SCHEME OF WORK
WEEK TOPIC
1. Forest and forest uses: (a) Definition and description of forest (b) Uses of forest resources. (Map of Nigeria showing vegetation belts is required).
2. Effects of forest on environment; Human activities: (a) deforestation, (b) depletion of wild life through bush burning, hunting, farming activities. (c) Poaching (illegal hunting of animals and lumbering activities).
3. Farm Animals Diseases: (i) Bacteria: mastitis, contagious abortion,( ruminants, pigs) (ii) Fungi: ring worm (all farm animals), (iii) Viral: foot and mouth diseases (all animals except poultry), (iv)Protozoan: coccidiosis (poultry and rabbits). Trypanosomiasis in cattle. (v) Worms: all farm animals. (vi) Nutritional diseases: Bloat (cattle).
4. Mode of transmission of farm animals diseases: contact with the infected animals, or discharges, or vectors (tsetse fly), etc. The symptoms of farm animal diseases: enlarged udder, sores, high fever, blood stain, diarrhea, and loss of weight, loss of hair, reduced productivity, abortion, and death.
5. Effects of diseases on farm animals: reduced productivity, loss of weight, loss of appetite, death. Methods of prevention and control: good sanitation
Practices, (ii) medication/immunization. (Iii) isolation/disposal etc.
6. Controlling Crop Pests: Crop pests damage; the concept and principles of Pests control and pest management; methods of pests control and Pests Management
7. Preservation of Farm Produce for marketing: (a) methods of preserving farm produce; drying, refrigerating, salting, canning etc. Specific preservation methods(I) Livestock: refrigeration, drying, salting etc (II) Crops: drying, milling, canning, refrigerating (III) Fish: drying, smoking, refrigerating, salting etc
8. Channels for Distribution of Agricultural Produce: (a) International market, Local market, Wholesaler, retailer (b) Activities taking place at the channels for distribution involve; transportation, loading, offloading, packaging etc (c) Challenges in Agricultural marketing: bulkiness of agricultural products, transportation, keeping quality etc.
9. Agricultural in Stock Exchange: (a) Meaning of stock-buying and selling of goods and services available now and future (b) People involve in stock exchange (c) Importance of stock exchange in Agriculture
10. Revision
1ST TERM
WEEK 1
LESSON 1
Topic: FOREST AND FOREST USES
Content: i. Definition and Description of Forest
ii. Forest Resources and its uses
iii. Map of Nigeria showing vegetation belts.
DEFINITION AND DESCRIPTION OF FOREST
Definition of forest: A Forest is an area of land covered with trees, shrubs and other plants. It could natural in nature or planted by man for a purpose. Forests are common in the southern part of Nigeria because of much rainfall.
FORESTRY is a branch of agriculture which deals with the control and management of forest for forest resources.
Classification of forest: Forest can be classified into:
1. Natural forest: A forest that grows on its own
2. Established forest: A forest that is planted by man
3. Regenerated forest: A forest which is allowed to grow naturally after the original forest has been cleared.
Important Forest Trees
1. Mahogany (Khaya ivorensis)
2. Iroko (Clorophora excels)
3. African Walnut (Lovoa klameana)
4. Obeche (Tripochiton scleroxylon)
5. Opepe (Sarocephalus diderrichii)
6. Black Afara (Terminalia superb)
7. Mansonia (Mansonia altissims)
8. Omo (Cordin platythysa)
9. Ebony (Diospryos spp)
10. Gmelina
11. Teak (Tectona grandis/Oldfieldia africana)

Forest tree crops.
1. Mango (Magnifera indica)
2. Kola (Kola acuminata/Kola nitida
3. Cocoa (Theobroma cacao)
4. Oil Palm (Elaeis guineensis)
5. Rubber (Hevea braziliensis)

Forest Animals
1. Elephant (Loxodonta agricana)
2. Green monkey (Phacopithecus aethiopicus)
3. Grass Cutter (Thryonomys swinderianus)
4. Antelope (Neotragus spp)
5. Bush fowl(Gallus spp)
6. Snail (Archachatina morgunata)

Evaluation:
Objective Test:
1. Forest is defined as an area of land covered with ------- a. shrubs, b. vegetation, c. wood, d. trees and other plants.
2. Which of these is a product from forest? a. Gum, b. dye, c. rock, d. wood
3. A natural forest is the one that a. has been cut down, b. has not been cut down, c. has grown back, d. has be replanted.
4. Which of the following is not an important of forest? a. provision of fruits, b. control of erosion, c. provision of job for the forest guards, d. home for wildlife.
5. The following are types of forest except a. acquired forest, b. natural forest, c. regenerated forest, d. established forest.
Essay Test:
1. Define forest
2. Name 5 forest trees and 5 forest animals
LESSON 2
Forest Resources and its uses
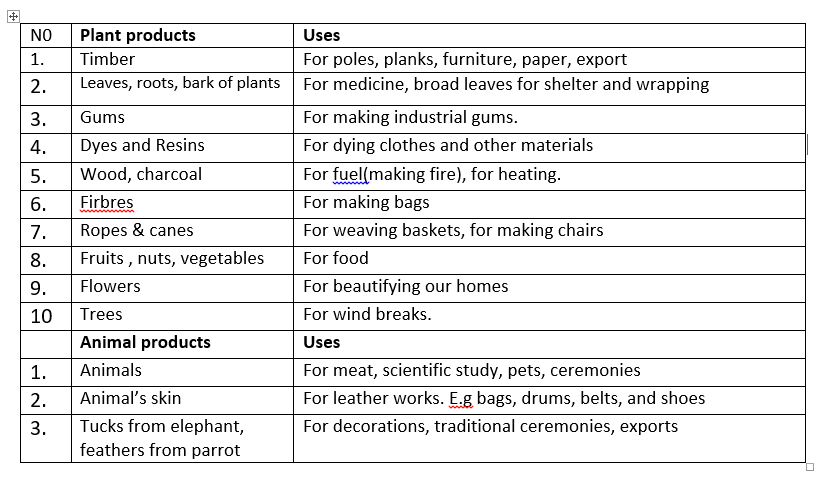
The table below shows some of the resources from the forest and their uses.
N0 Plant products Uses
1. Timber---- For poles, planks, furniture, paper, export
2. Leaves, roots, bark of plants ----For medicine, broad leaves for shelter and wrapping
3. Gums----For making industrial gums.
4. Dyes and Resins ----For dying clothes and other materials
5. Wood, charcoal ----For fuel(making fire), for heating.
6. Firbres ----For making bags
7. Ropes & canes ----For weaving baskets, for making chairs
8. Fruits , nuts, vegetables ----For food
9. Flowers ----For beautifying our homes
10 Trees---- For wind breaks.
Animal products---- Uses
1. Animals---- For meat, scientific study, pets, ceremonies
2. Animal’s skin---- For leather works. E.g bags, drums, belts, and shoes
3. Tucks from elephant, feathers from parrot ----For decorations, traditional ceremonies, exports
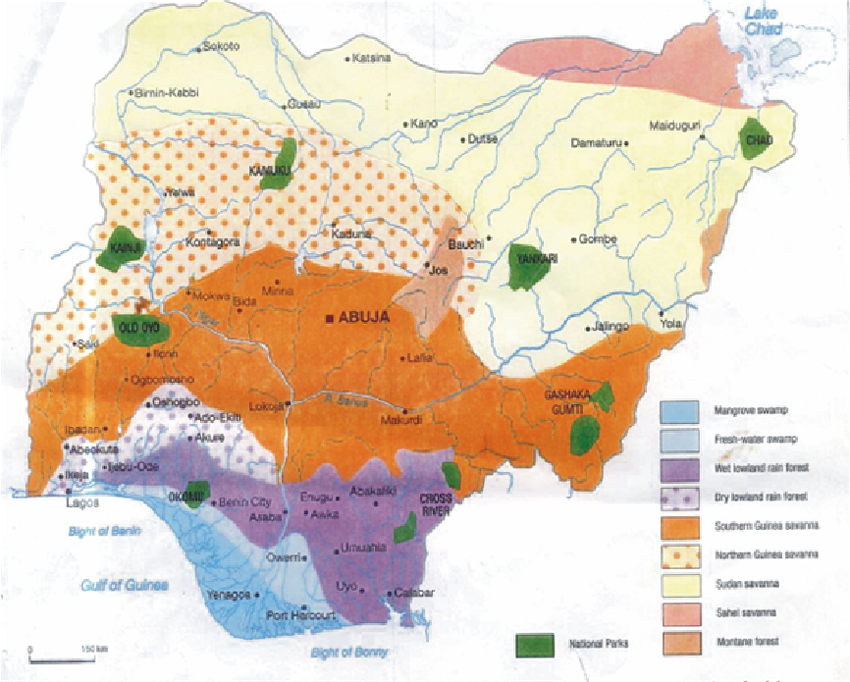
Map of Nigeria showing the vegetation belts.
Sahel savanna: found in the extreme North-east of Nigeria. Animals are mostly reared here. Dwarf sorghum and millets are cultivated.
Sudan savanna: Grasses are abundant in this area. Animals like cattle, sheep, goats, camels, donkeys and poultry are reared. Carrots and tomatoes are the crops cultivated.
Guinea savanna: It is the largest vegetation belt. Cattle, sheep, goats and poultry are reared.
Cereals, cowpea, groundnuts, cotton, yam, cassava, and potatoes are cultivated.
Rain forest: found in the southern part of Nigeria. Trees like Iroko, Obeche, Opepe, Mahogany, and Afara grow in this area. Cattle, sheep, pigs, poultry and dwarf goats are reared. Crops like yam, cocoyam, cassava, maize, rice, plantain, cocoa, rubber, kola, and mango, citrus are cultivated.
Evaluation:
Objective Test:
1, poles, planks, furniture, paper are products from the a. industry, b. factory, c. forest, d. farm.
2. Which of these products from the forest is used as fuel? a. charcoal, b. gum, c. bark, d. leaves
3. Tucks can be obtained from one of the following forest animals’ a. Lion, b. Antelope, c. Monkey, d. Snail.
4. Baskets and chairs can be made from the following forest products. A. timber, b. gum, c. ropes and canes
5. Carrots and tomatoes are cultivated majorly in the -------- belt of Nigeria. A. rain forest, b. Sahel savanna, c. mangrove and swamp forest, d. Sudan savanna
REFERENCE TEXTS:
1. New Intensive Agricultural Science for Upper Basic 7, 8 & 9 By B. E. U. Okarol
2. Junior Secondary Agricultural Science By O. Akinsanmi et al.
3. Spectrum Agricultural for JSS Book 3 By B. A. Adelekan et al
4. Prescribed Agricultural Science for JSS Book 3 By S. A. Omoruyi et al
Topic: FOREST AND FOREST USES
Content: i. Definition and Description of Forest
ii. Forest Resources and its uses
iii. Map of Nigeria showing vegetation belts.
DEFINITION AND DESCRIPTION OF FOREST
Definition of forest: A Forest is an area of land covered with trees, shrubs and other plants. It could natural in nature or planted by man for a purpose. Forests are common in the southern part of Nigeria because of much rainfall.
FORESTRY is a branch of agriculture which deals with the control and management of forest for forest resources.
Classification of forest: Forest can be classified into:
1. Natural forest: A forest that grows on its own
2. Established forest: A forest that is planted by man
3. Regenerated forest: A forest which is allowed to grow naturally after the original forest has been cleared.
Important Forest Trees
1. Mahogany (Khaya ivorensis)
2. Iroko (Clorophora excels)
3. African Walnut (Lovoa klameana)
4. Obeche (Tripochiton scleroxylon)
5. Opepe (Sarocephalus diderrichii)
6. Black Afara (Terminalia superb)
7. Mansonia (Mansonia altissims)
8. Omo (Cordin platythysa)
9. Ebony (Diospryos spp)
10. Gmelina
11. Teak (Tectona grandis/Oldfieldia africana)

Forest tree crops.
1. Mango (Magnifera indica)
2. Kola (Kola acuminata/Kola nitida
3. Cocoa (Theobroma cacao)
4. Oil Palm (Elaeis guineensis)
5. Rubber (Hevea braziliensis)

Forest Animals
1. Elephant (Loxodonta agricana)
2. Green monkey (Phacopithecus aethiopicus)
3. Grass Cutter (Thryonomys swinderianus)
4. Antelope (Neotragus spp)
5. Bush fowl(Gallus spp)
6. Snail (Archachatina morgunata)

Evaluation:
Objective Test:
1. Forest is defined as an area of land covered with ------- a. shrubs, b. vegetation, c. wood, d. trees and other plants.
2. Which of these is a product from forest? a. Gum, b. dye, c. rock, d. wood
3. A natural forest is the one that a. has been cut down, b. has not been cut down, c. has grown back, d. has be replanted.
4. Which of the following is not an important of forest? a. provision of fruits, b. control of erosion, c. provision of job for the forest guards, d. home for wildlife.
5. The following are types of forest except a. acquired forest, b. natural forest, c. regenerated forest, d. established forest.
Essay Test:
1. Define forest
2. Name 5 forest trees and 5 forest animals
LESSON 2
Forest Resources and its uses
The table below shows some of the resources from the forest and their uses.
N0 Plant products Uses
1. Timber---- For poles, planks, furniture, paper, export
2. Leaves, roots, bark of plants ----For medicine, broad leaves for shelter and wrapping
3. Gums----For making industrial gums.
4. Dyes and Resins ----For dying clothes and other materials
5. Wood, charcoal ----For fuel(making fire), for heating.
6. Firbres ----For making bags
7. Ropes & canes ----For weaving baskets, for making chairs
8. Fruits , nuts, vegetables ----For food
9. Flowers ----For beautifying our homes
10 Trees---- For wind breaks.
Animal products---- Uses
1. Animals---- For meat, scientific study, pets, ceremonies
2. Animal’s skin---- For leather works. E.g bags, drums, belts, and shoes
3. Tucks from elephant, feathers from parrot ----For decorations, traditional ceremonies, exports


