as a fuel and as a material of construction. A tree must grow and mature before enough wood can be obtained from its trunk.


PARTS OF A TREE
The major parts of a tree are its roots, trunk, leaves, Bark, Branches and. These components play vital roles in a tree's growth, development, and reproduction. Trees in large quantity can be found in the forest.
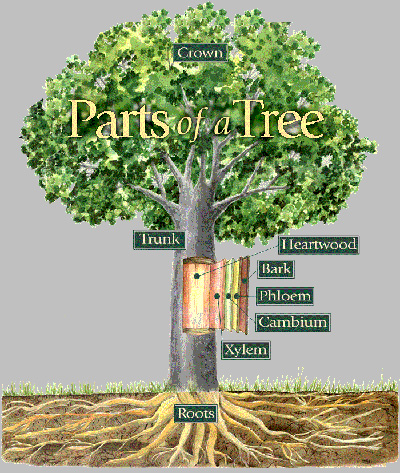
Root - Trees are held in place by anchoring organs called roots. In addition to anchoring the tree, roots also absorb water and minerals through tiny structures called root hairs.
Bark - is the outer protective covering of tree trunks. Because bark varies so widely in color, texture, and thickness, its characteristics provide one of the most important means of identifying species of trees.
Leaves - in trees, as in other green plants, the principal function of the leaves is the manufacture of sugars by the process of photosynthesis.
Trunk - most of a tree trunk is occupied by the wood, or xylem layer, which consists almost entirely of dead cells. Trunk or Stem is the part where we get most of the wood we need for our work, it also develop the branches.
Branches - these are the parts of a tree that develops the leaves. Branches of wood are used as firewood.
Differences and properties of hardwood and softwood.
Hardwood...................................Softwood
It is dark in colour......................It is lighter in colour than hard wood.
It is heavy..................................It is not heavy
It is difficult to work on..............It is not difficult to work on
Hardwood trees have broad leaves ....Softwood trees have needle like leaves
Hardwood trees shed their leaves annually.......Softwood tress have evergreen leaves
Hardwood trees enclose their seed in a seed case or pod...Softwood trees have naked seeds.
Examples of hardwood trees are Agba, Mausonia, Obeche, Teak, Mahogany, Iroko, Ekki, Afara, Opepe, Abura, Oak etc.
Examples of softwood are Redwood, Yew, larch, Pine, Sprince, Cedar, Fir, Samidore
https://drive.google.com/file/d/0Bz3Mh6 ... sp=sharing
EVALUATION:
Mention the classes of wood.
Differentiate between hardwood and softwood.
Mention examples of both wood.
ASSIGNMENT:
Write 20 uses of wood.
further studies
http://www.dummies.com/how-to/content/t ... rking.html
http://www.tis-gdv.de/tis_e/misc/holzart.htm
TOPIC: Properties of Materials - Wood
SUB-TOPICS:
(i) Properties of Materials and Identification of wood, timber, structure of wood
(ii) Five main parts of tree, cross section, classes and properties
Properties of Materials and Identification of wood, timber, structure of wood
Felling of trees can be done in two places: Free Areas and Forest Reserve.
Free area is one that is owned by individual. Trees can be cut down thereafter consulting the owner, but the contractor will pay certain amount of money through forest guard to the government, this is called ‘Tariff’.
A forest reserve is a very large area of land owned by the government. The wood can only be cut down there when getting approval from the government.
The company usually bought tree from forest reserve. The timber contractor pays for the total volume of timber taken out. The money paid is known as O.T.V i.e. Out Turn Volume.
The Growth of Timber and Wood Structure
The tree need food to grow, this food is absorbed by the roots in the soil. It passes through the sapwood to the leaves where chemical reaction takes place through the sunlight. The food will now be transferred to the tree through the blast.

EVALUATION
1. Mention two places where felling of wood can be done.
2. What is the full meaning of O.T.V?
LESSON 14
Five main parts cross section, classes and properties.[/b]
The five main parts of tree are:
1. Root: It searches for various mineral salts in the moist ground. They also hold the tree firmly in the ground.
2. Trunk or Stem: is part that acts as a support for the branches which rises as high as possible towards the light. It is from the trunk that we get our timber.
3. Branches: develop at leaves.
4. Leaves: These manufacture food for the tree through the action of sunlight and air.
5. Bark: protects the growing part of the tree from the weather, animals and any other injuries.

The features of the cross-section of a tree when felled are:
(i) The Cambium Layer is actual living part.
(ii) Sapwood is active part of tree.
(iii) Heartwood is the mature part of the tree.
(iv) Pith: The Central core of the trunk
(v) Medullar Rays are food storage cells.

The Structure of Wood
Wood is made up of a number of tiny tube- like units called ‘cells’. These cells are called fibres or tracheids. Wood is composed of cellulose (60%) lignin (28%) and other minor materials.
Wood can be classified into two namely:
1. Hardwood or Deciduous trees
2. Softwood or Coniferous trees or simply conifers
Hardwood or Deciduous Tree: These trees have broad leaves.
(a) Their seeds are enclosed in cases.
(b) The trees shed their leaves at least every year
(c) It produce the timbers used for our furniture and in construction (d) It grows in the temperate and tropical regions of the world.
Examples of Nigerian broad leaved trees are: Iroko, Afara, Mahogany, Opepe, Omo etc.

Softwood or Coniferous Trees or Simply Conifers
These trees have needle-like leaves.
(a) They bear naked seeds which are in cones that are why it is referred to as conifers.
(b) They do not shed their leaves.
(c) They are said to be evergreen because their branches always bear green leaves.
(d) It produces the commercial softwoods.


EVALUATION
1. How many classes of wood do we have?
2. Name three examples of Hardwood tree.
3. Mention two features of Softwood.
READING ASSIGNMENT: Read about Wood
TEXT: NERDC Basic Technology for Junior Secondary Schools 1 Chapter 3 pages 18-21
ASSIGNMENT
1. How many classes of wood do we have? (a) 6 (b) 4 (c) 2 (d) 10
2. ______ can also be called deciduous tree. (a) pawpaw tree (b) hardwood (c) softwood (d) water leaf
3. The central core of the truck is called _____ (a) medullar raw (b) pith (c) sapwood (d) heartwood
4. The money to be paid in Free Area is called ______ (a) O.T.V (b) coins (c) Tariff (d) naira
5. _________ protects the growing part of the tree from the weather, animal and other injuries. (a) Root (b) trunk (c) leaves (d) bark.
THEORY
1. State two differences between softwood and hardwood.
2. Draw and name five main parts of tree.
Marking Scheme
1. C
2. B
3. B
4. C
5. D
THEORY
1a. Hardwood has broad leaves while softwood has needlelike leaves.
b. The seeds of hardwood is enclosed in cases while softwood beans naked seed etc
2. (diagram of a tree labeled)
LESSON 15
TOPIC: IDENTIFICATION OF MATERIALS (WOOD)
OBJECTIVE: At the end of the lesson, the students should be able to:
1. Mention the classes of wood.
2. Differentiate between the two groups of wood.
CONTENT:
Materials are substances from which other things can be made. The common engineering materials are: (a) wood (b) metal (c) rubber (d) plastic (e) ceramic
Identification of Wood
One of the materials that is supplied by nature is wood. Wood is commonly used in some engineering work because it is light, strong and can be marked upon easily. Wood is obtained from tree. Mature trees can be found and felled in two places.
(a) Forest reserve area
(b) Free zone
It can be identified with their colour, appearance, weight, hardness, leaves and seed of trees. There are two types of wood:
(a) Softwood from coniferous tree.
(b) Hardwood from deciduous trees.
Wood is a hard, tough substance that forms the trunks of trees and that has been used for thousands of years as a fuel and as a material of construction. A tree must grow and mature before enough wood can be obtained from its trunk.


