SCHEME OF WORK
WEEK TOPIC
1. Revision of last year work.
2. Classification of Computers (i) Generation (First, Second, Third, Fourth, Fifth), (ii) Types of Computers (Analog, Digital Hybrid).
3. Classification of Computers: (iii) Sizes of computers micro-computers, mainframe, supercomputer (iv) Degree of versatility general purpose, special purpose.
4&5. The Computer System: (a) The concept of computer system (b) Component of computer system (i) Hardware component system, software, applications software (iii) People ware
Component: Computer professionals. Computer users.
6. Computer Software: (a) Definition of computer software (b) Types and examples of software (i) System software (operating system), (ii) Application Software (word processing spreadsheet, graphics, etc).
7. Operating System: (a) Definition of operating system (OS), (b) Examples of operating system (i) DOS (ii) Windows.
8. Number Bases: (i) Definition (ii) Binary
(iii) Octal (iv) Hexadecimal (Conversion from decimal to binary and hexadecimal and Vice-versa)
9. Units of Storage in Computer: Units of storage: Byte, Nibble, Byte, kilobyte, gigabyte, Word, etc.
10. Revision
1ST TERM
WEEK 1
LESSON 1
TOPIC: CLASSIFICATION OF COMPUTERS: Generations of computers, Types of computers
CONTENT
- Generations of computers
- Types of computers
OBJECTIVES
At the end of the lesson students should be able to:
- Classify computers by generation
- Classify computers by type
CONTENT
INTRODUCTION
The development of electronic computer is divided into stage referred to as generation. Each generation of computer is associated with a specific innovation and development in computer technology over the previous stage.
It is important to note that computer development came in different types and capacity. Generations of electronic computer are grouped into five innovations in technological development and advancement as at the date. The stages are 1st, 2nd, 3rd 4th and 5th generations. The generations of computers are not static, more stages are imminent as their search for knowledge and development in the area information and communication Technology (ICT).
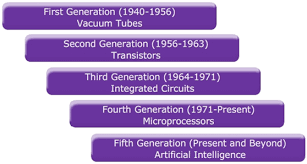
GENERATIONS OF COMPUTERS
CLASSIFICATION OF COMPUTER BY GENERATIONS