Map of Nigeria showing the vegetation belts.
Sahel savanna: found in the extreme North-east of Nigeria. Animals are mostly reared here. Dwarf sorghum and millets are cultivated.
Sudan savanna: Grasses are abundant in this area. Animals like cattle, sheep, goats, camels, donkeys and poultry are reared. Carrots and tomatoes are the crops cultivated.
Guinea savanna: It is the largest vegetation belt. Cattle, sheep, goats and poultry are reared.
Cereals, cowpea, groundnuts, cotton, yam, cassava, and potatoes are cultivated.
Rain forest: found in the southern part of Nigeria. Trees like Iroko, Obeche, Opepe, Mahogany, and Afara grow in this area. Cattle, sheep, pigs, poultry and dwarf goats are reared. Crops like yam, cocoyam, cassava, maize, rice, plantain, cocoa, rubber, kola, and mango, citrus are cultivated.
Evaluation:
Objective Test:
1, poles, planks, furniture, paper are products from the a. industry, b. factory, c. forest, d. farm.
2. Which of these products from the forest is used as fuel? a. charcoal, b. gum, c. bark, d. leaves
3. Tucks can be obtained from one of the following forest animals’ a. Lion, b. Antelope, c. Monkey, d. Snail.
4. Baskets and chairs can be made from the following forest products. A. timber, b. gum, c. ropes and canes
5. Carrots and tomatoes are cultivated majorly in the -------- belt of Nigeria. A. rain forest, b. Sahel savanna, c. mangrove and swamp forest, d. Sudan savanna
REFERENCE TEXTS:
1. New Intensive Agricultural Science for Upper Basic 7, 8 & 9 By B. E. U. Okarol
2. Junior Secondary Agricultural Science By O. Akinsanmi et al.
3. Spectrum Agricultural for JSS Book 3 By B. A. Adelekan et al
4. Prescribed Agricultural Science for JSS Book 3 By S. A. Omoruyi et al
WEEK 2
LESSON 3
Topic: EFFECTS OF FOREST ON THE ENVIRONMENT
The following human activities in the environment affect the forest.
(a) Deforestation
(b) Depletion of wild life through bush burning, hunting , farming activities
(c) Poaching (illegal hunting of animals and lumbering activities)
(d) Bush burning
(e) Industrialization and mining
DEFORESTATION: It involves the cutting down of forest trees. This often leads to soil erosion and scarcity of forest products. Other effects include destruction of soil structure, wild life is denied of their habitat, reduces wild life population, valuable trees are destroyed, reduces the amount of rain fall in an area.

DEPLETION OF WILD LIFE: Activities like bush burning, hunting, and farming contribute to the depletion of both plants and animals that are very important in the forest.

POACHING: Many people engage in illegal hunting of animals felling of forest tree without taking permission or license from the government.
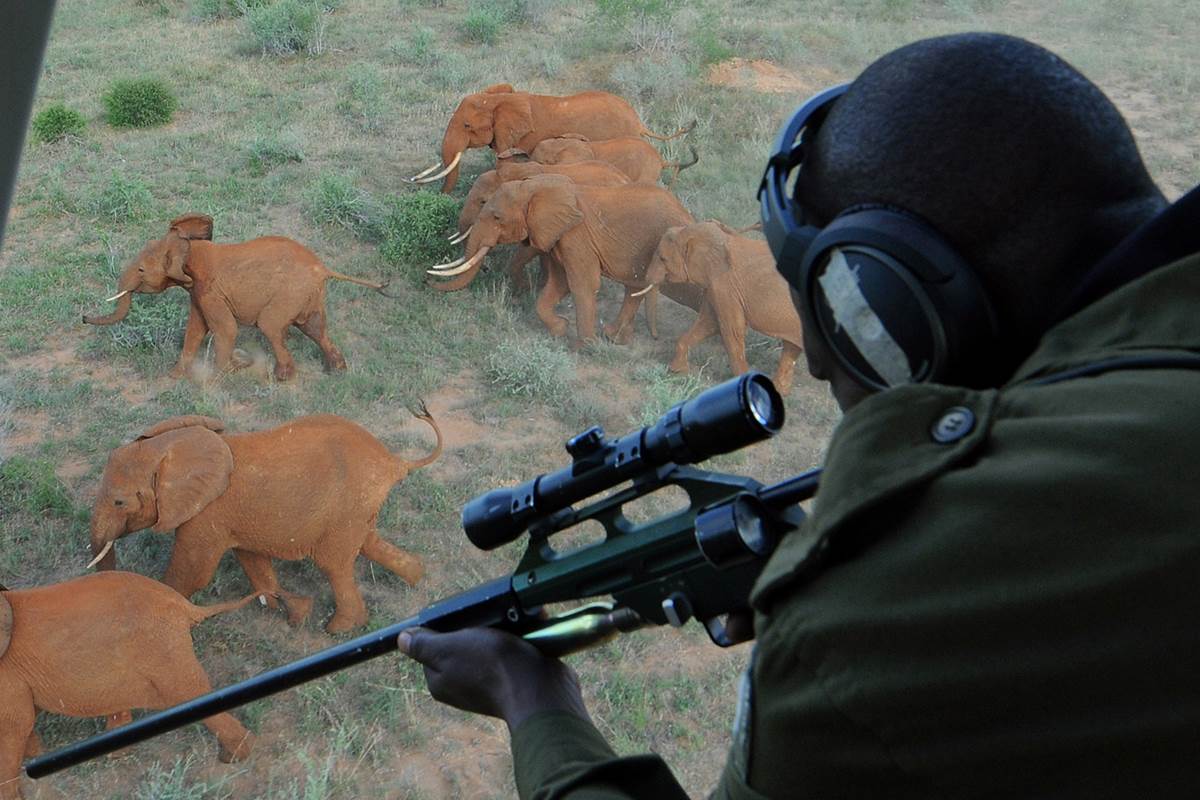

BUSH BURNING: The setting of fire in forest areas during dry season affects both plant and animas resources. Many good species of plants and animals are destroyed.

INDUSTRIALIZATION AND MINING: Many plants and animal species are wiped out of the forest as a result of clearing forest land for industry and mining activities.

EVALUATION:
Objectives:
1. Deforestation means the a. harvesting of crops, b. cutting down of forest trees, c. replanting of trees, d. growing of forest seedlings.
2. Poaching refers to a. indiscriminate cutting down of forest trees, b. illegal hunting of forest animals, c. harvesting of forest products, d. clearing of the forest vegetation.
3. Which of these activities does not contribute to the depletion of both plants and animals in the forest? a. bush burning, b. hunting, c. farming in the forest d. reseeding
4. Bush burning a. enables the forest to develop new species of plants, b. destroy both plants and animals in the forest, c. prevents people from entering into the forest.
5. Which of the following is not a forest animal?
a. (Loxodonta agricana)
b. (Phacopithecus aethiopicus)
c. Homo sapien
d.Snail (Archachatina morgunata)
ESSAY
1. State 4 effects of forest on the environment
2. Explain how the following affect forest. i. Poaching and depletion of wildlife
LESSON 4
IMPORTANCE OF FOREST
1. Forest provides timber trees.
2. It is a source of wild animals used for meat.
3. Provides income to people through hunting, felling of timber and sales of other products.
4. It protects the soil against erosion
5. It is a source of wild fruits, nuts, and flowers.
6. It is a source of fuel e.g. fire wood
7. It is a source of medicinal herbs
8. It is a source of fibre and ropes
9. It provides employment for people such as the forest guards
10. It is a source of revenue to the government
11. Forest reserve can serve as a tourist attraction.
12. It is a home for wild animals
13. Forest trees serves as wind breaks
14. It reduces atmospheric pollution.

FOREST MANAGEMENT: The following forest management practices are undertaken so as to ensure the maintenance of the forest.
a. Regeneration: It involves replacing the old forest trees with new ones.
b. Reforestation: It is the organized planting of trees in an area to create a forest in a place that has been deforested
c. Afforestation: It means establishing forest in areas where there has never been any .
d. Deforestation: It is the destruction of forest. It may or may not be deliberate.
e. Forest Reserve: It is a piece of land set apart for preservation of trees and animals.
f. Taungya system: It involves the integration of crop farming with forest trees like Obeche or Mahogany. Both the farmers and the government derived benefits from this practice


EVALUATION:
Objective Test:
1. Forest is a source of wild animals used a. for game, b. for research, c. for meat, d. sport
2. Which of these is not a product from the forest? a. wild fruits, b. wild leaves, c. nuts, d. flowers.
3. Forest trees serves as a. an obstacles, b. flowers, c. wind breaks, d. shrubs
4. Deforestation is the …….. a. clearing of land , b. planting of new tree seedlings c. destruction of forest, d. cutting down of trees.
5. The integration of crop farming with forest trees is term a. afforestation, b. deforestation, c. taungya farming, d. forest reserve.
Essay Test:
1. Write 6 importance of forest
2. Explain afforestation and deforestation
REFERENCE TEXTS:
1. New Intensive Agricultural Science for Upper Basic 7, 8 & 9 By B. E. U. Okarol
2. Junior Secondary Agricultural Science By O. Akinsanmi et al.
3. Spectrum Agricultural for JSS Book 3 By B. A. Adelekan et al
4. Prescribed Agricultural Science for JSS Book 3 By S. A. Omoruyi et al
Topic: EFFECTS OF FOREST ON THE ENVIRONMENT
The following human activities in the environment affect the forest.
(a) Deforestation
(b) Depletion of wild life through bush burning, hunting , farming activities
(c) Poaching (illegal hunting of animals and lumbering activities)
(d) Bush burning
(e) Industrialization and mining
DEFORESTATION: It involves the cutting down of forest trees. This often leads to soil erosion and scarcity of forest products. Other effects include destruction of soil structure, wild life is denied of their habitat, reduces wild life population, valuable trees are destroyed, reduces the amount of rain fall in an area.

DEPLETION OF WILD LIFE: Activities like bush burning, hunting, and farming contribute to the depletion of both plants and animals that are very important in the forest.

POACHING: Many people engage in illegal hunting of animals felling of forest tree without taking permission or license from the government.

BUSH BURNING: The setting of fire in forest areas during dry season affects both plant and animas resources. Many good species of plants and animals are destroyed.

INDUSTRIALIZATION AND MINING: Many plants and animal species are wiped out of the forest as a result of clearing forest land for industry and mining activities.

EVALUATION:
Objectives:
1. Deforestation means the a. harvesting of crops, b. cutting down of forest trees, c. replanting of trees, d. growing of forest seedlings.
2. Poaching refers to a. indiscriminate cutting down of forest trees, b. illegal hunting of forest animals, c. harvesting of forest products, d. clearing of the forest vegetation.
3. Which of these activities does not contribute to the depletion of both plants and animals in the forest? a. bush burning, b. hunting, c. farming in the forest d. reseeding
4. Bush burning a. enables the forest to develop new species of plants, b. destroy both plants and animals in the forest, c. prevents people from entering into the forest.
5. Which of the following is not a forest animal?
a. (Loxodonta agricana)
b. (Phacopithecus aethiopicus)
c. Homo sapien
d.Snail (Archachatina morgunata)
ESSAY
1. State 4 effects of forest on the environment
2. Explain how the following affect forest. i. Poaching and depletion of wildlife
LESSON 4
IMPORTANCE OF FOREST
1. Forest provides timber trees.
2. It is a source of wild animals used for meat.
3. Provides income to people through hunting, felling of timber and sales of other products.
4. It protects the soil against erosion
5. It is a source of wild fruits, nuts, and flowers.
6. It is a source of fuel e.g. fire wood
7. It is a source of medicinal herbs
8. It is a source of fibre and ropes
9. It provides employment for people such as the forest guards
10. It is a source of revenue to the government
11. Forest reserve can serve as a tourist attraction.
12. It is a home for wild animals
13. Forest trees serves as wind breaks
14. It reduces atmospheric pollution.