PARTS OF A TREE
The major parts of a tree are its roots, trunk, leaves, Bark, Branches and. These components play vital roles in a tree's growth, development, and reproduction. Trees in large quantity can be found in the forest.

Root - Trees are held in place by anchoring organs called roots. In addition to anchoring the tree, roots also absorb water and minerals through tiny structures called root hairs.
Bark - is the outer protective covering of tree trunks. Because bark varies so widely in color, texture, and thickness, its characteristics provide one of the most important means of identifying species of trees.
Leaves - in trees, as in other green plants, the principal function of the leaves is the manufacture of sugars by the process of photosynthesis.
Trunk - most of a tree trunk is occupied by the wood, or xylem layer, which consists almost entirely of dead cells. Trunk or Stem is the part where we get most of the wood we need for our work, it also develop the branches.
Branches - these are the parts of a tree that develops the leaves. Branches of wood are used as firewood.
Differences and properties of hardwood and softwood.
Hardwood...................................Softwood
It is dark in colour......................It is lighter in colour than hard wood.
It is heavy..................................It is not heavy
It is difficult to work on..............It is not difficult to work on
Hardwood trees have broad leaves ....Softwood trees have needle like leaves
Hardwood trees shed their leaves annually.......Softwood tress have evergreen leaves
Hardwood trees enclose their seed in a seed case or pod...Softwood trees have naked seeds.
Examples of hardwood trees are Agba, Mausonia, Obeche, Teak, Mahogany, Iroko, Ekki, Afara, Opepe, Abura, Oak etc.
Examples of softwood are Redwood, Yew, larch, Pine, Sprince, Cedar, Fir, Samidore
https://drive.google.com/file/d/0Bz3Mh6 ... sp=sharing
EVALUATION:
Mention the classes of wood.
Differentiate between hardwood and softwood.
Mention examples of both wood.
ASSIGNMENT:
Write 20 uses of wood.
further studies
http://www.dummies.com/how-to/content/t ... rking.html
http://www.tis-gdv.de/tis_e/misc/holzart.htm
WEEK 6
LESSON 16
TOPIC: Properties of materials (contd.) - Metals
SUB-TOPICS:
1) Identification of Metals by Physical Properties
2) Classification of Metals
Identification of Metals by Physical Properties
Identification of metals can be defined as method used to differentiate one particular type of metal from another and from other materials which are non-metals.
Metals can be identified through their properties.
(1) Density – This is the weight of a metal and it varies from metal to metal. E.g. aluminium is light and lead is heavy in weight.
(2) Colour/Lustre– This is the appearance of a metal when the surface is polished. For example, when polished and examined under a microscope, copper presents a different appearance from a polished mild steel.
(3) Fusibility – This is the property of a metal which makes it melt and join with other metals while in a liquid form.
(4) Magnetic property – This is property that if a metal possesses it, it is attracted by a magnet. It is used to identify ferrous metals from non-ferrous metals. A magnet will attract ferrous metal while non-ferrous metals will not be attracted by a magnet.
(5) Elasticity or Stretching - This is the elastic property of a metal i.e. ability to stretch
(6) Brittleness – When a metal breaks suddenly or cracks easily, then it is said to possess brittleness e.g. glass.
(7) Conductivity of Heat – When heat spreads from one part of the body of a metal to other parts much more quickly than it does in other metals when heated this is conductivity of heat.
(8) Sound Test – This is the sound heard when any metallic materials is hit with a different type of materials.
The sound heard differs from metal to metal.
Other properties of metals are hardness, malleability and tenacity.

EVALUATION
Explain three properties of metal.
LESSON 17
Sub-Topic 2 – Classification of Metals
The metals used in engineering can be classified into two categories or classes.
(1) Ferrous metals and their alloys
(2) Non-ferrous metals and their alloys
Ferrous metal and their alloys – This is group of metals that contain iron. The metals have no iron. The metals are therefore, not magnetic. Examples are aluminum, copper, brass etc. Ferrous metals have the different grades of cast iron and steel. The different grades of cast iron are grey cast iron, white cast iron and malleable cast iron. They are used a lot in engineering to make different parts. Different grade of steel used in engineering construction and machine fabrication are mild steel, medium carbon steel, high speed steel, high tensile steel etc.
An alloy is combination of two or more metal to produce another metal e.g. metal A + metal B = metal C. Therefore metal C is an alloy of metal A and B e.g. chromium and nickel gives stainless steel.
Non-ferrous metal are no iron based which include these:
(a) Aluminum – This is a non-magnetic metal. When polished, it is silvery-white. It is very light in weight. Aluminum has a resistance to corrosion under normal atmospheric conditions. It is malleable, soft, ductile and a good conductor of heat.
(b) Copper – it is reddish brown or salmon pink in color. It is malleable and ductile. Copper is a good conductor of heat and electricity.
(c) Tin – it is bright silvery color. It is used as an alloying element. Tin is very soft and can hammer and rolled into very thin sheets. It has a high corrosion resistance.
(d) Lead – It is very heavy in weight and have grey color
(e) Zinc – It is bluish-white in color. Zinc is brittle and has a good resistance to rust.
Ferrous alloys are those types of metals that are produced when two or more non-ferrous metals are alloyed together. A good example of this is brass. Brass is the mixture of copper, tin and phosphorus. Metal can be found or purchased in different forms. The forms are:
(a) Round section and rectangular
(b) Tubular and flat section
(c) Plates and strips.
(d) Wires and channel.