1ST GENERATION COMPUTERS
These include sets of computer built between 1945-1959. The employed electronic vales (vacuum tubes) for their circuits. Examples include Leo Mark III, Atlas Series. Universal Automatics computer (UNIVAC), Electronic Discrete Variable Automatic computer (EDVAC), Electronic Delay Storage Automatic computer (EDSAC).
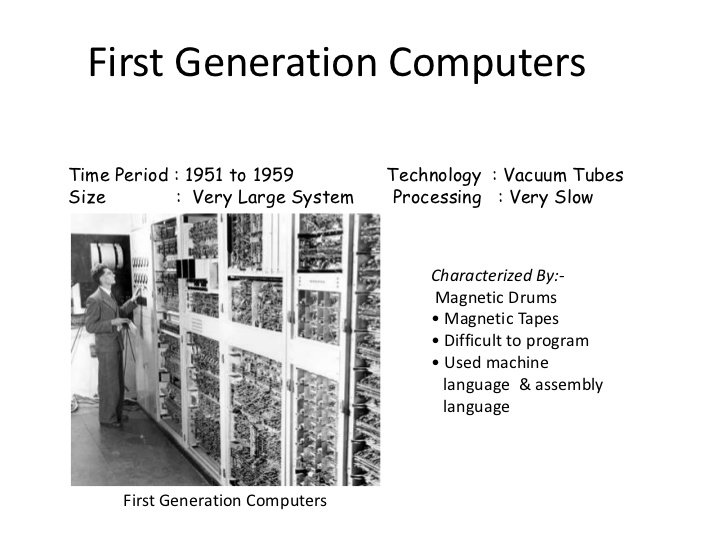
FEATURES
It uses punch card
It has valve-based machine and uses vacuum tube for storing and processing of data.
It has limited internal storage
It consumes too much electronic power and thereby generates too much heat.
2ND GENERATION COMPUTERS
This computer generation existed between (1960 - 1965). They used transistor in place of valve. They were smaller in size and faster in operation compared with the 1st generation. Besides, they were more reliable and then use English as computer language. High level language like BASIC, FORTRAN, COBOL etc. Examples are IBM 7000, series 7030, 7090, UNIVAC 1102, LEO MARK SERIES
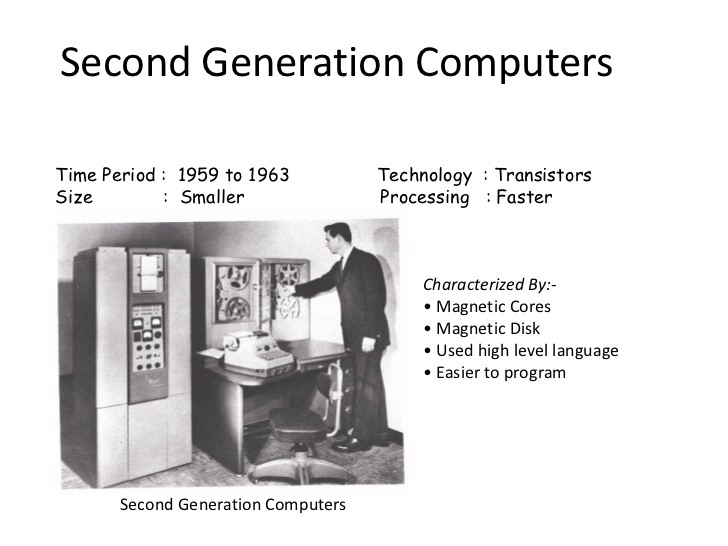
FEATURES
- It uses transistors instead of valves therefore more reliable.
- It is faster in operation more than the first generation computers
- It uses magnetic tape as storage medium
- It is smaller in size compared to first generation computer
- It accepts external storage device like magnetic tape or disk.
3RD GENERATIONS COMPUTERS
The third generation computers mark the beginning of keyboards for input and video display unit (monitor) for output. It between 1966-1975. some of the computers, its major component was integrated circuits (IC) instead of transistor used during second generation.
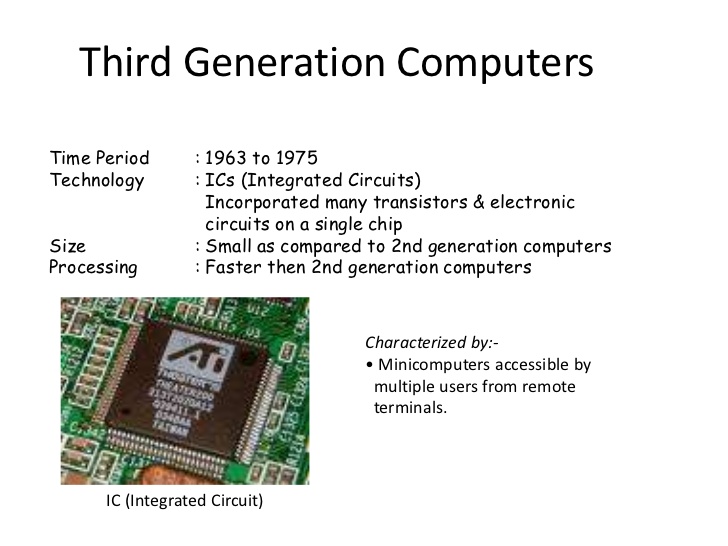
They came in three (3) different sizes ie mainframe, mini, micro computers.
Some of its features includes:
- use of circuits instead of transistors used in second generation
- it is more reliable than the second generation computers
- It has extensive processing storage
- It came in three different sizes – Mainframe, Mini, and Micro computers.
4TH GENERATION COMPUTERS