FOREST MANAGEMENT: The following forest management practices are undertaken so as to ensure the maintenance of the forest.
a. Regeneration: It involves replacing the old forest trees with new ones.
b. Reforestation: It is the organized planting of trees in an area to create a forest in a place that has been deforested
c. Afforestation: It means establishing forest in areas where there has never been any .
d. Deforestation: It is the destruction of forest. It may or may not be deliberate.
e. Forest Reserve: It is a piece of land set apart for preservation of trees and animals.
f. Taungya system: It involves the integration of crop farming with forest trees like Obeche or Mahogany. Both the farmers and the government derived benefits from this practice


EVALUATION:
Objective Test:
1. Forest is a source of wild animals used a. for game, b. for research, c. for meat, d. sport
2. Which of these is not a product from the forest? a. wild fruits, b. wild leaves, c. nuts, d. flowers.
3. Forest trees serves as a. an obstacles, b. flowers, c. wind breaks, d. shrubs
4. Deforestation is the …….. a. clearing of land , b. planting of new tree seedlings c. destruction of forest, d. cutting down of trees.
5. The integration of crop farming with forest trees is term a. afforestation, b. deforestation, c. taungya farming, d. forest reserve.
Essay Test:
1. Write 6 importance of forest
2. Explain afforestation and deforestation
REFERENCE TEXTS:
1. New Intensive Agricultural Science for Upper Basic 7, 8 & 9 By B. E. U. Okarol
2. Junior Secondary Agricultural Science By O. Akinsanmi et al.
3. Spectrum Agricultural for JSS Book 3 By B. A. Adelekan et al
4. Prescribed Agricultural Science for JSS Book 3 By S. A. Omoruyi et al
WEEK 3
LESSON 5
Topic: FARM ANIMAL DISEASES.
Content: - Names of disease causing organisms
-Type of diseases caused by the organisms and the animals affected
Names of disease causing organisms
Be reminded that a disease is an abnormality in health. They are caused majorly by micro-organisms such as Virus, Bacteria, Fungi, Protozoan
and Worms.
These disease organisms get into the animals by various means. 1. Droppings of infected animals, 2. Contaminated feeds and water, 3. Contact with infected animals, 4. Air, 5.insects, 6.feed or water troughs.
Diseases of livestock could be infectious or contagious.
Infectious disease affects animals without physical contact with the infected animals. It can be transmitted to healthy animals through water, air, or feed. E.g Anthrax, Coccidiosis, and Fowl typhoid. While Contagious disease affect animals when there is physical contact with the infected animals.E.g Contagious abortion (bucellosis) ,Foot and Mouth , and Mastitis(inflammation of the udder)
Diseases that are transmitted from animals to human are termed Zoonotic disease. E.g Bird flu and Swine fever. It could cause death if not treated properly.
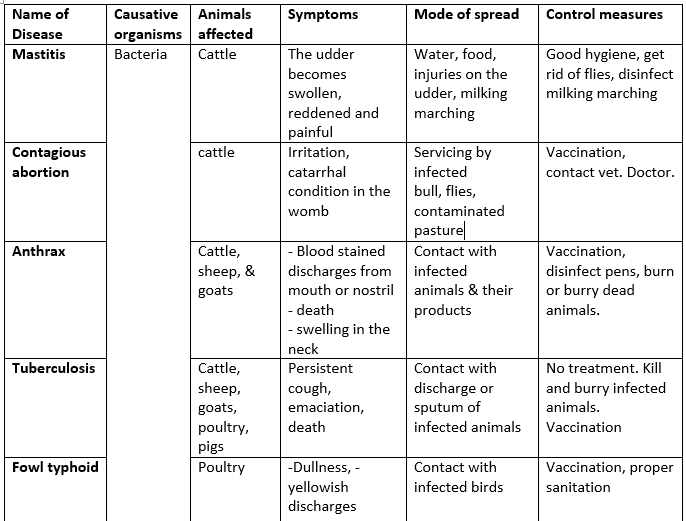
Disease Causing Organisms and Control Measures.
The table below shows the name of disease, the causative organism, the animals affected, symptoms, mode of spread and control measures.
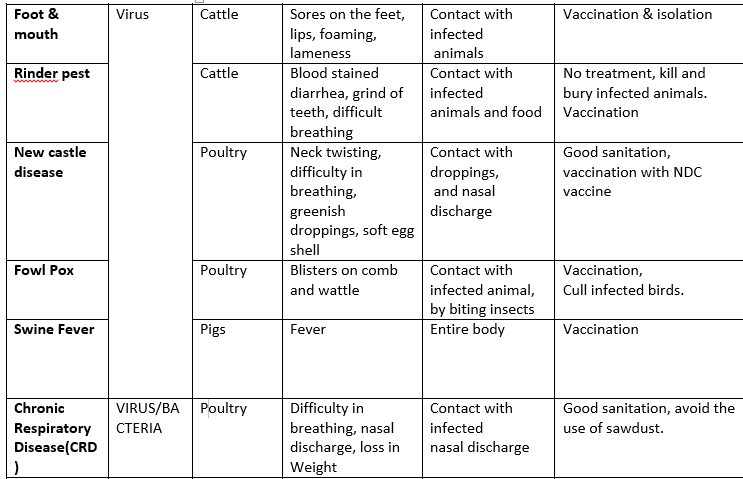
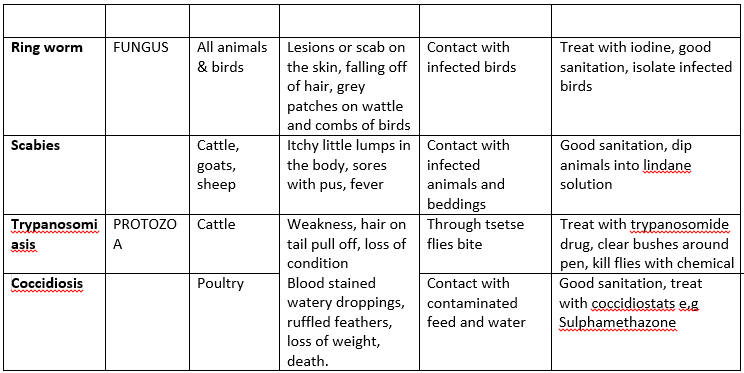
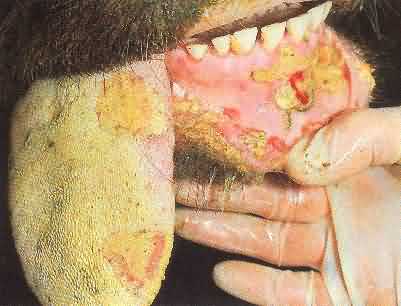
Foot & Mouth disease

Coccidiosis
Nutritional Diseases
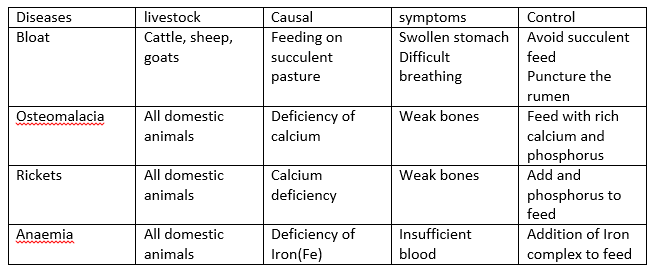
EVALUATION:
Objective Test:
1. Contagious abortion affects a. poultry, b. cattle, c. goats, d. swine
2. Persistent cough, emaciation, death are symptoms of a. Anthrax, b. Foot and Mouth, c. Tuberculosis
3. Fowl typhoid is caused by a. virus, b. bacteria, c. fungi, d. nematodes.
4. Blisters on comb and wattle is a symptom of a. Swine fever, b. Newcastle, c. Rinderpest, d. Fowl Pox.
5.Difficulty in breathing, nasal discharge, loss in Weight are symptoms of a. Chronic Respiratory Disease(CRD), b. Rinderpest, c. Newcastle, d. Typanosomiasis
6. New castle disease is caused by a. virus, b. bacteria, c. protozoan, d. nematodes
7. The causative organism of coccidiosis is a. protozoan , b. bacteria, c. Virus, d. nematodes
8. Feeding on succulent pasture can lead to a disease known as a. Rickets, b. Boat, c. Anaemia, d. Osteomalacia.
9. Insufficient blood is a symptom of a nutritional disease known as a. Bloat, b. Osteomalacia, c. Anaemia. d. Rickets
10. Feeding animals with rich calcium and phosphorus serves as the control measure of ------ a. Rickets, b. Boat, c. Anaemia, d. Osteomalacia.
Essay Test:
1. Copy and complete the table below:
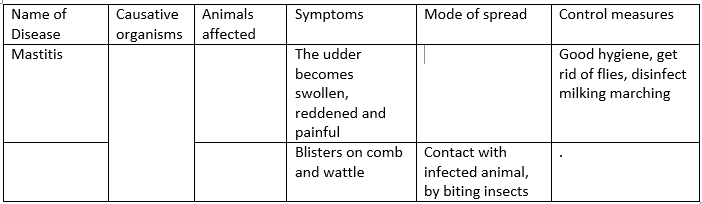
2. Differentiate between contagious disease and infectious disease and give two examples of each of them.
3. What is Zoonotic disease
4. Name the pathogens that caused the following disease
I . Trypanosomiasis
ii. Ring worm
iii. Swine fever
REFERENCE TEXTS:
1. New Intensive Agricultural Science for Upper Basic 7, 8 & 9 By B. E. U. Okarol
2. Junior Secondary Agricultural Science By O. Akinsanmi et al.
3. Spectrum Agricultural for JSS Book 3 By B. A. Adelekan et al
4. Prescribed Agricultural Science for JSS Book 3 By S. A. Omoruyi et al
Topic: FARM ANIMAL DISEASES.
Content: - Names of disease causing organisms
-Type of diseases caused by the organisms and the animals affected
Names of disease causing organisms
Be reminded that a disease is an abnormality in health. They are caused majorly by micro-organisms such as Virus, Bacteria, Fungi, Protozoan
and Worms.
These disease organisms get into the animals by various means. 1. Droppings of infected animals, 2. Contaminated feeds and water, 3. Contact with infected animals, 4. Air, 5.insects, 6.feed or water troughs.
Diseases of livestock could be infectious or contagious.
Infectious disease affects animals without physical contact with the infected animals. It can be transmitted to healthy animals through water, air, or feed. E.g Anthrax, Coccidiosis, and Fowl typhoid. While Contagious disease affect animals when there is physical contact with the infected animals.E.g Contagious abortion (bucellosis) ,Foot and Mouth , and Mastitis(inflammation of the udder)
Diseases that are transmitted from animals to human are termed Zoonotic disease. E.g Bird flu and Swine fever. It could cause death if not treated properly.

Disease Causing Organisms and Control Measures.
The table below shows the name of disease, the causative organism, the animals affected, symptoms, mode of spread and control measures.




Foot & Mouth disease

Coccidiosis
Nutritional Diseases

EVALUATION:
Objective Test:
1. Contagious abortion affects a. poultry, b. cattle, c. goats, d. swine
2. Persistent cough, emaciation, death are symptoms of a. Anthrax, b. Foot and Mouth, c. Tuberculosis
3. Fowl typhoid is caused by a. virus, b. bacteria, c. fungi, d. nematodes.
4. Blisters on comb and wattle is a symptom of a. Swine fever, b. Newcastle, c. Rinderpest, d. Fowl Pox.
5.Difficulty in breathing, nasal discharge, loss in Weight are symptoms of a. Chronic Respiratory Disease(CRD), b. Rinderpest, c. Newcastle, d. Typanosomiasis
6. New castle disease is caused by a. virus, b. bacteria, c. protozoan, d. nematodes
7. The causative organism of coccidiosis is a. protozoan , b. bacteria, c. Virus, d. nematodes
8. Feeding on succulent pasture can lead to a disease known as a. Rickets, b. Boat, c. Anaemia, d. Osteomalacia.
9. Insufficient blood is a symptom of a nutritional disease known as a. Bloat, b. Osteomalacia, c. Anaemia. d. Rickets
10. Feeding animals with rich calcium and phosphorus serves as the control measure of ------ a. Rickets, b. Boat, c. Anaemia, d. Osteomalacia.
Essay Test:
1. Copy and complete the table below:

2. Differentiate between contagious disease and infectious disease and give two examples of each of them.
3. What is Zoonotic disease
4. Name the pathogens that caused the following disease
I . Trypanosomiasis
ii. Ring worm
iii. Swine fever
REFERENCE TEXTS:
1. New Intensive Agricultural Science for Upper Basic 7, 8 & 9 By B. E. U. Okarol
2. Junior Secondary Agricultural Science By O. Akinsanmi et al.
3. Spectrum Agricultural for JSS Book 3 By B. A. Adelekan et al
4. Prescribed Agricultural Science for JSS Book 3 By S. A. Omoruyi et al
WEEK 4
LESSON 6
Topic: GENERAL EFFECTS OF DISEASES OF ON FARM ANIMALS.
Content: i. Effects of Disease
ii. General Methods of Prevention and Control of Farm Animals Diseases.
EFFECTS OF DISEASE
The following are the effects of diseases on farm animals
1. Reduced productivity
2. Loss of appetite
3. Loss of weight
4. Death
5. Loss of body condition called emaciation
6. Coughing and vomiting
7. Reduction of economic value of the animals
8. Reduction in nutritive value
9. Retarded growth
10. Diarrhea
11. Transmission of disease to human beings.
12. Increases cost of production

GENERAL METHODS OF PREVENTION AND CONTROL OF FARM ANIMALS DISEASES.
1. Good sanitation practices
2. Isolation of sick animals
3. Disposal waste materials
4. Immunization/vaccination of animals
5. Remove or kill and burn/burry animals that are infected with disease
6. Disinfection of livestock buildings and equipment.
7. Burning of contaminated feed and other materials
8. Avoid contamination of pasture with faeces of infected animal.
9. Quarantine
10. Use resistance breeds
11. Seek the advice of veterinary doctors.
12. Give animals’ balanced diet.


EVALUATION:
Objective Test:
1. The right person to contact for treatment of sick animals is a. medical doctor, b. nutritionist, c. veterinary doctor, d. farm attendant.
2. Giving balanced diet to animals is an effective way of preventing ----- disease a. Anthrax , b. coccidiosis, c. malnutrition. d. Rinderpest
3. Which of the following is not preventive/control measure of animal’s disease
a. Good sanitation practices b. Isolation of sick animals c. Disposal waste materials
d. ensuring constant light in the pen.
4. Culling refers to a. feeding sick animals, b. treating sick animals, c. removal or isolating
sick animals from the healthy ones, d. killing sick animals and burying them.
5. Lindane solution can be used to control one of the following diseases of farm animals.
a. Scabies, b. foot and mouth , c. Rinderpest, d. coccidiosis
Essay Test:
1. Write 5 effects of diseases in farm animals.
2. Give any 6 ways of preventing and controlling animal’s diseases.
REFERENCE TEXTS:
1. New Intensive Agricultural Science for Upper Basic 7, 8 & 9 By B. E. U. Okarol
2. Junior Secondary Agricultural Science By O. Akinsanmi et al.
3. Spectrum Agricultural for JSS Book 3 By B. A. Adelekan et al
4. Prescribed Agricultural Science for JSS Book 3 By S. A. Omoruyi et al
Topic: GENERAL EFFECTS OF DISEASES OF ON FARM ANIMALS.
Content: i. Effects of Disease
ii. General Methods of Prevention and Control of Farm Animals Diseases.
EFFECTS OF DISEASE
The following are the effects of diseases on farm animals
1. Reduced productivity
2. Loss of appetite
3. Loss of weight
4. Death
5. Loss of body condition called emaciation
6. Coughing and vomiting
7. Reduction of economic value of the animals
8. Reduction in nutritive value
9. Retarded growth
10. Diarrhea
11. Transmission of disease to human beings.
12. Increases cost of production

GENERAL METHODS OF PREVENTION AND CONTROL OF FARM ANIMALS DISEASES.
1. Good sanitation practices
2. Isolation of sick animals
3. Disposal waste materials
4. Immunization/vaccination of animals
5. Remove or kill and burn/burry animals that are infected with disease
6. Disinfection of livestock buildings and equipment.
7. Burning of contaminated feed and other materials
8. Avoid contamination of pasture with faeces of infected animal.
9. Quarantine
10. Use resistance breeds
11. Seek the advice of veterinary doctors.
12. Give animals’ balanced diet.