EVALUATION
(1) Mention and explain five properties of metal.
(2) List four examples of non-ferrous metal.
READING ASSIGNMENT – Students should read about Metals
Text: NERDC Basic Technology for Junior Secondary School 1 Chapter 3 pages 21 – 26
ASSIGNMENT
1. Metals can be identified through their _______ (a) properties (b) ability (c) energy (d) power
2. Ferrous metal contain ______ (a) battery (b) chemical (c) salt (d) iron
THEORY
1. What is an alloy?
2. Mention four forms of metal
MARKING SCHEME
1. A
2. D
THEORY
1. An alloy is a combination of two or more metals to produce another metal.
2. Round section and rectangular, tubular and flat section, plates and strips, wires and channel
LESSON 18
TOPIC: IDENTIFICATION OF METALS
OBJECTIVE: At the end of the lesson, the students should be able to:
1. Mention the two classes of metal.
2. Mention all the properties of metal.
CONTENT:
Metal is another important engineering material used in various areas of manufacturing of equipment, machines etc. metals are classified into two
1. Ferrous metals
2. Non-ferrous metals
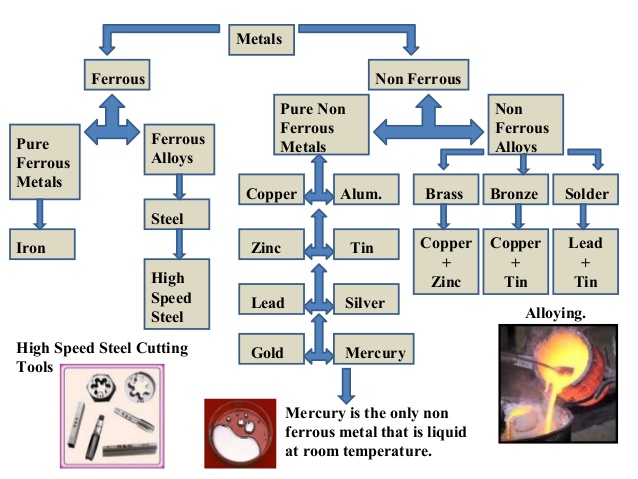
Ferrous metals are those metals which contain iron and they are magnetic. Examples are pig iron, cast iron, wrought iron, carbon steel, allot steel etc.

Non-ferrous metals are those that do not contain iron and they are not magnetic. Examples are copper, aluminium, lead, zinc etc.

PROPERTIES OF METALS
1. Ductility
2. Fusibility
3. Conductivity of heat and electricity
4. Density
5. Luster
6. Malleability
7. Toughness
EVALUATION:
Mention and explain the classes of metal.
Mention the properties of metal.
further studies
http://www.slideshare.net/tomwheats/fer ... ous-metals
http://www.wlfuller.com/html/steel_types.html
LESSON 19
SPECIFIC TOPIC : Properties of Metal
REFERENCE BK :Basic technology for JSS by Evans and Nation Building Basic Technology by E.K AJAYI.
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVE : At the end of the lesson the students should be able to:
(1) Mention the properties of metal
(2) Explain the properties of metal
CONTENT :
Properties of metal
Though there is considerable variation from one metal to the next, there are significant differences between metals and other materials. In general metals are identified by the following properties such as:
Hardness, the resistance to surface deformation or abrasion;
Tensile strength, the resistance to breakage;
Elasticity, the ability to return to the original shape after deformation;
Malleability, the ability to be shaped by hammering;
Fatigue resistance, the ability to resist repeated stresses;
Ductility, the ability to be drawn into wire without breaking
Fusibility, ability to melt and turn to liquid and be mixed with another material
Conductivity of electricity and heat, ability of metal to conduct electricity and heat.
Colour or lustre, this is the appearance of metal which in most case is shining.
Densities, this deal with the weight of metal most metals are generally heavy except aluminum and few others.
EVALUATION/CLASSWORK
Mention the properties of metal
Explain properties of metal
further studies
http://chemistry.about.com/od/elementgr ... metals.htm
practice test
http://www.sciencekids.co.nz/quizzes/metal.html
http://chemistry.about.com/library/weekly/bl050303a.htm
TOPIC: Properties of materials (contd.) - Metals
SUB-TOPICS:
1) Identification of Metals by Physical Properties
2) Classification of Metals
Identification of Metals by Physical Properties
Identification of metals can be defined as method used to differentiate one particular type of metal from another and from other materials which are non-metals.
Metals can be identified through their properties.
(1) Density – This is the weight of a metal and it varies from metal to metal. E.g. aluminium is light and lead is heavy in weight.
(2) Colour/Lustre– This is the appearance of a metal when the surface is polished. For example, when polished and examined under a microscope, copper presents a different appearance from a polished mild steel.
(3) Fusibility – This is the property of a metal which makes it melt and join with other metals while in a liquid form.
(4) Magnetic property – This is property that if a metal possesses it, it is attracted by a magnet. It is used to identify ferrous metals from non-ferrous metals. A magnet will attract ferrous metal while non-ferrous metals will not be attracted by a magnet.
(5) Elasticity or Stretching - This is the elastic property of a metal i.e. ability to stretch
(6) Brittleness – When a metal breaks suddenly or cracks easily, then it is said to possess brittleness e.g. glass.
(7) Conductivity of Heat – When heat spreads from one part of the body of a metal to other parts much more quickly than it does in other metals when heated this is conductivity of heat.
(8) Sound Test – This is the sound heard when any metallic materials is hit with a different type of materials.
The sound heard differs from metal to metal.
Other properties of metals are hardness, malleability and tenacity.

EVALUATION
Explain three properties of metal.
LESSON 17
Sub-Topic 2 – Classification of Metals
The metals used in engineering can be classified into two categories or classes.
(1) Ferrous metals and their alloys
(2) Non-ferrous metals and their alloys
Ferrous metal and their alloys – This is group of metals that contain iron. The metals have no iron. The metals are therefore, not magnetic. Examples are aluminum, copper, brass etc. Ferrous metals have the different grades of cast iron and steel. The different grades of cast iron are grey cast iron, white cast iron and malleable cast iron. They are used a lot in engineering to make different parts. Different grade of steel used in engineering construction and machine fabrication are mild steel, medium carbon steel, high speed steel, high tensile steel etc.
An alloy is combination of two or more metal to produce another metal e.g. metal A + metal B = metal C. Therefore metal C is an alloy of metal A and B e.g. chromium and nickel gives stainless steel.
Non-ferrous metal are no iron based which include these:
(a) Aluminum – This is a non-magnetic metal. When polished, it is silvery-white. It is very light in weight. Aluminum has a resistance to corrosion under normal atmospheric conditions. It is malleable, soft, ductile and a good conductor of heat.
(b) Copper – it is reddish brown or salmon pink in color. It is malleable and ductile. Copper is a good conductor of heat and electricity.
(c) Tin – it is bright silvery color. It is used as an alloying element. Tin is very soft and can hammer and rolled into very thin sheets. It has a high corrosion resistance.
(d) Lead – It is very heavy in weight and have grey color
(e) Zinc – It is bluish-white in color. Zinc is brittle and has a good resistance to rust.
Ferrous alloys are those types of metals that are produced when two or more non-ferrous metals are alloyed together. A good example of this is brass. Brass is the mixture of copper, tin and phosphorus. Metal can be found or purchased in different forms. The forms are:
(a) Round section and rectangular
(b) Tubular and flat section
(c) Plates and strips.
(d) Wires and channel.