This generation of electronic computer came into existence (1975-1990). They made use Larger Scale integrated Circuit (LSIC). This marked the ear of micro processor with input and output devices connected to the system unit. The arrival of this generation of computer gave rise to more powerful and less expensive but realistic computers development. Examples IBM 3030 and 7700.
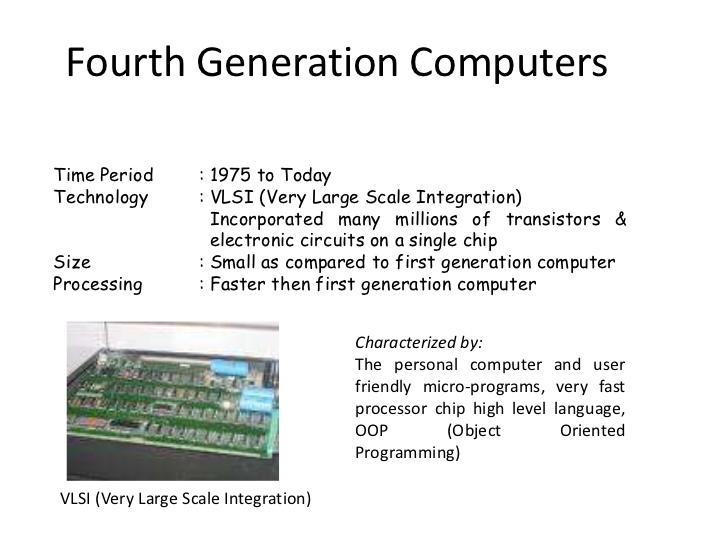
FEATURES
It uses very large scale integrated circuit.
It has high speed and higher storage capacity
It is faster in operation and cheaper than the earlier ones
It has extensive processing storage
5TH GENERATION
The present day computers are classified into this category. The fifth generation of computers are capable of performing functions of human experts solving problems that require human intelligent, judgment, insight and experience.
Fight generation computers can learn, take decisions and perform other activities exclusive of human beings. It marks the era of Pentium i.e. Pentium 1 Pentium 2, 3, 4, and M which combine artificial intelligence with expert system.
Artificial intelligence is the ability of the computer to behave like an intelligent human being while expert system is the capability of computer to the judgement and decisions like an expert in a specialized field i.e. Diagnosis and prescription of drugs like a medical doctor.
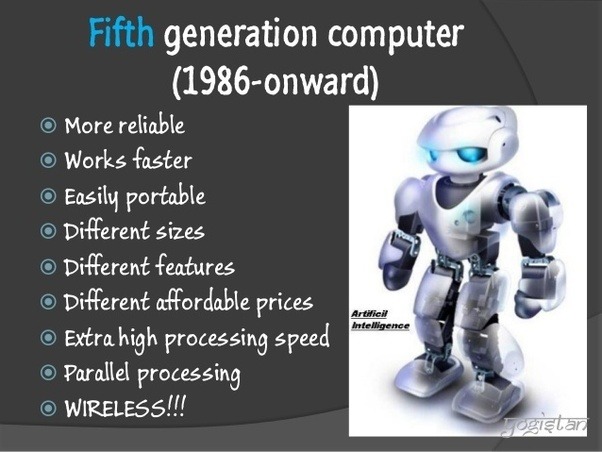
FEATURES
It uses very large scale integrated circuits (VLSIC)
It appears to be reasoning in some type of work.
It helps in planning financial management
EVALUATION:
1. Mention at least 3 generations of computers and their features.
2. Distinguish between the first generations of computers and the
Second generations of computers.
LESSON 2
CLASSIFICATION OF COMPUTER BY TYPES
When computers are classified according to type, three different groups or classes of computers are recognized. They are the digital analogue and hybrid computer.
DIGITAL COMPUTER
This is most common type of computer today. It is used in processing discrete data that have to do with counting. Digit is a number therefore, digital computers measure physical quantities by counting. Most applications of computer have to do with data processing. As such, the digital computer is so much in use. Many modern devices are now using digital system. Examples of such devices are: calculator, digital wrist watches, digital fuel dispenser etc.