EVALUATION:
Objective Test:
1. The right person to contact for treatment of sick animals is a. medical doctor, b. nutritionist, c. veterinary doctor, d. farm attendant.
2. Giving balanced diet to animals is an effective way of preventing ----- disease a. Anthrax , b. coccidiosis, c. malnutrition. d. Rinderpest
3. Which of the following is not preventive/control measure of animal’s disease
a. Good sanitation practices b. Isolation of sick animals c. Disposal waste materials
d. ensuring constant light in the pen.
4. Culling refers to a. feeding sick animals, b. treating sick animals, c. removal or isolating
sick animals from the healthy ones, d. killing sick animals and burying them.
5. Lindane solution can be used to control one of the following diseases of farm animals.
a. Scabies, b. foot and mouth , c. Rinderpest, d. coccidiosis
Essay Test:
1. Write 5 effects of diseases in farm animals.
2. Give any 6 ways of preventing and controlling animal’s diseases.
REFERENCE TEXTS:
1. New Intensive Agricultural Science for Upper Basic 7, 8 & 9 By B. E. U. Okarol
2. Junior Secondary Agricultural Science By O. Akinsanmi et al.
3. Spectrum Agricultural for JSS Book 3 By B. A. Adelekan et al
4. Prescribed Agricultural Science for JSS Book 3 By S. A. Omoruyi et al
WEEK 5
LESSON 7
TOPIC: CONTROLLING CROP PESTS:
Contents: i Crop pest damage,
ii The concept and principles of pest control and pest management,
iii Method of pest control and management.
CROP PEST DAMAGE
Introduction: Pest is defined as any living organism, plant or animals, which can cause damage to cultivated crops, farm animals and humans. The most common pests include insects like grasshoppers, aphids, termites, weevils, beetles, mammals such as rats, monkeys and birds such as weaver birds. Some worms live in the soil, and are called nematodes, are also very notable pests of crops.
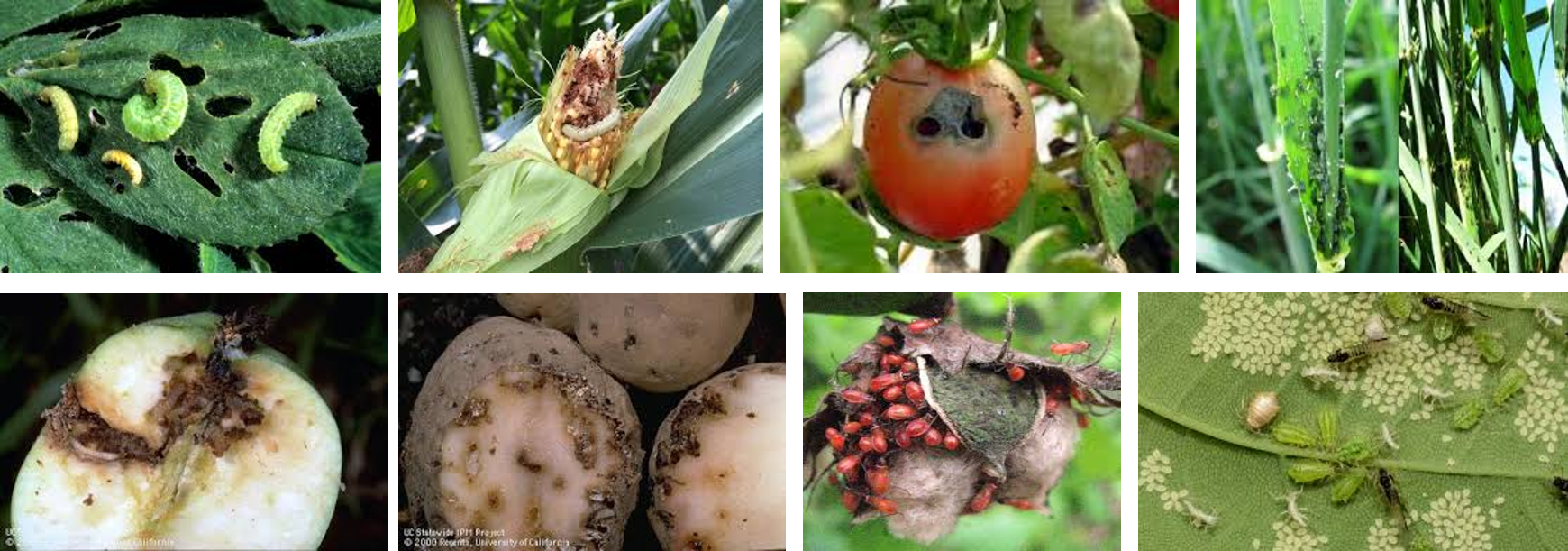

CROP PEST DAMAGE
Pests often cause a lot of damage to crop plants and the damage lead to what is called crop loss. This means that pests have removed large quantities of harvests which farmers should have obtained from their crops.
The pattern of damage differs in terms of the kind of pest involved and the crop which is damaged; such crops are called host plants.
Pests cause damage to crops in three different ways:
1. By eating up the whole parts of plants e.g. grasshoppers and termites,
2. They bore holes in various parts of the plants e.g. stem borers and;
3. Suck juice from the fruits and flowers, e.g. aphids and mealy bugs which suck juice from cassava plants and in the process transmit diseases.

Evaluation:
Objective Test:
1 Crops damage lead to what is called ………A. crop sickness B. crop management
C. crop loss D. crop destruction.
2. Which of these is not an effect of pests on crops A. reduction in quality B. sickness C. crop improvement D. infection?
3 crops is affected by different pests such crop is called…A .host plant B. affected plant C. eaten plant D. damaged crop.
4. Which of these is not a pest of cassava and yam?
A. rodents B. birds C. nematode D. grasshoppers.
5 Grasshopper may likely cause damage to …..A. root B. flower C. leaves D tuber.
Essay Test:
1. List some common examples of pest that affect farm produce.
2. Discuss the various ways by which pests can cause damage to crops?
LESSON 8
THE CONCEPT AND PRINCIPLES OF PEST CONTROL AND PEST MANAGEMENT:

Agricultural scientists use the term pest control to describe the methods which are applied to reduce the populations of insect pests and other organisms which are causing crops damage.
In the past people talk about pests control as eliminating pests completely but we now know that this is not possible because eliminating pests create an ecological vacuum which leads to various problems. The term pest management is used to describe this option which has proved very successful in reducing pest damage to crops and crop losses.
The most important types of information required for the successful management of pests include the following:
I. The exact scientific name and identity of the pest organisms.
II. The behaviour of the pest, as well as the exact stage of the crops when the pest occurs.
III. The nature of the damage done to crops by pests.
IV. The natural enemies of the pest and how the populations of the natural enemies change with the weather and the pest.
V. The best method to control pest or manage the pests is the one that is most cost–effective and the method which will not leave any problems in the farm and the general environment. The method should also not affect the harvested products in any way to reduce their qualities
Scientific principle for successful pest control and pest management
I. Observation: Farmers must first regularly observe crops in the farm to see how they are growing and which pests are causing damage to the crops; when the pests occur, how many pests are present on the crops.
II. Nature of damage: Through observation, understand the nature of the crop damage caused.
III. Decision making: Make a decision on the kind of method that can be applied and how the method should be applied to reduce the pests damage; and
IV. Eradication: Take necessary action to remove pests and reduce the crop damage.
METHODS OF PEST CONTROL AND PEST MANAGEMENT
Pest organisms are normal components of the farming environment. To reduce pest damage to crops and to prevent crop losses, pests and crop damage must be controlled. Therefore, the purpose of applying pest control or pest management methods is to drastically reduce the numbers or populations of pests to low levels which cause very little damage to crops.
Not all pests are controlled in the same way. The method of control selected will depend on the crop, the kind of pest concern, the nature of damage caused and the cost of the control method. Common methods of pest control are described under the following headings.
I. CULTURAL METHODS:
This is the application of exalt farm operation in other to prevent crops from insect attack or to reduce and destroy insect populations in the farm.
1. Adequate spacing and correct seed rate per hectare will assist aeration with crops unsuitable for pest development.
2. The practice of crop rotation which involves growing crops which are normally heavily damaged by pests and alternating them with cops which are not heavily damaged.
3. Growing many crops together in the same farm, a practice called mixed cropping.
4. Timelines or early planting of crops.
5. Other cultural methods which reduce pest numbers are tilling and ploughing of soil to bring up the eggs and larvae of some pests which are exposed to the heat of the sun and are killed or are eaten by birds.
ii Physical methods
These are simple method which use physical means to reduce the numbers of pests; for example
1. Hand picking, picking individual large insect pests like grasshoppers from crops.
2. Using traps and cages to catch pests, for example, traps are used for controlling rat and other rodents in rice field
3. Bird pests are also effectively controlled by the use of mist nets placed on the flight paths to trap them. The birds trapped are collected and destroyed.
4. Placing artificially constructed images of the human figure with clothes, in different parts of the farm.
5. Scarecrow to scare away birds.
6. Shooting and rodents with guns.
Iii Use of resistant crop varieties
Agricultural research scientists have produce some types of crops which insects do not like to feed on. Such crops are called pests resistant varieties.
IV Biological control
The natural enemies of crop pests can be used to control them. Natural enemies of pests may be predators, parasites or pathogenic organisms that cause diseases in pests or kill them.
V use of chemicals (Pesticides)
The most common and easiest method of controlling pests is the use of chemicals to spray crops infested with pests. Chemicals which have been developed for controlling pests are called pesticides.
Pesticides kill pests in three major ways:
1. By contact poisoning (spraying directly on pests),
2. As stomach poisoning (when pests eat the crops) and
3. As fumigant (when pests inhaled the poisonous fumes from pesticides which are spray onto infected crops)
IV Integrated Pest Management
Farmers and agricultural scientists have discovered that the most popular method of dealing with pests in their farms and the method that has proven to be highly effective is called Integrated Pest Management, abbreviated as IPM.
Evaluation:
Objective Test:
1 One of these is not a scientific method A. observation B. decision taking C. taking of action D. picking.
2. The methods applied on pest reduction is called A. pest elimination B crop reduction. C Crop preservation D. crop rotation.
3 The use natural enemies of pest in controlling pests is called……….A. biological pest control B. mechanical pest control C. planting of resistant varieties D. physical method.
4. Hand picking, use of trap, setting of net along the pathway of birds is……….
A physical method B. chemical method C. fumigation D. cultural method.
5. The pest control that is very expensive is …..A .chemical method B. cultural method C. physical method D. biological method.
Essay Test:
1. Explain the following:
A. Cultural method of pest control
B. Physical pest control
C. Biological pest control
2. What is pest elimination and the problem that may occur.
3. Discuss pest control and management.
References:
1 Spectrum Agricultural Science 3 by B .A. Adelekan et al
2 VIU Agricultural Science 3
3 JS Agriculture for Nigerian Schools. Book 3 Anthony Youdeowei et al
TOPIC: CONTROLLING CROP PESTS:
Contents: i Crop pest damage,
ii The concept and principles of pest control and pest management,
iii Method of pest control and management.
CROP PEST DAMAGE
Introduction: Pest is defined as any living organism, plant or animals, which can cause damage to cultivated crops, farm animals and humans. The most common pests include insects like grasshoppers, aphids, termites, weevils, beetles, mammals such as rats, monkeys and birds such as weaver birds. Some worms live in the soil, and are called nematodes, are also very notable pests of crops.

CROP PEST DAMAGE
Pests often cause a lot of damage to crop plants and the damage lead to what is called crop loss. This means that pests have removed large quantities of harvests which farmers should have obtained from their crops.
The pattern of damage differs in terms of the kind of pest involved and the crop which is damaged; such crops are called host plants.
Pests cause damage to crops in three different ways:
1. By eating up the whole parts of plants e.g. grasshoppers and termites,
2. They bore holes in various parts of the plants e.g. stem borers and;
3. Suck juice from the fruits and flowers, e.g. aphids and mealy bugs which suck juice from cassava plants and in the process transmit diseases.