EVALUATION
(1) Mention and explain five properties of metal.
(2) List four examples of non-ferrous metal.
READING ASSIGNMENT – Students should read about Metals
Text: NERDC Basic Technology for Junior Secondary School 1 Chapter 3 pages 21 – 26
ASSIGNMENT
1. Metals can be identified through their _______ (a) properties (b) ability (c) energy (d) power
2. Ferrous metal contain ______ (a) battery (b) chemical (c) salt (d) iron
THEORY
1. What is an alloy?
2. Mention four forms of metal
MARKING SCHEME
1. A
2. D
THEORY
1. An alloy is a combination of two or more metals to produce another metal.
2. Round section and rectangular, tubular and flat section, plates and strips, wires and channel
LESSON 18
TOPIC: IDENTIFICATION OF METALS
OBJECTIVE: At the end of the lesson, the students should be able to:
1. Mention the two classes of metal.
2. Mention all the properties of metal.
CONTENT:
Metal is another important engineering material used in various areas of manufacturing of equipment, machines etc. metals are classified into two
1. Ferrous metals
2. Non-ferrous metals

Ferrous metals are those metals which contain iron and they are magnetic. Examples are pig iron, cast iron, wrought iron, carbon steel, allot steel etc.

Non-ferrous metals are those that do not contain iron and they are not magnetic. Examples are copper, aluminium, lead, zinc etc.

PROPERTIES OF METALS
1. Ductility
2. Fusibility
3. Conductivity of heat and electricity
4. Density
5. Luster
6. Malleability
7. Toughness
EVALUATION:
Mention and explain the classes of metal.
Mention the properties of metal.
further studies
http://www.slideshare.net/tomwheats/fer ... ous-metals
http://www.wlfuller.com/html/steel_types.html
LESSON 19
SPECIFIC TOPIC : Properties of Metal
REFERENCE BK :Basic technology for JSS by Evans and Nation Building Basic Technology by E.K AJAYI.
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVE : At the end of the lesson the students should be able to:
(1) Mention the properties of metal
(2) Explain the properties of metal
CONTENT :
Properties of metal
Though there is considerable variation from one metal to the next, there are significant differences between metals and other materials. In general metals are identified by the following properties such as:
Hardness, the resistance to surface deformation or abrasion;
Tensile strength, the resistance to breakage;
Elasticity, the ability to return to the original shape after deformation;
Malleability, the ability to be shaped by hammering;
Fatigue resistance, the ability to resist repeated stresses;
Ductility, the ability to be drawn into wire without breaking
Fusibility, ability to melt and turn to liquid and be mixed with another material
Conductivity of electricity and heat, ability of metal to conduct electricity and heat.
Colour or lustre, this is the appearance of metal which in most case is shining.
Densities, this deal with the weight of metal most metals are generally heavy except aluminum and few others.
EVALUATION/CLASSWORK
Mention the properties of metal
Explain properties of metal
further studies
http://chemistry.about.com/od/elementgr ... metals.htm
practice test
http://www.sciencekids.co.nz/quizzes/metal.html
http://chemistry.about.com/library/weekly/bl050303a.htm
WEEK 7
LESSON 20
TOPIC: Ceramic and glass
SUB-TOPIS:(I) Ceramics
(II) Glass
Ceramics

Clay exists naturally in many parts of the world. When it is wet, it can easily be molded into different shapes and sizes. We use clay to mould various objects like storage pots, cooking pots and dishes.
We use mud to construct support for cooking pots, to build houses and also to make bricks for building houses. We make cement blocks that we use for building houses by mixing sand and cement to get typical shape. All the above solid objects made from clay, mud or cement are called ceramics.
Ceramics break easily when dropped. We say they are brittle, this differentiates ceramics from metals, plastics, wood and rubber. Ceramics are less dense than most metals. Ceramics have high melting points.


Classification of Ceramic materials
Ceramic materials are classified based on the types of materials used in making them. They are;
1. The clay materials: These include: objects like age pot, dishes, and cups.
2. The mud materials: These are used to construct support for king pots, make bricks for building houses.
3. The cement materials: These are mixture of cement, sand and water for molding blocks use for building houses.
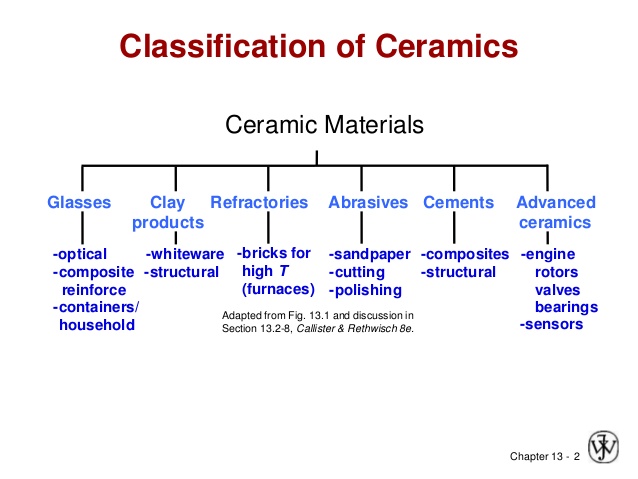
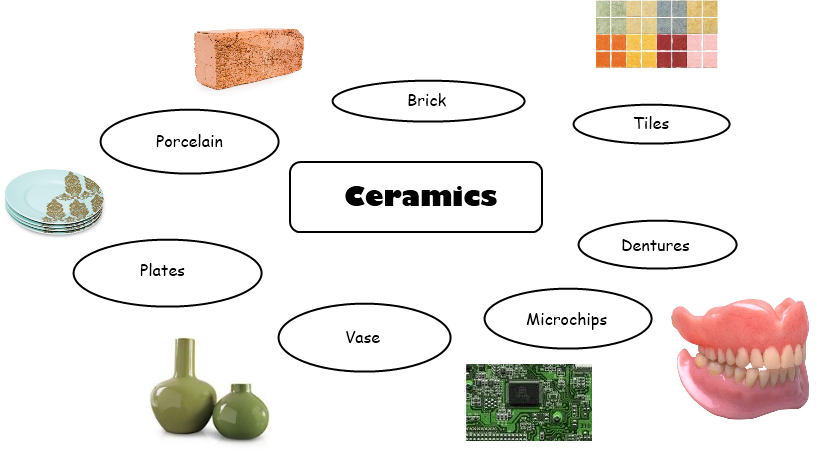
Properties of Ceramics
1. They are brittle: They can easily break into pieces.
2. They can easily be molded.
3. They can withstand very high temperature.
4. They have resistance to heat.
5. They are malleable when mixed with water.
6. They are resistance to corrosion.
7. They have high melting point

Evaluation
1. Mention two uses of mud
2. Name four properties of ceramic
LESSON 21
Glass
Glass is made from inorganic materials. That is they are not dug from the ground.