ANALOGUE COMPUTERS
Analogue computer processes continuous data such as speed, temperature, heartbeat etc. They are mostly used in scientific measurement which may require the processing of continuous data. These are the type of specialized computers you are likely to see in the hospitals connected to patients.

HYBRID COMPUTER
This type of computer combines the features of digital and analogue computers together. It can count and as well as measure.

EVALUATION:
1. State three type of computers with examples.
2. Explain briefly the most common type of computer.
READING ASSIGNMENT:
Read ‘handbook on computer studies(practical guide)for schools and colleges ‘Book 2,pages 4-7,By Niyi Adekolegan.
ASSIGNMENT:
1.The following are features of first generation computers except...........
(a)It uses punch card (b)It has limited internal storage (c)It consumes too much electricity (d)It does not generate much heat.
2. The following are examples of fifth generation computers except_____
(a)Pentium I (b) Pentium 2(c) Pentium M (d)Pentium None
3. All of the following are sizes of microcomputers except____
(a)Desktop (b) Laptop (c) Notebook (d) UNIVAC
4. Third generations of computers uses ____ technology in its build-up.
(a)VLSIC (b) IC (c) Vacuum tube (d) Transistor
TOPIC: CLASSIFICATION OF COMPUTERS: Generations of computers, Types of computers
CONTENT
- Generations of computers
- Types of computers
OBJECTIVES
At the end of the lesson students should be able to:
- Classify computers by generation
- Classify computers by type
CONTENT
INTRODUCTION
The development of electronic computer is divided into stage referred to as generation. Each generation of computer is associated with a specific innovation and development in computer technology over the previous stage.
It is important to note that computer development came in different types and capacity. Generations of electronic computer are grouped into five innovations in technological development and advancement as at the date. The stages are 1st, 2nd, 3rd 4th and 5th generations. The generations of computers are not static, more stages are imminent as their search for knowledge and development in the area information and communication Technology (ICT).

GENERATIONS OF COMPUTERS
CLASSIFICATION OF COMPUTER BY GENERATIONS
1ST GENERATION COMPUTERS
These include sets of computer built between 1945-1959. The employed electronic vales (vacuum tubes) for their circuits. Examples include Leo Mark III, Atlas Series. Universal Automatics computer (UNIVAC), Electronic Discrete Variable Automatic computer (EDVAC), Electronic Delay Storage Automatic computer (EDSAC).

FEATURES
It uses punch card
It has valve-based machine and uses vacuum tube for storing and processing of data.
It has limited internal storage
It consumes too much electronic power and thereby generates too much heat.
2ND GENERATION COMPUTERS
This computer generation existed between (1960 - 1965). They used transistor in place of valve. They were smaller in size and faster in operation compared with the 1st generation. Besides, they were more reliable and then use English as computer language. High level language like BASIC, FORTRAN, COBOL etc. Examples are IBM 7000, series 7030, 7090, UNIVAC 1102, LEO MARK SERIES

FEATURES
- It uses transistors instead of valves therefore more reliable.
- It is faster in operation more than the first generation computers
- It uses magnetic tape as storage medium
- It is smaller in size compared to first generation computer
- It accepts external storage device like magnetic tape or disk.
3RD GENERATIONS COMPUTERS
The third generation computers mark the beginning of keyboards for input and video display unit (monitor) for output. It between 1966-1975. some of the computers, its major component was integrated circuits (IC) instead of transistor used during second generation.

They came in three (3) different sizes ie mainframe, mini, micro computers.
Some of its features includes:
- use of circuits instead of transistors used in second generation
- it is more reliable than the second generation computers
- It has extensive processing storage
- It came in three different sizes – Mainframe, Mini, and Micro computers.
4TH GENERATION COMPUTERS
This generation of electronic computer came into existence (1975-1990). They made use Larger Scale integrated Circuit (LSIC). This marked the ear of micro processor with input and output devices connected to the system unit. The arrival of this generation of computer gave rise to more powerful and less expensive but realistic computers development. Examples IBM 3030 and 7700.

FEATURES
It uses very large scale integrated circuit.
It has high speed and higher storage capacity
It is faster in operation and cheaper than the earlier ones
It has extensive processing storage
5TH GENERATION
The present day computers are classified into this category. The fifth generation of computers are capable of performing functions of human experts solving problems that require human intelligent, judgment, insight and experience.
Fight generation computers can learn, take decisions and perform other activities exclusive of human beings. It marks the era of Pentium i.e. Pentium 1 Pentium 2, 3, 4, and M which combine artificial intelligence with expert system.

Artificial intelligence is the ability of the computer to behave like an intelligent human being while expert system is the capability of computer to the judgement and decisions like an expert in a specialized field i.e. Diagnosis and prescription of drugs like a medical doctor.