Evaluation:
Objective Test:
1 Crops damage lead to what is called ………A. crop sickness B. crop management
C. crop loss D. crop destruction.
2. Which of these is not an effect of pests on crops A. reduction in quality B. sickness C. crop improvement D. infection?
3 crops is affected by different pests such crop is called…A .host plant B. affected plant C. eaten plant D. damaged crop.
4. Which of these is not a pest of cassava and yam?
A. rodents B. birds C. nematode D. grasshoppers.
5 Grasshopper may likely cause damage to …..A. root B. flower C. leaves D tuber.
Essay Test:
1. List some common examples of pest that affect farm produce.
2. Discuss the various ways by which pests can cause damage to crops?
LESSON 8
THE CONCEPT AND PRINCIPLES OF PEST CONTROL AND PEST MANAGEMENT:

Agricultural scientists use the term pest control to describe the methods which are applied to reduce the populations of insect pests and other organisms which are causing crops damage.
In the past people talk about pests control as eliminating pests completely but we now know that this is not possible because eliminating pests create an ecological vacuum which leads to various problems. The term pest management is used to describe this option which has proved very successful in reducing pest damage to crops and crop losses.
The most important types of information required for the successful management of pests include the following:
I. The exact scientific name and identity of the pest organisms.
II. The behaviour of the pest, as well as the exact stage of the crops when the pest occurs.
III. The nature of the damage done to crops by pests.
IV. The natural enemies of the pest and how the populations of the natural enemies change with the weather and the pest.
V. The best method to control pest or manage the pests is the one that is most cost–effective and the method which will not leave any problems in the farm and the general environment. The method should also not affect the harvested products in any way to reduce their qualities
Scientific principle for successful pest control and pest management
I. Observation: Farmers must first regularly observe crops in the farm to see how they are growing and which pests are causing damage to the crops; when the pests occur, how many pests are present on the crops.
II. Nature of damage: Through observation, understand the nature of the crop damage caused.
III. Decision making: Make a decision on the kind of method that can be applied and how the method should be applied to reduce the pests damage; and
IV. Eradication: Take necessary action to remove pests and reduce the crop damage.
METHODS OF PEST CONTROL AND PEST MANAGEMENT
Pest organisms are normal components of the farming environment. To reduce pest damage to crops and to prevent crop losses, pests and crop damage must be controlled. Therefore, the purpose of applying pest control or pest management methods is to drastically reduce the numbers or populations of pests to low levels which cause very little damage to crops.
Not all pests are controlled in the same way. The method of control selected will depend on the crop, the kind of pest concern, the nature of damage caused and the cost of the control method. Common methods of pest control are described under the following headings.
I. CULTURAL METHODS:
This is the application of exalt farm operation in other to prevent crops from insect attack or to reduce and destroy insect populations in the farm.
1. Adequate spacing and correct seed rate per hectare will assist aeration with crops unsuitable for pest development.
2. The practice of crop rotation which involves growing crops which are normally heavily damaged by pests and alternating them with cops which are not heavily damaged.
3. Growing many crops together in the same farm, a practice called mixed cropping.
4. Timelines or early planting of crops.
5. Other cultural methods which reduce pest numbers are tilling and ploughing of soil to bring up the eggs and larvae of some pests which are exposed to the heat of the sun and are killed or are eaten by birds.
ii Physical methods
These are simple method which use physical means to reduce the numbers of pests; for example
1. Hand picking, picking individual large insect pests like grasshoppers from crops.
2. Using traps and cages to catch pests, for example, traps are used for controlling rat and other rodents in rice field
3. Bird pests are also effectively controlled by the use of mist nets placed on the flight paths to trap them. The birds trapped are collected and destroyed.
4. Placing artificially constructed images of the human figure with clothes, in different parts of the farm.
5. Scarecrow to scare away birds.
6. Shooting and rodents with guns.
Iii Use of resistant crop varieties
Agricultural research scientists have produce some types of crops which insects do not like to feed on. Such crops are called pests resistant varieties.
IV Biological control
The natural enemies of crop pests can be used to control them. Natural enemies of pests may be predators, parasites or pathogenic organisms that cause diseases in pests or kill them.

V use of chemicals (Pesticides)
The most common and easiest method of controlling pests is the use of chemicals to spray crops infested with pests. Chemicals which have been developed for controlling pests are called pesticides.
Pesticides kill pests in three major ways:
1. By contact poisoning (spraying directly on pests),
2. As stomach poisoning (when pests eat the crops) and
3. As fumigant (when pests inhaled the poisonous fumes from pesticides which are spray onto infected crops)
IV Integrated Pest Management
Farmers and agricultural scientists have discovered that the most popular method of dealing with pests in their farms and the method that has proven to be highly effective is called Integrated Pest Management, abbreviated as IPM.
Evaluation:
Objective Test:
1 One of these is not a scientific method A. observation B. decision taking C. taking of action D. picking.
2. The methods applied on pest reduction is called A. pest elimination B crop reduction. C Crop preservation D. crop rotation.
3 The use natural enemies of pest in controlling pests is called……….A. biological pest control B. mechanical pest control C. planting of resistant varieties D. physical method.
4. Hand picking, use of trap, setting of net along the pathway of birds is……….
A physical method B. chemical method C. fumigation D. cultural method.
5. The pest control that is very expensive is …..A .chemical method B. cultural method C. physical method D. biological method.
Essay Test:
1. Explain the following:
A. Cultural method of pest control
B. Physical pest control
C. Biological pest control
2. What is pest elimination and the problem that may occur.
3. Discuss pest control and management.
References:
1 Spectrum Agricultural Science 3 by B .A. Adelekan et al
2 VIU Agricultural Science 3
3 JS Agriculture for Nigerian Schools. Book 3 Anthony Youdeowei et al
WEEK 6
LESSON 9
TOPIC: PRESERVATION OF FARM PRODUCE FOR MARKETING
Contents: 1. Method of preserving farm produce: i Livestock
ii Crops
iii Fish
2. Methods of food preservation
3. Preservation Method of Livestock
METHOD OF PRESERVING FARM PRODUCE
INTRODUCTION:
Most agricultural produce such as vegetable, maize, fish, yam fresh milk and others get bad if they are not properly stored or preserved. Also, many crops have their particular seasons whereby they are available in the year. Different methods have been derived in order to preserve and ensure the availability of food crops in all the seasons of the year.
Preservation:
Preservation refers to methods of keeping food in order to deny access to pests as well as protection from unfavorable weather. Storage of farm produce particularly minimizes the loss of farm produce from pests while waiting for sales or eventual disposal.
REASONS FOR PRESERVATION:
Farm produce are preserved for the following reasons:
1. To prevent spoilage due to the actions of micro-organisms (Bacteria and Fungi)
2. To ensure the degree of originality and conservation of the quality of the farm produce.
3. To ensure food is stored for a long period of time.
4. To ensure food availability at all times.
5. To ensure wider and proper distributions of farm produce in large markets (exportation and importation)
Preservation of food can be achieved through a variety of preservation methods such as following:
Drying
Salting
Canning /bottling
Sugaring
Milling
Smoking
Refrigeration
Vacuum packing
Picking
Sodium hydroxide (Lye)
Jelling
Juggling
Irradiation
Modified atmosphere

METHODS OF FOOD PRESERVATION
Preservation of food can be achieved through a number of measures:
1.Drying
Drying of agricultural produce ensures the removal excess water that could be responsible for spoilage. Drying is best done by spreading the items in sun or any source of heat. The farm produce that can be dried are: fish, animals skins, bones, pepper, tomatoes, cassava, cereals, legumes, leaves, etc.
Advantages of drying
1 It is a cheap method of preservation
2 The required taste, flavor and quality of food is retained.
3 Little labour is required in preserving the food.
Disadvantages
1 Food is exposed to flies and other diseases vectors
2 The food can be contaminated by dust, sand other micro-organisms.
2. Refrigeration
This is known as cold storage. It involved the storing of food at a temperature below 4 degree Celsius. This render bacteria and other decay causing agents inactive. It however slows down spoilage. Fish and meat kept in this way can remain in good condition for a long time. Cold storage warehouses are used to preserve large quantities of fruits cheese, eggs, fresh fish and meat etc. for up to eight months.
Advantages
1 The freshness of the food is retained.
2. There is no loss of weight or quality of the food.
3 There is no exposure to flies or other micro-organisms.
Disadvantages
1 It is expensive to afford by the small scale farmers.
2 Spoilage and wastage occur in the events of power failures.
3 Over exposure of human body to cold room could be dangerous to human health.
3. Salting
This is the application of appreciable quantity of salt on the surface of fish, meat and others in order to prevent spoilage by fungi and bacteria and also to remove moisture.
Advantages
1 Maggot IS prevented from investing the food.
2 Large quantities of fish can be preserved.
3 Food e.g. fish and meat can be preserved for to two years.
Disadvantages
1 It leads to reduction in food weight.
2 Too much of salt changes the original taste of food.
3 Excess salt may be dangerous to health.
4. Canning:
This is a process of placing raw food in sterilized cans. The raw food is first carefully cleansed and prepared for use then sealed in air tight containers. Meat, fish, milk, poultry, tomatoes etc can be canned.
Advantages
1. They are not exposed to contamination by air or micro organisms.
2. They possess and retained their good taste and flavors.
3. They are portable for distribution and marketing.
Disadvantages
1. There is possibility of food poisoning over the expiring of food that is canned.
2. It is very expensive to practice hence; poor farmers cannot afford to use it.
4 Highly qualified and experience personnel services are required.
PRESERVATION METHOD OF LIVESTOCKS
1. Drying:
Drying of agricultural produce ensures the removal excess water that could be responsible for spoilage. Drying is best done by spreading the items in sun or any source of heat. The farm produce that can be dried are: fish, animals skins, bones, pepper, tomatoes, cassava, cereals, legumes, leaves, etc.

2. Smoking
Smoking is used mainly for fish and meat. The heat of the smoke removes the water from the fish and the meat thereby brings about drying.

3. Salting:
When salt and sugar are rubbed into farm produce, they extract water from the food tissues through a process known as osmosis. This ensures that the micro-organisms are deprived of the much needed water for their growth and sustenance.

4. Canning:
Canning is used to preserve wide varieties of crops, including fruits, vegetables and juice. As soon as the can is opened, it should be emptied. Some canned food can last for years.

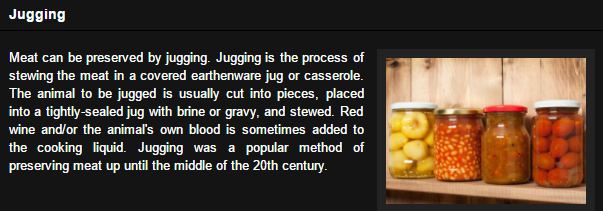
5. Jugging:
This is the process of stewing the meat in a covered earthen jug or casserole. Before jugging, the meat is cut into pieces, placed in an air tight sealed jug with brine or gravy, and stewed. Jugging can be used effectively to preserve meat and fish.
6 Refrigeration/ Freezing:
Freezing readily preserves meat, fish and other aquatic food for a long period of time.

Evaluation:
Objective Test:
1. The food preservation method of cooling food to a temperature just above the freezing point of water is known as……..A. irradiation B. freezing C refrigeration D. steaming.
2. The method of grinding crop grains and storing them as powder is known as……
A. Milling. B Bickling, C. Curing. D. Irradiation.
3. Refrigeration is best used for preserving………..
A. Oranges and other fruits B. Fresh meat and fresh meat C.Amaranthus and Okra
D. banana and plantain.
4. Which of the following sets of crops are best stored in sacks?
A.yam, cassava and potatoes B. millet, kola nut and plantain C.vegetables, tomatoes and okra. D.cowpea, rice and maize.
5. Refrigeration is best for which of these farms produce……..
A. yam B. okra C fish D potato.
Essay Test:
1 How do farm produce get spoilt? Explain details.
2. List ways of preserving sea food.
LESSON 10
CROP PRESERVATION METHODS
1 Drying:
Drying is one of the oldest methods of food preservation. Drying reduces water activity sufficiently to delay or prevent bacterial growth.

2. Canning:
Canning involves cooking fruits or vegetables and sealing them in sterile cans or jars and boiling the containers to kill or weaken any remaining bacteria as a form of pasteurization.

3. Refrigeration/Freezing
Freezing is also one of the most commonly used preservation methods. It is used commercially and domestically for preserving a wide range of food stuffs including fish and sea foods. Cold stores provide large, volume, long –term storage for strategic food stocks in case of national emergency in many countries.

4. Lye:
NAOH (Lye), makes food too alkaline for bacteria to grow. Fruits e.g. grape and vegetables can be dipped as quickly as possible into almost boiling lye to preserve them. After this process it is advisable to rinse the fruits or vegetables with cold water.

5. Irradiation method:
This is the use of x-ray or gamma radiation to kill micro- organisms and parasites that may be present in food.

6. Modified atmosphere:
Food is preserved in this method by changing the composition of air within that environment e.g. Salad are now being packed in sealed bags with an atmosphere designed to reduce the concentration of oxygen (O2) and increase the concentration of Carbon dioxide (CO2).

7. Jellying:
In this method, food is preserved by cooking it in a material that solidifies to form a gel e.g. rice flour and maize.

8. Clumps:
Many root vegetables are highly resistant to spoilage and they do not require any other preservation apart from storage in cold dark condition, particularly in field clumps e.g. vegetable, carrot.

9. Milling:
This is the practice of grinding of grains in a mill and storing in sacks or polythene bags e.g. Millet, Maize, guinea corn etc.

10. Curing method:
Curing methods of produce preservation include the following:
a. Addition of salt, sugar, and vinegar to food.
b. Smoking,
c. Cooking.
These curing methods usually destroy many of the micro-organisms on the surfaces of foods and also slow down the growth of other micro-organisms inside the food.