Properties of glass
1. They are brittle: They can easily break into pieces
2. They are transparent: You can see through them

Uses of glass
1. Glass is used in making window materials
2. Glass is used in making mirrors, eye sunglasses, household materials such as wall clock etc
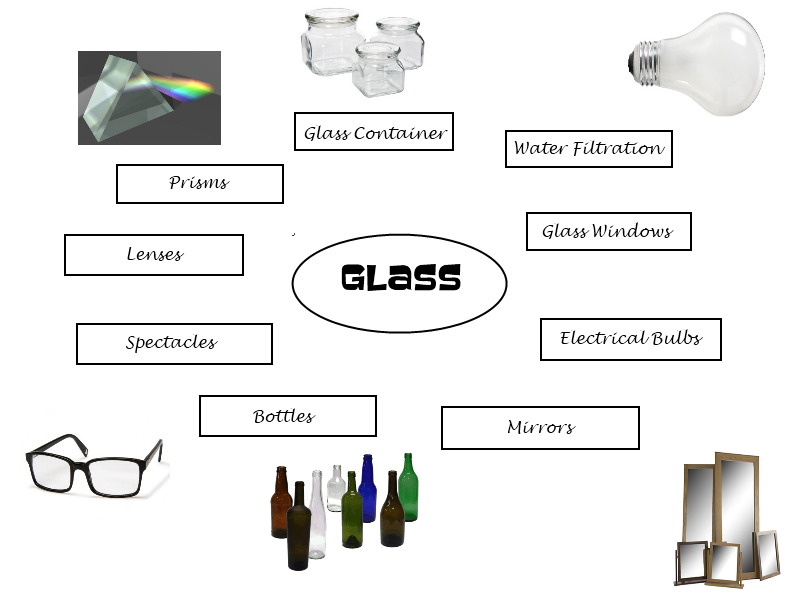
Evaluation
1. Mention two properties of glass
2. Give two uses of glass
READING ASSIGNMENT – Students should read about Ceramics and Glass
TEXT: NERDC Basic Technology for Schools 1 Chapter 4 Pages 28 – 33.
ASSIGNMENT
List and draw 5 ceramic products and 5 glass products you use in your house.
http://depts.washington.edu/matseed/mse ... ramics.htm
http://www.flmnh.ufl.edu/histarch/galle ... _intro.asp
TOPIC: Ceramic and glass
SUB-TOPIS:(I) Ceramics
(II) Glass
Ceramics

Clay exists naturally in many parts of the world. When it is wet, it can easily be molded into different shapes and sizes. We use clay to mould various objects like storage pots, cooking pots and dishes.
We use mud to construct support for cooking pots, to build houses and also to make bricks for building houses. We make cement blocks that we use for building houses by mixing sand and cement to get typical shape. All the above solid objects made from clay, mud or cement are called ceramics.
Ceramics break easily when dropped. We say they are brittle, this differentiates ceramics from metals, plastics, wood and rubber. Ceramics are less dense than most metals. Ceramics have high melting points.


Classification of Ceramic materials
Ceramic materials are classified based on the types of materials used in making them. They are;
1. The clay materials: These include: objects like age pot, dishes, and cups.
2. The mud materials: These are used to construct support for king pots, make bricks for building houses.
3. The cement materials: These are mixture of cement, sand and water for molding blocks use for building houses.


Properties of Ceramics
1. They are brittle: They can easily break into pieces.
2. They can easily be molded.
3. They can withstand very high temperature.
4. They have resistance to heat.
5. They are malleable when mixed with water.
6. They are resistance to corrosion.
7. They have high melting point

Evaluation
1. Mention two uses of mud
2. Name four properties of ceramic
LESSON 21
Glass
Glass is made from inorganic materials. That is they are not dug from the ground.

Properties of glass
1. They are brittle: They can easily break into pieces
2. They are transparent: You can see through them

Uses of glass
1. Glass is used in making window materials
2. Glass is used in making mirrors, eye sunglasses, household materials such as wall clock etc

Evaluation
1. Mention two properties of glass
2. Give two uses of glass
READING ASSIGNMENT – Students should read about Ceramics and Glass
TEXT: NERDC Basic Technology for Schools 1 Chapter 4 Pages 28 – 33.
ASSIGNMENT
List and draw 5 ceramic products and 5 glass products you use in your house.
http://depts.washington.edu/matseed/mse ... ramics.htm
http://www.flmnh.ufl.edu/histarch/galle ... _intro.asp
WEEK 8
LESSON 22
TOPIC: Drawing Instruments and Materials.
SUB-TOPICS: (i) Definition of technical drawing.
(ii) Drawing Instruments and Materials
iii. Basic Techniques of handling and caring for drawing instruments and
materials.
Definition of Technical drawing
Technical drawing is a universal language used for communication among technical people. A good and accurate drawing can only be made through constant practice with the aid of drawing instruments and materials.
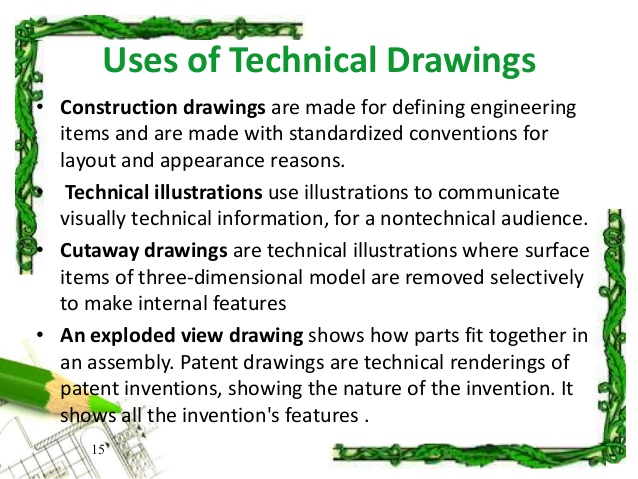
Drawing Instruments and Materials
Drawing instruments and materials for technical drawing are:
(i) Drawing board
(ii) Tee square
(iii) Sets squares
(iv) Protractor
(v) Compasses
(vi) Dividers
(vii) Drawing paper clips
(viii) Scale rules
(ix) French curves
(x) Metric rules
(xi) Drawing paper
(xii) Drawing pencils
(xiii) Eraser
(xiv) Sharpener or blade