FEATURES
It uses very large scale integrated circuits (VLSIC)
It appears to be reasoning in some type of work.
It helps in planning financial management
EVALUATION:
1. Mention at least 3 generations of computers and their features.
2. Distinguish between the first generations of computers and the
Second generations of computers.
LESSON 2
CLASSIFICATION OF COMPUTER BY TYPES
When computers are classified according to type, three different groups or classes of computers are recognized. They are the digital analogue and hybrid computer.
DIGITAL COMPUTER
This is most common type of computer today. It is used in processing discrete data that have to do with counting. Digit is a number therefore, digital computers measure physical quantities by counting. Most applications of computer have to do with data processing. As such, the digital computer is so much in use. Many modern devices are now using digital system. Examples of such devices are: calculator, digital wrist watches, digital fuel dispenser etc.

ANALOGUE COMPUTERS
Analogue computer processes continuous data such as speed, temperature, heartbeat etc. They are mostly used in scientific measurement which may require the processing of continuous data. These are the type of specialized computers you are likely to see in the hospitals connected to patients.

HYBRID COMPUTER
This type of computer combines the features of digital and analogue computers together. It can count and as well as measure.

EVALUATION:
1. State three type of computers with examples.
2. Explain briefly the most common type of computer.
READING ASSIGNMENT:
Read ‘handbook on computer studies(practical guide)for schools and colleges ‘Book 2,pages 4-7,By Niyi Adekolegan.
ASSIGNMENT:
1.The following are features of first generation computers except...........
(a)It uses punch card (b)It has limited internal storage (c)It consumes too much electricity (d)It does not generate much heat.
2. The following are examples of fifth generation computers except_____
(a)Pentium I (b) Pentium 2(c) Pentium M (d)Pentium None
3. All of the following are sizes of microcomputers except____
(a)Desktop (b) Laptop (c) Notebook (d) UNIVAC
4. Third generations of computers uses ____ technology in its build-up.
(a)VLSIC (b) IC (c) Vacuum tube (d) Transistor
WEEK 2
LESSON 3
TOPIC: CLASSIFICATION OF COMPUTERS: By Sizes and Degree of versatility
OBJECTIVE:
At the end of the lesson students should be able to;
- Classify computers by purpose and degree of versality
- Classify computer by size and capacity
CLASSIFICATION OF COMPUTERS BY SIZE AND CAPABILITIES
Computer classification according to the size and capacity are grouped into four (4) categories. These are: micro computers, mini computers, mainframe and super computers.
MICRO COMPUTERS
This is the smallest and most popular class of computers.
Micro computers are also called personal computers (PC) or desktop computers. They are the most widely used and the fastest growing type of computers. They are accessible, relatively cheap and interactive. It is an example of general purpose computers.