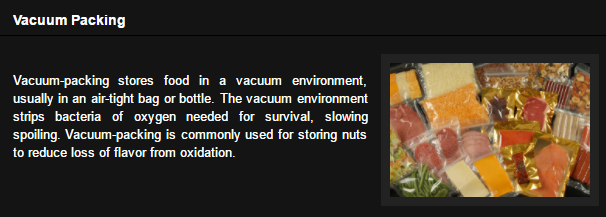
11. Vacuum packing:
This is the preservation of food in an air tight bottle or bags i.e. air is excluded from the environment.
Evaluation:
1. Differentiate between storage of farm produce and preservation.
2. List the methods of preservation of livestock produce and crop produce.
Objective Test:
1. Which of the following methods cannot be used for preserving fish?
A. Drying. B. Smoking. C. Freezing. D. Non of the above.
2. Which of the following causes freshly harvested food to get spoiled?
A. yeast B. Bacteria C. Mould D. Enzymes
3. The most reliable method for long term preservation at room temperature is ……..
A. refrigeration B. cooking C. Canning D. baking.
4. Which of the following is not a curing method of food preservation?
A. Smoking B. Addition of vinegar C. Salting D. Canning
5. Which of these is not an hygienic method of food preservation.
A. Drying B. Refrigeration C. Irradiation D. Canning.
References:
1 Spectrum Agricultural Science 3 by B .A. Adelekan et al
2 VIU Agricultural Science 3
3 JS Agriculture for Nigerian Schools book 3 by Anthony Youdeowei et al
TOPIC: PRESERVATION OF FARM PRODUCE FOR MARKETING
Contents: 1. Method of preserving farm produce: i Livestock
ii Crops
iii Fish
2. Methods of food preservation
3. Preservation Method of Livestock
METHOD OF PRESERVING FARM PRODUCE
INTRODUCTION:
Most agricultural produce such as vegetable, maize, fish, yam fresh milk and others get bad if they are not properly stored or preserved. Also, many crops have their particular seasons whereby they are available in the year. Different methods have been derived in order to preserve and ensure the availability of food crops in all the seasons of the year.
Preservation:
Preservation refers to methods of keeping food in order to deny access to pests as well as protection from unfavorable weather. Storage of farm produce particularly minimizes the loss of farm produce from pests while waiting for sales or eventual disposal.
REASONS FOR PRESERVATION:
Farm produce are preserved for the following reasons:
1. To prevent spoilage due to the actions of micro-organisms (Bacteria and Fungi)
2. To ensure the degree of originality and conservation of the quality of the farm produce.
3. To ensure food is stored for a long period of time.
4. To ensure food availability at all times.
5. To ensure wider and proper distributions of farm produce in large markets (exportation and importation)
Preservation of food can be achieved through a variety of preservation methods such as following:
Drying
Salting
Canning /bottling
Sugaring
Milling
Smoking
Refrigeration
Vacuum packing
Picking
Sodium hydroxide (Lye)
Jelling
Juggling
Irradiation
Modified atmosphere

METHODS OF FOOD PRESERVATION
Preservation of food can be achieved through a number of measures:
1.Drying
Drying of agricultural produce ensures the removal excess water that could be responsible for spoilage. Drying is best done by spreading the items in sun or any source of heat. The farm produce that can be dried are: fish, animals skins, bones, pepper, tomatoes, cassava, cereals, legumes, leaves, etc.
Advantages of drying
1 It is a cheap method of preservation
2 The required taste, flavor and quality of food is retained.
3 Little labour is required in preserving the food.
Disadvantages
1 Food is exposed to flies and other diseases vectors
2 The food can be contaminated by dust, sand other micro-organisms.
2. Refrigeration
This is known as cold storage. It involved the storing of food at a temperature below 4 degree Celsius. This render bacteria and other decay causing agents inactive. It however slows down spoilage. Fish and meat kept in this way can remain in good condition for a long time. Cold storage warehouses are used to preserve large quantities of fruits cheese, eggs, fresh fish and meat etc. for up to eight months.
Advantages
1 The freshness of the food is retained.
2. There is no loss of weight or quality of the food.
3 There is no exposure to flies or other micro-organisms.
Disadvantages
1 It is expensive to afford by the small scale farmers.
2 Spoilage and wastage occur in the events of power failures.
3 Over exposure of human body to cold room could be dangerous to human health.
3. Salting
This is the application of appreciable quantity of salt on the surface of fish, meat and others in order to prevent spoilage by fungi and bacteria and also to remove moisture.
Advantages
1 Maggot IS prevented from investing the food.
2 Large quantities of fish can be preserved.
3 Food e.g. fish and meat can be preserved for to two years.
Disadvantages
1 It leads to reduction in food weight.
2 Too much of salt changes the original taste of food.
3 Excess salt may be dangerous to health.
4. Canning:
This is a process of placing raw food in sterilized cans. The raw food is first carefully cleansed and prepared for use then sealed in air tight containers. Meat, fish, milk, poultry, tomatoes etc can be canned.
Advantages
1. They are not exposed to contamination by air or micro organisms.
2. They possess and retained their good taste and flavors.
3. They are portable for distribution and marketing.
Disadvantages
1. There is possibility of food poisoning over the expiring of food that is canned.
2. It is very expensive to practice hence; poor farmers cannot afford to use it.
4 Highly qualified and experience personnel services are required.
PRESERVATION METHOD OF LIVESTOCKS
1. Drying:
Drying of agricultural produce ensures the removal excess water that could be responsible for spoilage. Drying is best done by spreading the items in sun or any source of heat. The farm produce that can be dried are: fish, animals skins, bones, pepper, tomatoes, cassava, cereals, legumes, leaves, etc.

2. Smoking
Smoking is used mainly for fish and meat. The heat of the smoke removes the water from the fish and the meat thereby brings about drying.

3. Salting:
When salt and sugar are rubbed into farm produce, they extract water from the food tissues through a process known as osmosis. This ensures that the micro-organisms are deprived of the much needed water for their growth and sustenance.

4. Canning:
Canning is used to preserve wide varieties of crops, including fruits, vegetables and juice. As soon as the can is opened, it should be emptied. Some canned food can last for years.

5. Jugging:
This is the process of stewing the meat in a covered earthen jug or casserole. Before jugging, the meat is cut into pieces, placed in an air tight sealed jug with brine or gravy, and stewed. Jugging can be used effectively to preserve meat and fish.

6 Refrigeration/ Freezing:
Freezing readily preserves meat, fish and other aquatic food for a long period of time.

Evaluation:
Objective Test:
1. The food preservation method of cooling food to a temperature just above the freezing point of water is known as……..A. irradiation B. freezing C refrigeration D. steaming.
2. The method of grinding crop grains and storing them as powder is known as……
A. Milling. B Bickling, C. Curing. D. Irradiation.
3. Refrigeration is best used for preserving………..
A. Oranges and other fruits B. Fresh meat and fresh meat C.Amaranthus and Okra
D. banana and plantain.
4. Which of the following sets of crops are best stored in sacks?
A.yam, cassava and potatoes B. millet, kola nut and plantain C.vegetables, tomatoes and okra. D.cowpea, rice and maize.
5. Refrigeration is best for which of these farms produce……..
A. yam B. okra C fish D potato.
Essay Test:
1 How do farm produce get spoilt? Explain details.
2. List ways of preserving sea food.
LESSON 10
CROP PRESERVATION METHODS
1 Drying:
Drying is one of the oldest methods of food preservation. Drying reduces water activity sufficiently to delay or prevent bacterial growth.

2. Canning:
Canning involves cooking fruits or vegetables and sealing them in sterile cans or jars and boiling the containers to kill or weaken any remaining bacteria as a form of pasteurization.

3. Refrigeration/Freezing
Freezing is also one of the most commonly used preservation methods. It is used commercially and domestically for preserving a wide range of food stuffs including fish and sea foods. Cold stores provide large, volume, long –term storage for strategic food stocks in case of national emergency in many countries.

4. Lye:
NAOH (Lye), makes food too alkaline for bacteria to grow. Fruits e.g. grape and vegetables can be dipped as quickly as possible into almost boiling lye to preserve them. After this process it is advisable to rinse the fruits or vegetables with cold water.

5. Irradiation method:
This is the use of x-ray or gamma radiation to kill micro- organisms and parasites that may be present in food.

6. Modified atmosphere:
Food is preserved in this method by changing the composition of air within that environment e.g. Salad are now being packed in sealed bags with an atmosphere designed to reduce the concentration of oxygen (O2) and increase the concentration of Carbon dioxide (CO2).

7. Jellying:
In this method, food is preserved by cooking it in a material that solidifies to form a gel e.g. rice flour and maize.

8. Clumps:
Many root vegetables are highly resistant to spoilage and they do not require any other preservation apart from storage in cold dark condition, particularly in field clumps e.g. vegetable, carrot.

9. Milling:
This is the practice of grinding of grains in a mill and storing in sacks or polythene bags e.g. Millet, Maize, guinea corn etc.

10. Curing method:
Curing methods of produce preservation include the following:
a. Addition of salt, sugar, and vinegar to food.
b. Smoking,
c. Cooking.
These curing methods usually destroy many of the micro-organisms on the surfaces of foods and also slow down the growth of other micro-organisms inside the food.

11. Vacuum packing:
This is the preservation of food in an air tight bottle or bags i.e. air is excluded from the environment.

Evaluation:
1. Differentiate between storage of farm produce and preservation.
2. List the methods of preservation of livestock produce and crop produce.
Objective Test:
1. Which of the following methods cannot be used for preserving fish?
A. Drying. B. Smoking. C. Freezing. D. Non of the above.
2. Which of the following causes freshly harvested food to get spoiled?
A. yeast B. Bacteria C. Mould D. Enzymes
3. The most reliable method for long term preservation at room temperature is ……..
A. refrigeration B. cooking C. Canning D. baking.
4. Which of the following is not a curing method of food preservation?
A. Smoking B. Addition of vinegar C. Salting D. Canning
5. Which of these is not an hygienic method of food preservation.
A. Drying B. Refrigeration C. Irradiation D. Canning.
References:
1 Spectrum Agricultural Science 3 by B .A. Adelekan et al
2 VIU Agricultural Science 3
3 JS Agriculture for Nigerian Schools book 3 by Anthony Youdeowei et al
WEEK 7
LESSON 11
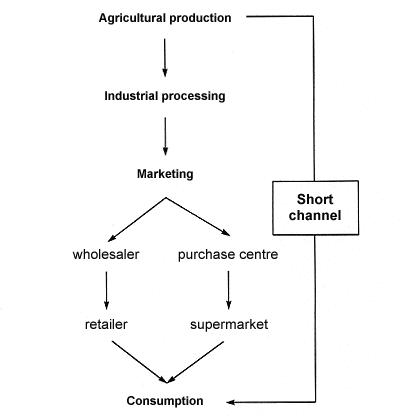
TOPIC: CHANNELS FOR DISTRIBUTION OF AGRICULTURAL PRODUCE
Contents: 1. Channels of distribution in Agriculture
2. Activities taking place at the channels of distribution,
3. Challenges in agricultural marketing.
CHANNELS OF DISTRIBUTION IN AGRICULTURE
Introduction: Channels of distribution refers to the various ways through which agricultural produce are carried form the producers (farmers) to the final consumers.
The place where producers and consumers meet to sell and buy their materials is known as a market. Since producers (farmers) and consumers do not live in the same place, it is therefore important for farmers to carry their produce from the place of production (farm) to markets where consumers buy from them. Agricultural produce distribution is not complete until it gets to the door step of the final consumers.
CHANNEL OF DISTRIBUTION IN AGRICULTURE
The channels for the distribution of Agricultural produce are as follows:
Producers .... Assemblers .... Wholesalers .... Retailers .... Consumers

Producers:
These are the farmers that are responsible for the direct production of crops and livestock. The producers are also responsible for the marketing of their produces so as to get full benefit of their farm activities.

Assemblers:
These are individuals who go from one farm to another in other to gather large quantities of agricultural produce to the market. The assemblers may sort produce according to their grades and provide temporary storage facilities, they assist the producers by providing loans facilities to farmers and put agricultural products on a state that is ideal for marketing.

Wholesalers:
These are people who buy agricultural produces in large quantities from the producers and sell them to the retailers. They have large stores for keeping their stocks called, ware house.
Retailers:
The retailers buy agricultural produce directly from farmers or wholesalers and sell in small quantities to consumers. They have storage facilities where they protect their produce until they are sold.

Consumers:
Consumers are refers to as end user of Agricultural produce. Many consumers buy their agricultural produce at the farm gate in order to buy at cheaper rate. Consumers can also buy from retailers and industries that use agricultural products as raw materials in the manufacture of goods e.g. palm fruits to soap, kola nut to medicine etc.

Local market:
Local markets are places within a country particularly a local Government area where agricultural produce are sold. Every town or village has local market. Farmers take their produce to these markets on particular days. Some operate daily while others may be three days, five days or weekly. Examples are Ogba market in Edo state and other well established city markets such as Oba market and Agbado Market in Edo state, Oyingbo Market in Lagos state, central market in Katsina State, Kofar wambe market in Kano State etc.

Sales of commodities in a local market.
International Market:
International markets are places where agricultural produce obtained from the farm are sold overseas. International Market set minimum standard that agricultural product to be sold must meet. These international marketing may take place electronically on the internet where individuals or organization engage in or make transaction through internet or physical location e.g. international Trade fair, Dawanau International grain market in Kano.
The produce of our farmers sold to buyer is called Agricultural Export. These include Cocoa, Coffee, Palm oil, Kola, Groundnut, Tea, and Grains etc.

Evaluation
Objective Test:
1 An agent who purchases goods directly from middlemen and sells them in small quantities to consumers is called…..A. buyer B. sellers C. wholesaler D. retailers.
2. Who among the following is a middleman?
A. Consumer, B. Farmer C Manufacturer D. Retailer.
3. The producers are ……A farmers B people C. manufacturer D. wholesaler.
4. The place where producers and consumers meet is …………
A. bank B. farm C. market D. home.
5. The market where farm produce are sold within the country is called……….
A. international market B. Local market C farm gate market D. super market.
LESSON 12
ACTIVITIES AT THE CHANNELS OF DISTRIBUTION OF AGRICULTURAL PRODUCE
Activities at the channels of distribution of Agricultural produce include the following:
1 Assembling:
Assembling is the gathering of agricultural products from several individual farmers so that the products are available in large amounts to buyers.

[b]2 sorting and grading:[/b]
After harvesting agricultural products they are usually stored into various categories using specifications or standard. Some factors considered during grading include evenness of their sizes shapes and qualities. These produce are graded into grade I and II, grade I earn higher money than grade II. These function of grading can be done by farmers.

3 packaging:
This is the practice of putting agricultural produce in small practice or bundles, packing prevent wastage, pests’ infection and contamination e.g. packaging of cocoa, kola nut, cotton, tobacco etc.

4 bulking:
This is the practice of collecting agricultural produce from small scale farmers at their farm gate for delivery to the co-operative societies or consumers. The purpose of this is to ensure products quantity and stable price.

5 bulk- breaking:
This involves intermediaries buying in bulk and later splitting them into various sizes, weights, colors and cost in a manner that will interest the final consumers. For example wholesalers may buy in tones, rolls, cartons, packets, bales or bags for later sales to retailers in kilograms, dozens and sachets.