1. A drawing board is the wooden platform on which the drawing paper is placed before the drawing starts. The two main types are (a) full imperial size which is 812 x 585mm (b) half imperial (585 x 452mm) size.
2. Tee square is used for drawing horizontal or parallel lines in conjunction with drawing board.
3. Drawing pencils are of different grades used for general drawing, lettering or freehand sketching and technical or engineering drawing. We have B, 2B, 3B, 4B up to 8B and H, 2H, 3H, 4 H up to 8H pencils.
4. A Compass: Used for drawing circles and arcs.
5. A Divider: used for transferring measurement from the metric rule to the drawing.
6. Set Squares: Are used to draw vertical or diagonal lines.
7. Drawing Papers: are best held on the boards with the aid of clips or adhesive tape.
8. The Protractor: is used for measuring and marking out angles.
9. Scale Rules: Are used to produce reduced or enlarged sizes of objects.
10. A Metric Rule: is used for drawing various types of curves.
11. Drawing paper: This is the paper on which the drawing is produced.
12. Eraser: A good eraser must erase cleanly without picking or tearing the surface of the paper.
EVALUATION
What is Technical Drawing?
Name four types of drawing instruments.
http://www.slideshare.net/DdLhiin/d-r-a ... -t-revised
LESSON 23
Sub-Topic 3:Basic techniques of handling and caring for drawing instruments and
materials.
We need to take care of our drawing instruments in order to prolong their service life.
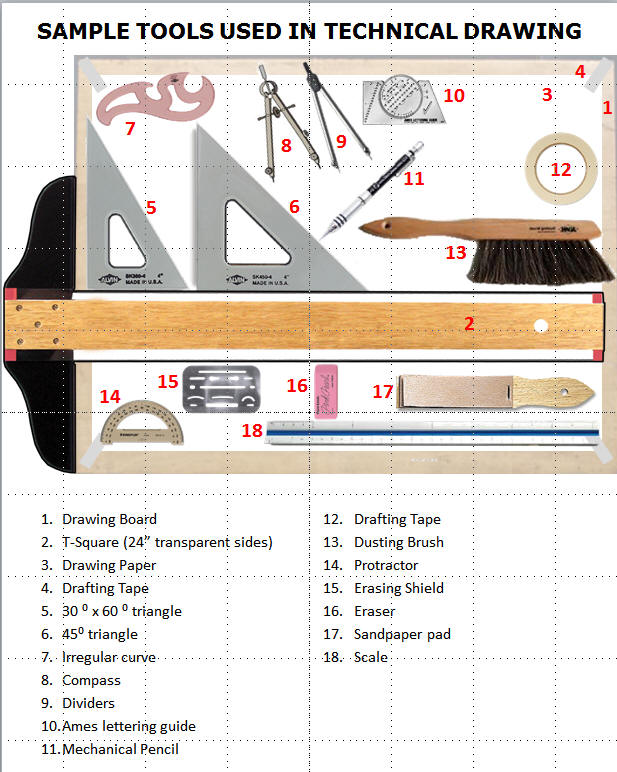
Drawing Board
(a) Do not use pins for fastening your paper to the board, use tapes or clips.
(b) Do not use blade or knife to cut something on the surface of your drawing board.
(c) Always cover the surface with cardboard or thick paper.
(d) Keep the drawing board in a safe place when not in use.
Tee-Square
(a) Never use the tee-square as a walking stick or as a cane.
(b) Do not use pen-knife or blade along the edge of the tee-square
(c) Always hand your square when not in use.
(d) Always keep your tee-square clean.
Set-Square, Scale Rules, Protractor and French Curves
(a) Do not use any sharp object such as razor blade or knife on their edges.
(b) Keep them away from fire.
(c) Always keep them in a safe place immediately after use to prevent leakage.
Pair of Compasses or Dividers
(a) When not in use, keep them away in a safe container.
(b) Never use compasses or dividers as paper holders.
(c) Do not use their needle points to punch holes.
Other Instruments
All other instruments should be kept in their packets after use. A cupboard should be made available for complete storage of the drawing boards and all other instruments.
EVALUATION
(1) Why do we need to take care of our drawing instrument?
(2) How do we take care of tee-square?
(3) What are the uses of (a) drawing board (b) tee-square (c) set-square
READING ASSIGNMENT
Read about Drawing Instruments and Materials
TEXT: NERDC Basic Technology for Junior Secondary School 1 Chapter 5 pages 34 – 42
ASSIGNMENT
(1) _________ is used for drawing horizontal lines (a) French curves (b) compass (c) tee-square (d) divider
(2) French curves is made of ______ (a) wood (b) rubber (c) glass (d) plastic
(3) All of these are drawing instruments except (a) compass (b) drawing pencils (c) scale rule (d) knife
(4) It is good to use pins for fastening your paper to the board ______ Yes/No
(5) __________ is used for circle construction (a) compass (b) divider (c) eraser (d) scale rules
THEORY
1. What is Technical Drawing
2. How can we take care of Tee-Square
MARKING SCHEME
(1) C
(2) D
(3) D
(4) No
(5) A(2 marks each)
1. Never use it as walking stick
(a) Always hang your tee-square when not in use
(b) Always keep your tee-square clean.
(c) Do not use blade along the edge
(5 marks each)
LESSON 24
TOPIC: DRAWING PRACTICE
OBJECTIVE: At the end of the lesson, the student should be able to:
1. Define technology drawing.
2. Mention the drawing instruments
CONTENT:
TECHNICAL DRAWING
Technical drawing is an international means of communicating the intentions of a designer to the builder, user and manufacturer. Good drawings can be achieved by the use of equipments and materials which include:
1. Drawing board
2. Tee square
3. Set-squares
4. Lettering sets
5. Drawing sets
6. Protractor
7. Pencils
8. Paper and eraser
9. French curve
EVALUATION:
Define technical drawing.
Mention the drawing instruments and materials.
State the uses of technical drawing.
further studies
http://www.technicaldrawingequipment.co.uk/
LESSON 25
TOPIC: BOARD PRACTICE
OBJECTIVES: At the end of the lesson, the students should be able to:
1. Set drawing paper on the drawing board correctly.
2. Draw vertical and inclined line correctly.
CONTENT:
Since drawings are transferable from one part of the world to another, the procedures should be the same for all draftsmen and students all over the world. The mastery of these procedures is essential if the students or draftsman is to produce neat, clear and precise drawings.
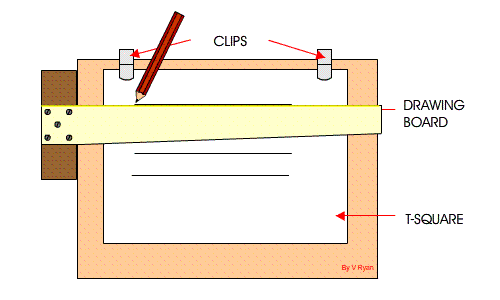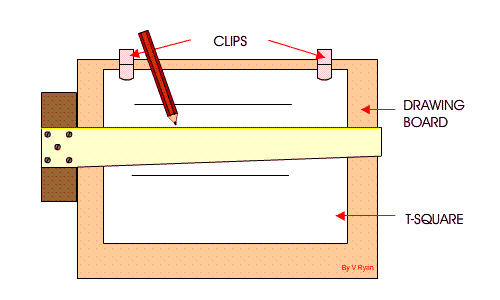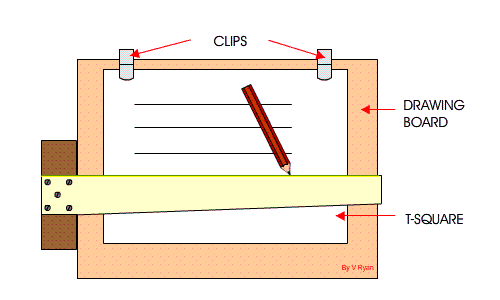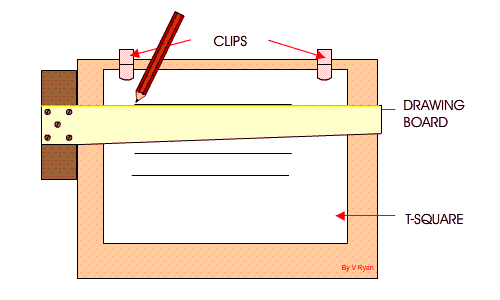
PROCEDURES FOR BOARD SETTING
Drawing board is where the paper is clipped or taped.
To Fasten a Sheet of Drawing Paper
Step 1: cut out four pieces of masking tape.
Step 2: place the paper on the board.
Step 3: set the left vertical edge of the paper to be about 25mm from the left edge of the board.
Step 4: set the bottom edge.
Step 5: align the top edge of paper with the tee-square and hold the paper with the masking tape.
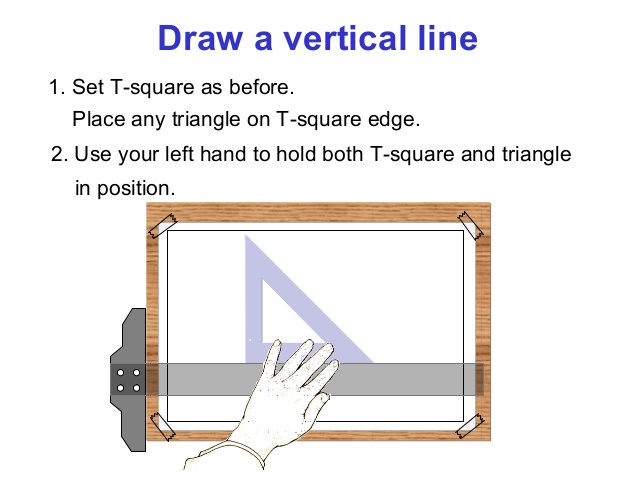
Use of set squares
1. Draw vertical perpendicular and inclined lines in combination with the tee square.
2. Set square is also used to draw angles e.g. 450, 600 and 300.
3. Set square is also used in measuring dimensions.
EVALUATION:
Set your drawing paper on the drawing board.
Draw vertical, incline line on your drawing paper.
further studies
http://www.ehow.com/list_6762592_techni ... tml#page=0
practice test
http://www.proprofs.com/quiz-school/sto ... ting-tools
TOPIC: Drawing Instruments and Materials.
SUB-TOPICS: (i) Definition of technical drawing.
(ii) Drawing Instruments and Materials
iii. Basic Techniques of handling and caring for drawing instruments and
materials.
Definition of Technical drawing

Technical drawing is a universal language used for communication among technical people. A good and accurate drawing can only be made through constant practice with the aid of drawing instruments and materials.

Drawing Instruments and Materials
Drawing instruments and materials for technical drawing are:
(i) Drawing board
(ii) Tee square
(iii) Sets squares
(iv) Protractor
(v) Compasses
(vi) Dividers
(vii) Drawing paper clips
(viii) Scale rules
(ix) French curves
(x) Metric rules
(xi) Drawing paper
(xii) Drawing pencils
(xiii) Eraser
(xiv) Sharpener or blade
1. A drawing board is the wooden platform on which the drawing paper is placed before the drawing starts. The two main types are (a) full imperial size which is 812 x 585mm (b) half imperial (585 x 452mm) size.
2. Tee square is used for drawing horizontal or parallel lines in conjunction with drawing board.
3. Drawing pencils are of different grades used for general drawing, lettering or freehand sketching and technical or engineering drawing. We have B, 2B, 3B, 4B up to 8B and H, 2H, 3H, 4 H up to 8H pencils.
4. A Compass: Used for drawing circles and arcs.
5. A Divider: used for transferring measurement from the metric rule to the drawing.
6. Set Squares: Are used to draw vertical or diagonal lines.
7. Drawing Papers: are best held on the boards with the aid of clips or adhesive tape.
8. The Protractor: is used for measuring and marking out angles.
9. Scale Rules: Are used to produce reduced or enlarged sizes of objects.
10. A Metric Rule: is used for drawing various types of curves.
11. Drawing paper: This is the paper on which the drawing is produced.
12. Eraser: A good eraser must erase cleanly without picking or tearing the surface of the paper.
EVALUATION
What is Technical Drawing?
Name four types of drawing instruments.
http://www.slideshare.net/DdLhiin/d-r-a ... -t-revised
LESSON 23
Sub-Topic 3:Basic techniques of handling and caring for drawing instruments and
materials.
We need to take care of our drawing instruments in order to prolong their service life.

Drawing Board
(a) Do not use pins for fastening your paper to the board, use tapes or clips.
(b) Do not use blade or knife to cut something on the surface of your drawing board.
(c) Always cover the surface with cardboard or thick paper.
(d) Keep the drawing board in a safe place when not in use.
Tee-Square
(a) Never use the tee-square as a walking stick or as a cane.
(b) Do not use pen-knife or blade along the edge of the tee-square
(c) Always hand your square when not in use.
(d) Always keep your tee-square clean.
Set-Square, Scale Rules, Protractor and French Curves
(a) Do not use any sharp object such as razor blade or knife on their edges.
(b) Keep them away from fire.
(c) Always keep them in a safe place immediately after use to prevent leakage.
Pair of Compasses or Dividers
(a) When not in use, keep them away in a safe container.
(b) Never use compasses or dividers as paper holders.
(c) Do not use their needle points to punch holes.
Other Instruments
All other instruments should be kept in their packets after use. A cupboard should be made available for complete storage of the drawing boards and all other instruments.
EVALUATION
(1) Why do we need to take care of our drawing instrument?
(2) How do we take care of tee-square?
(3) What are the uses of (a) drawing board (b) tee-square (c) set-square
READING ASSIGNMENT
Read about Drawing Instruments and Materials
TEXT: NERDC Basic Technology for Junior Secondary School 1 Chapter 5 pages 34 – 42
ASSIGNMENT
(1) _________ is used for drawing horizontal lines (a) French curves (b) compass (c) tee-square (d) divider
(2) French curves is made of ______ (a) wood (b) rubber (c) glass (d) plastic
(3) All of these are drawing instruments except (a) compass (b) drawing pencils (c) scale rule (d) knife
(4) It is good to use pins for fastening your paper to the board ______ Yes/No
(5) __________ is used for circle construction (a) compass (b) divider (c) eraser (d) scale rules
THEORY
1. What is Technical Drawing
2. How can we take care of Tee-Square
MARKING SCHEME
(1) C
(2) D
(3) D
(4) No
(5) A(2 marks each)
1. Never use it as walking stick
(a) Always hang your tee-square when not in use
(b) Always keep your tee-square clean.
(c) Do not use blade along the edge
(5 marks each)
LESSON 24
TOPIC: DRAWING PRACTICE
OBJECTIVE: At the end of the lesson, the student should be able to:
1. Define technology drawing.
2. Mention the drawing instruments
CONTENT:
TECHNICAL DRAWING
Technical drawing is an international means of communicating the intentions of a designer to the builder, user and manufacturer. Good drawings can be achieved by the use of equipments and materials which include:
1. Drawing board
2. Tee square
3. Set-squares
4. Lettering sets
5. Drawing sets
6. Protractor
7. Pencils
8. Paper and eraser
9. French curve