6 loading:
This is the process of carrying agricultural produce in large quantities or amount by vehicles. These vehicles (Lorries) distribute these products to specific companies, market or middle men.

7 offloading:
This is the removal of agricultural produce from vehicles e.g. lorry, train and ship when they get to the point of arrival for distribution e.g. market.

8 stocking:
This refers to how agriculture produce that have been bagged and piled or arranged in the store. It is advisable that the first piles of bags of agricultural produce is first arranged on wooden plate from called stead of direct arrangement on the dare floor of the store.
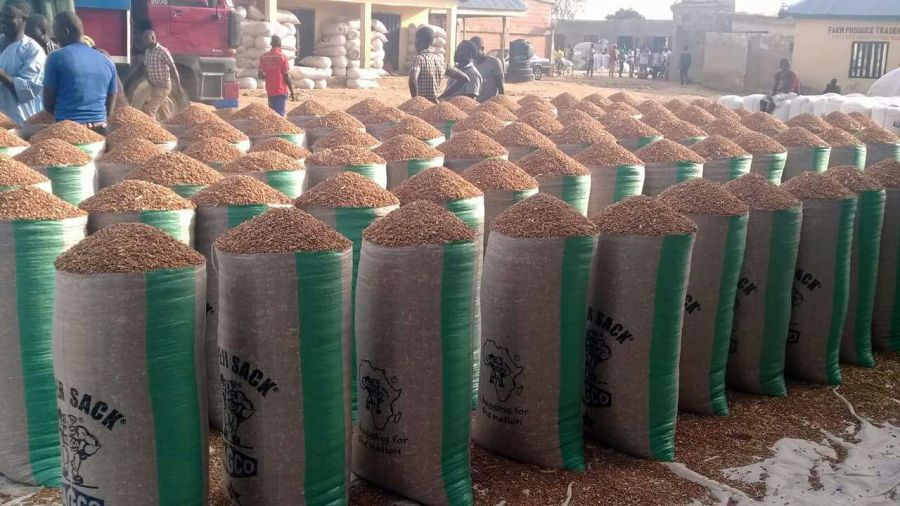

9 Transportation: This is the system of moving agricultural produce from the farm to the market place using road and any other means.

10 Advertisements:
This practice is connected with the display or exhibition of the farm product to the buyer for awareness .this can be done verbally, through newspaper, radio etc.

11 Pricing (marketing):
This is the buying and selling of farm produce through the registration of price that are paid by buyer and collected by sellers.
CHALLENGES IN AGRICULTURAL MARKETING
Marketing of agricultural products from the farm gate to the consumer is as important as production. If these products fail to get to the consumer, all effort, money and time invested would have been wasted.
The main challenges in agricultural marketing are as follows:
1. Lack of transport facilities:
2 .Lack of storage facilities: Lack or inadequate storage facilities such as silo rhombus, cribs, barns, and rafter cause loss and wastage.
3. Instability of price in the market.
4. Bulkiness of agricultural produce
5. Inadequate packaging and processing facilities.
7. Keeping qualities
8. Transportation
9. Lack of standard weight and measure
10. Inadequate access to loan.

Evaluation:
1. List five challenges in agricultural stock exchange.
2Discuss the activities that take place at the channel of distribution of farm produce.
Objectives:
1……is the putting of goods into closed or open containers of convenient sizes, shapes and types for the purpose of sale, storage or transport.
2Consumers of farm produce are….A. people generally B. agro-allied industries
C. beverages D. all of the above.
3Which of these is not challenge in agricultural marketing?
A. Keeping qualities B. Transportation
C. Lack of standard weight and measure D. presence of standard weight.
4. The movement of agricultural produce from farm to market is called………
A sorting B marketing C. planting D transportation.
5Which of these is not one of the activities of channel of distribution.
A. Offloading B. packaging. C. stocking d. planting.
References:
1 Spectrum Agricultural Science 3 by B .A. Adelekan et al
2 VIU Agricultural Science 3
3 JS Agriculture for Nigerian Schools book 3 by Anthony Youdeowei et al
TOPIC: CHANNELS FOR DISTRIBUTION OF AGRICULTURAL PRODUCE
Contents: 1. Channels of distribution in Agriculture
2. Activities taking place at the channels of distribution,
3. Challenges in agricultural marketing.
CHANNELS OF DISTRIBUTION IN AGRICULTURE
Introduction: Channels of distribution refers to the various ways through which agricultural produce are carried form the producers (farmers) to the final consumers.
The place where producers and consumers meet to sell and buy their materials is known as a market. Since producers (farmers) and consumers do not live in the same place, it is therefore important for farmers to carry their produce from the place of production (farm) to markets where consumers buy from them. Agricultural produce distribution is not complete until it gets to the door step of the final consumers.
CHANNEL OF DISTRIBUTION IN AGRICULTURE
The channels for the distribution of Agricultural produce are as follows:
Producers .... Assemblers .... Wholesalers .... Retailers .... Consumers

Producers:
These are the farmers that are responsible for the direct production of crops and livestock. The producers are also responsible for the marketing of their produces so as to get full benefit of their farm activities.

Assemblers:
These are individuals who go from one farm to another in other to gather large quantities of agricultural produce to the market. The assemblers may sort produce according to their grades and provide temporary storage facilities, they assist the producers by providing loans facilities to farmers and put agricultural products on a state that is ideal for marketing.

Wholesalers:
These are people who buy agricultural produces in large quantities from the producers and sell them to the retailers. They have large stores for keeping their stocks called, ware house.
Retailers:
The retailers buy agricultural produce directly from farmers or wholesalers and sell in small quantities to consumers. They have storage facilities where they protect their produce until they are sold.

Consumers:
Consumers are refers to as end user of Agricultural produce. Many consumers buy their agricultural produce at the farm gate in order to buy at cheaper rate. Consumers can also buy from retailers and industries that use agricultural products as raw materials in the manufacture of goods e.g. palm fruits to soap, kola nut to medicine etc.

Local market:
Local markets are places within a country particularly a local Government area where agricultural produce are sold. Every town or village has local market. Farmers take their produce to these markets on particular days. Some operate daily while others may be three days, five days or weekly. Examples are Ogba market in Edo state and other well established city markets such as Oba market and Agbado Market in Edo state, Oyingbo Market in Lagos state, central market in Katsina State, Kofar wambe market in Kano State etc.

Sales of commodities in a local market.
International Market:
International markets are places where agricultural produce obtained from the farm are sold overseas. International Market set minimum standard that agricultural product to be sold must meet. These international marketing may take place electronically on the internet where individuals or organization engage in or make transaction through internet or physical location e.g. international Trade fair, Dawanau International grain market in Kano.
The produce of our farmers sold to buyer is called Agricultural Export. These include Cocoa, Coffee, Palm oil, Kola, Groundnut, Tea, and Grains etc.

Evaluation
Objective Test:
1 An agent who purchases goods directly from middlemen and sells them in small quantities to consumers is called…..A. buyer B. sellers C. wholesaler D. retailers.
2. Who among the following is a middleman?
A. Consumer, B. Farmer C Manufacturer D. Retailer.
3. The producers are ……A farmers B people C. manufacturer D. wholesaler.
4. The place where producers and consumers meet is …………
A. bank B. farm C. market D. home.
5. The market where farm produce are sold within the country is called……….
A. international market B. Local market C farm gate market D. super market.
LESSON 12
ACTIVITIES AT THE CHANNELS OF DISTRIBUTION OF AGRICULTURAL PRODUCE
Activities at the channels of distribution of Agricultural produce include the following:

1 Assembling:
Assembling is the gathering of agricultural products from several individual farmers so that the products are available in large amounts to buyers.

[b]2 sorting and grading:[/b]
After harvesting agricultural products they are usually stored into various categories using specifications or standard. Some factors considered during grading include evenness of their sizes shapes and qualities. These produce are graded into grade I and II, grade I earn higher money than grade II. These function of grading can be done by farmers.

3 packaging:
This is the practice of putting agricultural produce in small practice or bundles, packing prevent wastage, pests’ infection and contamination e.g. packaging of cocoa, kola nut, cotton, tobacco etc.

4 bulking:
This is the practice of collecting agricultural produce from small scale farmers at their farm gate for delivery to the co-operative societies or consumers. The purpose of this is to ensure products quantity and stable price.

5 bulk- breaking:
This involves intermediaries buying in bulk and later splitting them into various sizes, weights, colors and cost in a manner that will interest the final consumers. For example wholesalers may buy in tones, rolls, cartons, packets, bales or bags for later sales to retailers in kilograms, dozens and sachets.

6 loading:
This is the process of carrying agricultural produce in large quantities or amount by vehicles. These vehicles (Lorries) distribute these products to specific companies, market or middle men.

7 offloading:
This is the removal of agricultural produce from vehicles e.g. lorry, train and ship when they get to the point of arrival for distribution e.g. market.

8 stocking:
This refers to how agriculture produce that have been bagged and piled or arranged in the store. It is advisable that the first piles of bags of agricultural produce is first arranged on wooden plate from called stead of direct arrangement on the dare floor of the store.

9 Transportation: This is the system of moving agricultural produce from the farm to the market place using road and any other means.

10 Advertisements:
This practice is connected with the display or exhibition of the farm product to the buyer for awareness .this can be done verbally, through newspaper, radio etc.

11 Pricing (marketing):
This is the buying and selling of farm produce through the registration of price that are paid by buyer and collected by sellers.

CHALLENGES IN AGRICULTURAL MARKETING
Marketing of agricultural products from the farm gate to the consumer is as important as production. If these products fail to get to the consumer, all effort, money and time invested would have been wasted.
The main challenges in agricultural marketing are as follows:
1. Lack of transport facilities:
2 .Lack of storage facilities: Lack or inadequate storage facilities such as silo rhombus, cribs, barns, and rafter cause loss and wastage.
3. Instability of price in the market.
4. Bulkiness of agricultural produce
5. Inadequate packaging and processing facilities.
7. Keeping qualities
8. Transportation
9. Lack of standard weight and measure
10. Inadequate access to loan.

Evaluation:
1. List five challenges in agricultural stock exchange.
2Discuss the activities that take place at the channel of distribution of farm produce.
Objectives:
1……is the putting of goods into closed or open containers of convenient sizes, shapes and types for the purpose of sale, storage or transport.
2Consumers of farm produce are….A. people generally B. agro-allied industries
C. beverages D. all of the above.
3Which of these is not challenge in agricultural marketing?
A. Keeping qualities B. Transportation
C. Lack of standard weight and measure D. presence of standard weight.
4. The movement of agricultural produce from farm to market is called………
A sorting B marketing C. planting D transportation.
5Which of these is not one of the activities of channel of distribution.
A. Offloading B. packaging. C. stocking d. planting.
References:
1 Spectrum Agricultural Science 3 by B .A. Adelekan et al
2 VIU Agricultural Science 3
3 JS Agriculture for Nigerian Schools book 3 by Anthony Youdeowei et al
WEEK 8
LESSON 13
TOPIC: AGRICULTURE IN STOCK EXCHANGE
Content: I. Meaning of stock exchange,
ii .People involve in stock exchange,
iii. Importance of stock exchange.
MEANING OF STOCK EXCHANGE
INTRODUCTION:
The activities of stock exchange are about selling part or all of an enterprise or corporation to numerous part-owners so as to generate money to finance that enterprise. The money which is called Capital is generated by a corporation or organization through the sales and distribution of parts or all to several part-owners is called Stock. One unit of stock is called Shares, while the combination of those who bought shares i.e. those who contributed money towards the setting up of the business is called Shareholders.
The shareholders are given Share Certificate as a clear evidence of the amount of money contributed and that makes them a part-owners.
Share Certificate:
The document clearly shows the number of shares each holder contributed to the business and other relevant information.
MEANING OF STOCK EXCHANGE:
What is stock exchange?
A stock exchange is an organization that provides a place where investors may buy and sell shares of a wide range of companies.
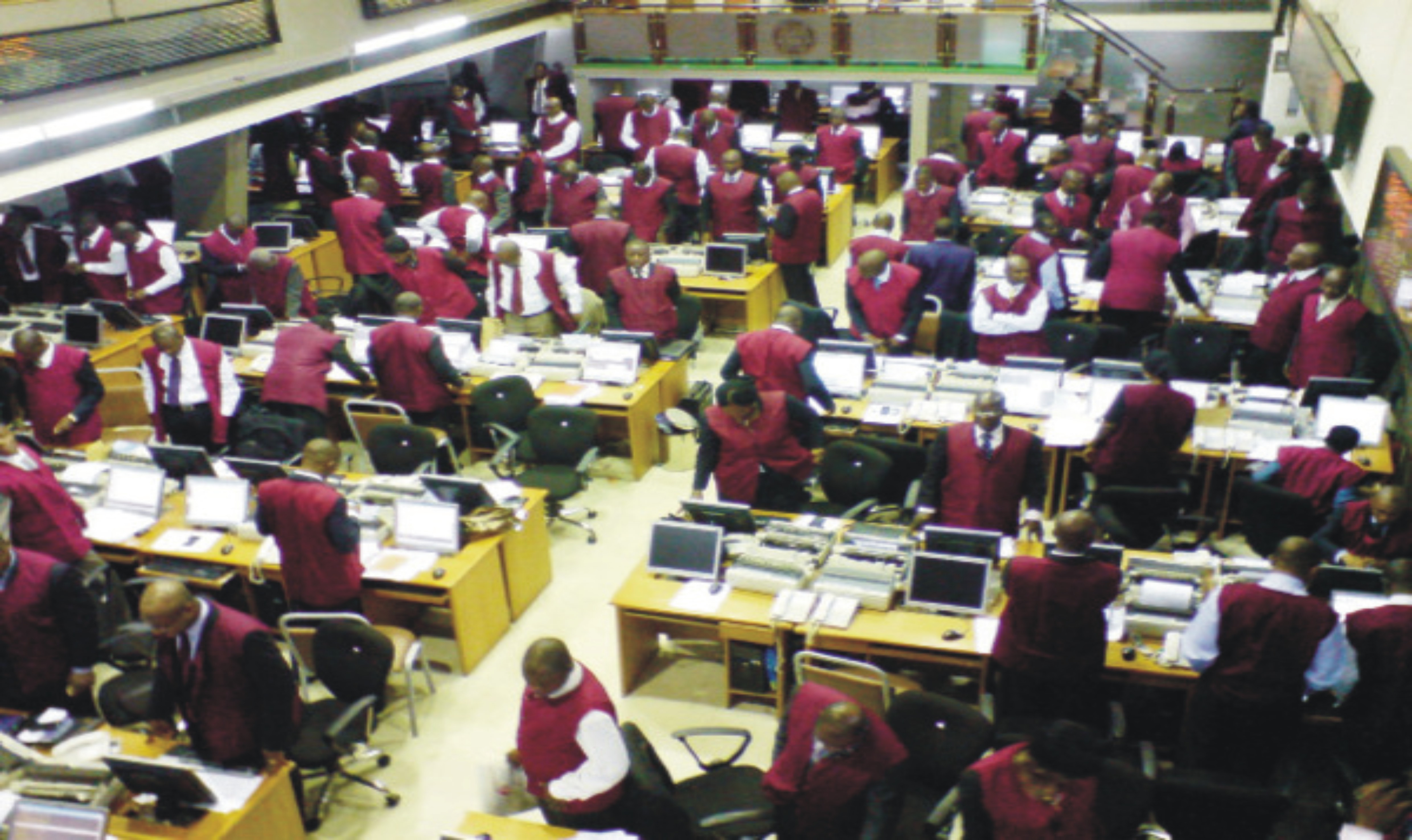