EVALUATION:
Define technical drawing.
Mention the drawing instruments and materials.
State the uses of technical drawing.
further studies
http://www.technicaldrawingequipment.co.uk/
LESSON 25
TOPIC: BOARD PRACTICE
OBJECTIVES: At the end of the lesson, the students should be able to:
1. Set drawing paper on the drawing board correctly.
2. Draw vertical and inclined line correctly.
CONTENT:
Since drawings are transferable from one part of the world to another, the procedures should be the same for all draftsmen and students all over the world. The mastery of these procedures is essential if the students or draftsman is to produce neat, clear and precise drawings.

PROCEDURES FOR BOARD SETTING
Drawing board is where the paper is clipped or taped.
To Fasten a Sheet of Drawing Paper
Step 1: cut out four pieces of masking tape.
Step 2: place the paper on the board.
Step 3: set the left vertical edge of the paper to be about 25mm from the left edge of the board.
Step 4: set the bottom edge.
Step 5: align the top edge of paper with the tee-square and hold the paper with the masking tape.

Use of set squares
1. Draw vertical perpendicular and inclined lines in combination with the tee square.
2. Set square is also used to draw angles e.g. 450, 600 and 300.
3. Set square is also used in measuring dimensions.
EVALUATION:
Set your drawing paper on the drawing board.
Draw vertical, incline line on your drawing paper.
further studies
http://www.ehow.com/list_6762592_techni ... tml#page=0
practice test
http://www.proprofs.com/quiz-school/sto ... ting-tools
WEEK 9
LESSON 26
TOPIC: FREEHAND SKETCHING
OBJECTIVE: At the end of the lesson, the students should be able to:
1. Describe freehand sketching.
2. Demonstrate some freehand techniques.
CONTENT:
FREEHAND SKETCHING
Freehand sketching is a quick way of drawing objects without the use of drawing instruments. Regular practice helps to develop one's ability to observe details in an object and draw them on paper.
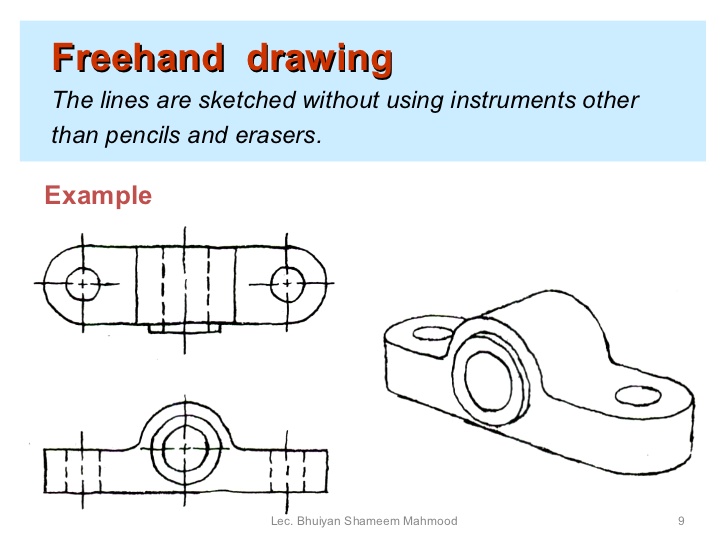
SKETCHING MATERIALS
Paper
HB pencil
Soft eraser
TECHNIQUES OF SKETCHING
Sketching a Straight Line
Straight line is defined as the shortest distance between two points.
To sketch a straight line, fix two points at a distance to each other, draw a line from the point at the left with your eye focused on the one at the right side to join the point.
To Sketch a Curved Line
Locate different points according to your curve and join the points together to form the curve.
To sketch the curve, use the point method or the line method. For the line method, sketch the vertical and horizontal centre lines and add four other radial lines and join the end together to form the circle.
https://youtu.be/LI9bM-mZ06U
EVALUATION:
Describe freehand sketching.
Draw the following objects using freehand sketching (a) box (b) cup (c) spanner
practice test
http://www.proprofs.com/quiz-school/qui ... wNextQ=yes
http://www.fanpop.com/spots/sketching/q ... es-include
LESSON 27
TOPIC: TITLE BLOCK
OBJECTIVES: At the end of the lesson, the students should be able to:
1. Describe the title block.
2. Draw a title block.
CONTENT:
Title block is a box at the right bottom corner of the drawing paper which contains information such as name, scale, date and title of the drawing. It shows information about the drawing and the person that produces the drawing.
NAME
CLASS
SCALE
TITLE
DATE
EVALUATION:
Describe the title block.
Mention the content of the title block.
Draw a title block.
TOPIC: FREEHAND SKETCHING
OBJECTIVE: At the end of the lesson, the students should be able to:
1. Describe freehand sketching.
2. Demonstrate some freehand techniques.
CONTENT:
FREEHAND SKETCHING
Freehand sketching is a quick way of drawing objects without the use of drawing instruments. Regular practice helps to develop one's ability to observe details in an object and draw them on paper.

SKETCHING MATERIALS
Paper
HB pencil
Soft eraser
TECHNIQUES OF SKETCHING
Sketching a Straight Line
Straight line is defined as the shortest distance between two points.
To sketch a straight line, fix two points at a distance to each other, draw a line from the point at the left with your eye focused on the one at the right side to join the point.
To Sketch a Curved Line
Locate different points according to your curve and join the points together to form the curve.
To sketch the curve, use the point method or the line method. For the line method, sketch the vertical and horizontal centre lines and add four other radial lines and join the end together to form the circle.

https://youtu.be/LI9bM-mZ06U
EVALUATION:
Describe freehand sketching.
Draw the following objects using freehand sketching (a) box (b) cup (c) spanner
practice test
http://www.proprofs.com/quiz-school/qui ... wNextQ=yes
http://www.fanpop.com/spots/sketching/q ... es-include
LESSON 27
TOPIC: TITLE BLOCK
OBJECTIVES: At the end of the lesson, the students should be able to:
1. Describe the title block.
2. Draw a title block.
CONTENT:
Title block is a box at the right bottom corner of the drawing paper which contains information such as name, scale, date and title of the drawing. It shows information about the drawing and the person that produces the drawing.
NAME
CLASS
SCALE
TITLE
DATE

EVALUATION:
Describe the title block.
Mention the content of the title block.
Draw a title block.