Stock exchange market in Nigeria.
In Nigeria this transactions are regulated by the Nigeria stock exchange (N.S.E). Buying and selling of stock exchange may be by physical exchange or electronic through the use of computer net working i.e. visual exchange which is commonly known as forex trading.
Stock exchange transactions are conducted by Stock Brokers, jobbers and staff. Stock brokers represents potential buyers binding specific price for stocks while other stock brokers represents potential sellers who offer specific price, when there is agreement between the binding and the offering price , the transaction takes place.
The Nigeria stock exchange is a good example of visual exchange; participants in any stock exchange include the buyers, seller and their representatives. Potential buyers who legally own one or more share or stock of a joint stock company are referred to as shareholders; they are entitled to participate in:
1. Vote during the election of the Board of Directors.
2. Share in the distribution of the company’s income
3. Purchase new shares of the company; and
4. Purchase the company’s assets when it becomes financially unviable.
Stock brokers are licensed to buy and sell company’s shares and they also have adequate information on the current values and quantities of various company shares available at any given time.
Examples of Agro-allied (Agribusiness) enterprises whose shares are traded in Nigeria stock exchange include:
1. Livestock Feed Plc.
2. Nigeria Breweries Plc.
3 Nestle Nigeria Plc.
4. Unilever Nigeria plc.
5. Flour Mills of Nigeria Plc etc.
6. Dunlop Nigeria Plc.
7 Nigeria Bottling Co. Plc
8. Cadbury Nigeria Plc.
LESSON 14
PEOPLE INVOLVED IN STOCK EXCHANGE
The people involved in stock exchange are as follow:
1 Buyers: these are potential investors who wish to buy shares of company and become shareholder.
2 Sellers: these are shareholders who decide to sell their shares to potential buyers or investors and they are also called spectators in that; they buy shares when the price is low and sell when the price increases.
3 Buyers and sellers: these are those that engage in the business of transaction on shares and the activities that are carried out in the place that is referred to as the stock market.
4 Representatives: These are stockbrokers, jobbers and staff. These individuals represent potential buyers binding for specific share of various companies.

Evaluation
1Define the following: stock exchange, shares, stock.
2 Discuss the functions of stock brokers
Objectives:
1. The money generated by the organization is called………
A. capital B. profit C. company money D. salary.
2. One unit of stock is called………A. property B. capital C shares D profit.
3. The combination of those who bought share is called….
A. stock B. company personnel C. shareholders D. farmers.
4. When the company could not continue, the company sell the properties to..
A. farmers B market women C shareholder D stock.
5. One of people is not part of stock exchange
Seller B buyer C student D representatives
IMPORTANCE OF STOCK EXCHANGE IN AGRICULTURE
1. It encourages investors in agriculture.
2. Redistribution of wealth.
3. It creates investment opportunities for small investors.
4. It creates employment for the youths.
5. It provides a wide range market for agricultural produce.
6. It boosts individuals, organizations and national economic status.
7. It attracts investment from bank of industry (BOI) through the use of provision of assistance from:
(I ) National Economic Reconstruction Fund(NERFUND)
(ii) Community bank i.e Agricultural Cooperative development bank,
(iii) Nigeria Export and import Banks (NEXIM).
8. It is an indicator of the state of the national economy.
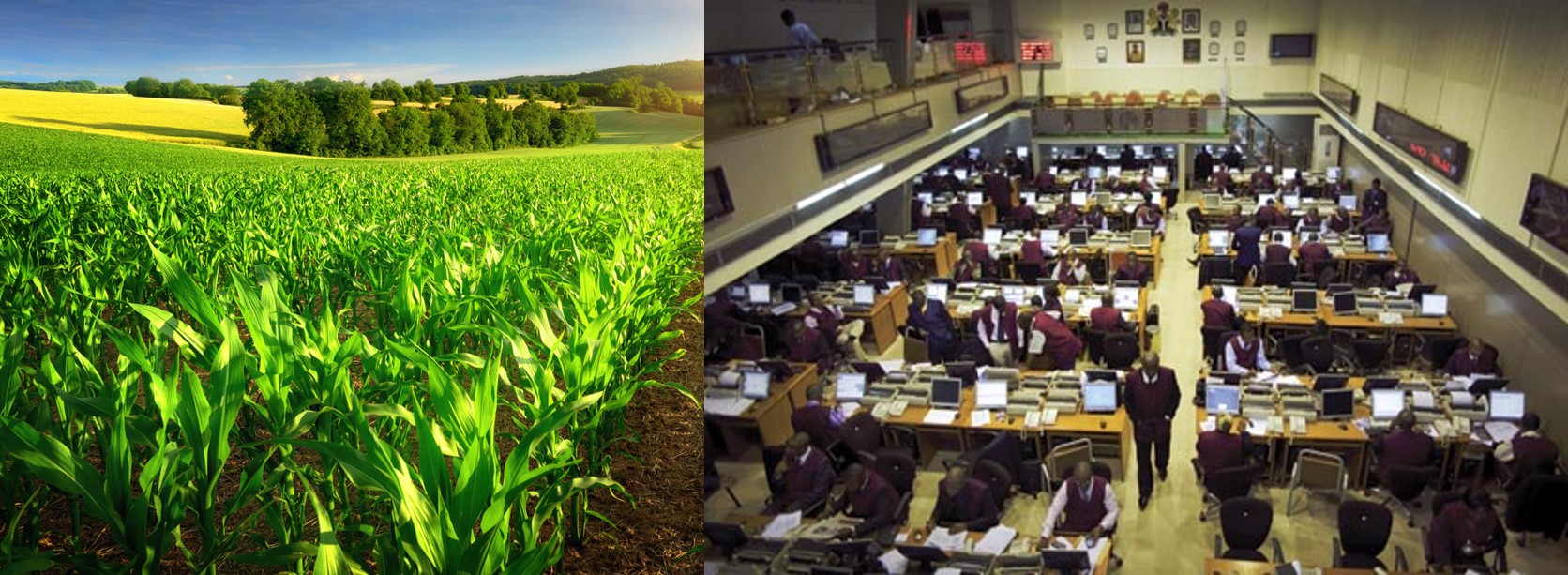

Evaluation:
Objective Test:
1. The sale representative in the stock exchange is called …………
A. Share B. Shareholder C. stockbroker D.
2. Which of these is not an important of stock exchange?
A. It encourages investors in agriculture.
B Redistribution of wealth.
C It creates investment opportunities for small investors.
D none of the above.
3. The organization that provides investment opportunity in agriculture is…
A. education. B training C. stock exchange. D. farming.
4. The document that indicates the number of share an individual has is called…….
A. share certificate B. school certificate C. stock certificate D stock certificate.
5…………is the head of Stock Exchange Company. A. principal B. president C. the share holder
D the Board of Director.
Essay Test:
1. Explain five ways in which stock exchange is important to agriculture.
2. List the people that are involved in stock exchange
References:
1 Spectrum Agricultural Science 3 by B .A. Adelekan et al
2 VIU Agricultural Science 3
3 JS Agriculture for Nigerian Schools book 3 by Anthony Youdeowei et al
TOPIC: AGRICULTURE IN STOCK EXCHANGE
Content: I. Meaning of stock exchange,
ii .People involve in stock exchange,
iii. Importance of stock exchange.
MEANING OF STOCK EXCHANGE
INTRODUCTION:
The activities of stock exchange are about selling part or all of an enterprise or corporation to numerous part-owners so as to generate money to finance that enterprise. The money which is called Capital is generated by a corporation or organization through the sales and distribution of parts or all to several part-owners is called Stock. One unit of stock is called Shares, while the combination of those who bought shares i.e. those who contributed money towards the setting up of the business is called Shareholders.
The shareholders are given Share Certificate as a clear evidence of the amount of money contributed and that makes them a part-owners.
Share Certificate:
The document clearly shows the number of shares each holder contributed to the business and other relevant information.
MEANING OF STOCK EXCHANGE:
What is stock exchange?
A stock exchange is an organization that provides a place where investors may buy and sell shares of a wide range of companies.

Stock exchange market in Nigeria.
In Nigeria this transactions are regulated by the Nigeria stock exchange (N.S.E). Buying and selling of stock exchange may be by physical exchange or electronic through the use of computer net working i.e. visual exchange which is commonly known as forex trading.
Stock exchange transactions are conducted by Stock Brokers, jobbers and staff. Stock brokers represents potential buyers binding specific price for stocks while other stock brokers represents potential sellers who offer specific price, when there is agreement between the binding and the offering price , the transaction takes place.
The Nigeria stock exchange is a good example of visual exchange; participants in any stock exchange include the buyers, seller and their representatives. Potential buyers who legally own one or more share or stock of a joint stock company are referred to as shareholders; they are entitled to participate in:
1. Vote during the election of the Board of Directors.
2. Share in the distribution of the company’s income
3. Purchase new shares of the company; and
4. Purchase the company’s assets when it becomes financially unviable.
Stock brokers are licensed to buy and sell company’s shares and they also have adequate information on the current values and quantities of various company shares available at any given time.
Examples of Agro-allied (Agribusiness) enterprises whose shares are traded in Nigeria stock exchange include:
1. Livestock Feed Plc.
2. Nigeria Breweries Plc.
3 Nestle Nigeria Plc.
4. Unilever Nigeria plc.
5. Flour Mills of Nigeria Plc etc.
6. Dunlop Nigeria Plc.
7 Nigeria Bottling Co. Plc
8. Cadbury Nigeria Plc.
LESSON 14
PEOPLE INVOLVED IN STOCK EXCHANGE
The people involved in stock exchange are as follow:
1 Buyers: these are potential investors who wish to buy shares of company and become shareholder.
2 Sellers: these are shareholders who decide to sell their shares to potential buyers or investors and they are also called spectators in that; they buy shares when the price is low and sell when the price increases.
3 Buyers and sellers: these are those that engage in the business of transaction on shares and the activities that are carried out in the place that is referred to as the stock market.
4 Representatives: These are stockbrokers, jobbers and staff. These individuals represent potential buyers binding for specific share of various companies.

Evaluation
1Define the following: stock exchange, shares, stock.
2 Discuss the functions of stock brokers
Objectives:
1. The money generated by the organization is called………
A. capital B. profit C. company money D. salary.
2. One unit of stock is called………A. property B. capital C shares D profit.
3. The combination of those who bought share is called….
A. stock B. company personnel C. shareholders D. farmers.
4. When the company could not continue, the company sell the properties to..
A. farmers B market women C shareholder D stock.
5. One of people is not part of stock exchange
Seller B buyer C student D representatives
IMPORTANCE OF STOCK EXCHANGE IN AGRICULTURE
1. It encourages investors in agriculture.
2. Redistribution of wealth.
3. It creates investment opportunities for small investors.
4. It creates employment for the youths.
5. It provides a wide range market for agricultural produce.
6. It boosts individuals, organizations and national economic status.
7. It attracts investment from bank of industry (BOI) through the use of provision of assistance from:
(I ) National Economic Reconstruction Fund(NERFUND)
(ii) Community bank i.e Agricultural Cooperative development bank,
(iii) Nigeria Export and import Banks (NEXIM).
8. It is an indicator of the state of the national economy.

Evaluation:
Objective Test:
1. The sale representative in the stock exchange is called …………
A. Share B. Shareholder C. stockbroker D.
2. Which of these is not an important of stock exchange?
A. It encourages investors in agriculture.
B Redistribution of wealth.
C It creates investment opportunities for small investors.
D none of the above.
3. The organization that provides investment opportunity in agriculture is…
A. education. B training C. stock exchange. D. farming.
4. The document that indicates the number of share an individual has is called…….
A. share certificate B. school certificate C. stock certificate D stock certificate.
5…………is the head of Stock Exchange Company. A. principal B. president C. the share holder
D the Board of Director.
Essay Test:
1. Explain five ways in which stock exchange is important to agriculture.
2. List the people that are involved in stock exchange
References:
1 Spectrum Agricultural Science 3 by B .A. Adelekan et al
2 VIU Agricultural Science 3
3 JS Agriculture for Nigerian Schools book 3 by Anthony Youdeowei et al