CLASSES OR SIZE OF MICRO COMPUTERS
Micro computers came in different sizes ranging from desktop, laptop, palmtop, notebook computers etc.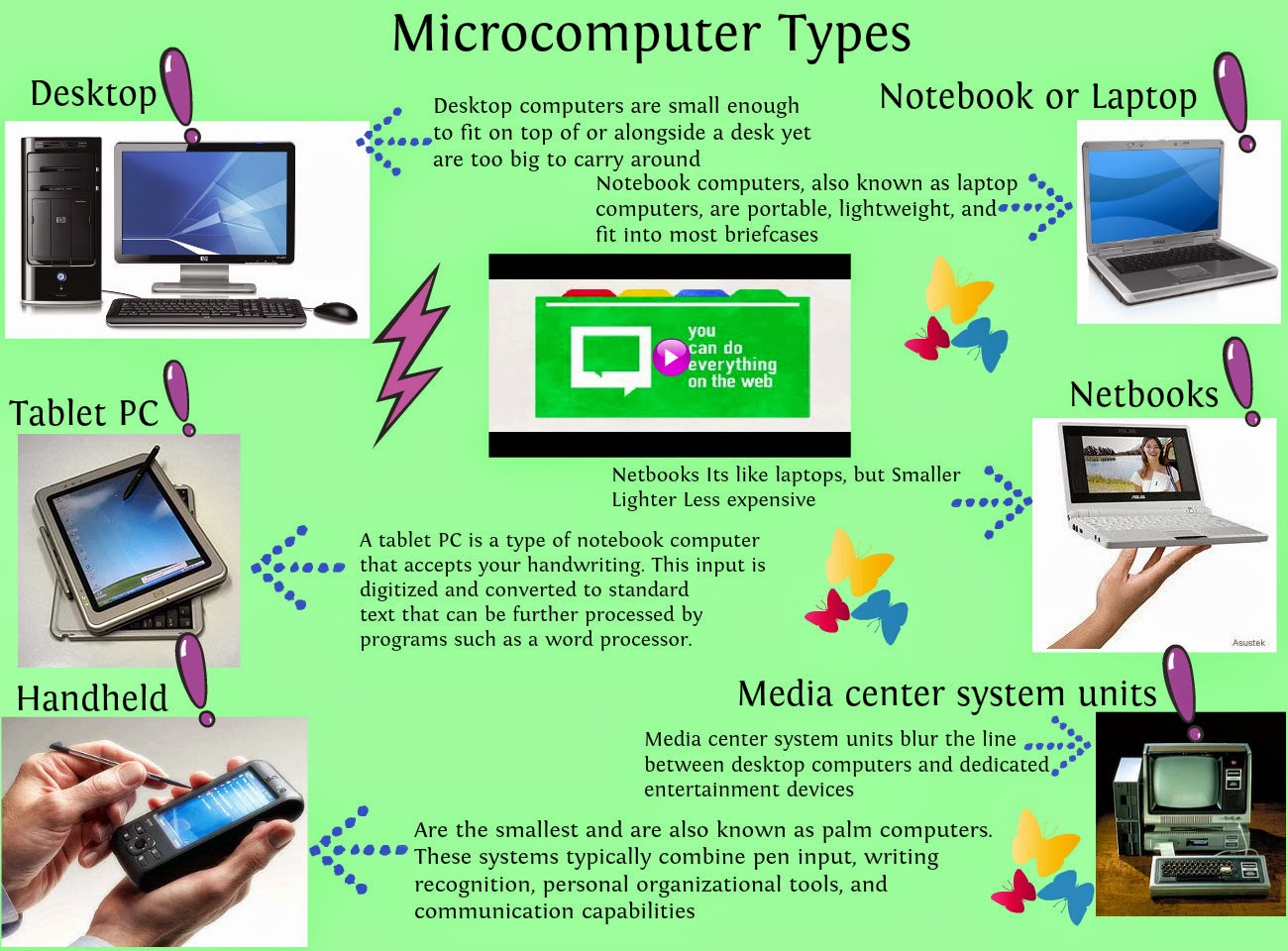
DESKTOP
This category of micro computer can be set on the top of a desk “Desktop”. It supports other peripherals and has a very high storage capacity and speed.

LAPTOP COMPUTER
This type of computer can be placed on the lap and also in a belief case. They can be either AC powered, battery powered or both. They combine the power of the PC with mobility.

NOTEBOOK COMPUTERS
These are very high PCs but have all the capacities of a PC.
Palm top: They are small enough to be held in the palm of your hand: They are equally as powerful as the Desktop.

WORK STATIONS
These are more powerful than the PCs. They are used by the engineers and scientists who process a lot of data. It is a kind of special purpose computer.

MINICOMPUTER
This is a medium size general purpose digital.
It is a multi-user i.e. it allows many users at once and has the ability to perform many tasks simultaneously. The distinguished features of mini from micro computers are: memory size, speed of operation, faster input and output devices and higher cost. They are specially designed to solve and handle wide variety of commuting problems. It has become a popular and powerful network server to help manage large internet web sites, corporate intranet and client server networks.

MAINFRAME COMPUTER
These are multi-user and multi-tasking general purpose computers.
They have large storage capacity and cost more than typical mini computers. They are used by large organizations such as banks, universities, central bank, national population commission etc.

SUPER COMPUTER
This can be seen as technological improvement on mainframe computers. It is used in the scientific environment such as for space studies and weather forecast.
They have higher processing powers and large storage capacities.

CLASSIFICATION OF COMPUTER BY PURPOSES
Classification of computer according to purpose can be grouped into two, namely:
1. General purpose computers
2. Special purposes computers
SPECIAL PURPOSE COMPUTERS
These are computers designed solely to solve a restricted class of problems e.g. computer for medical diagnosis, weapon guidance, traffic control, wealth study and forecast, control of airplanes and production control of refinery and guidance etc.
GENERAL PURPOSE COMPUTER
This class of computers is also called multi-purpose computers and are used for variety of works. They have the ability to store various programs of instructions and perform variety of operations such as graphics, database inventory and sales analysis.
Most computers are general purpose computers and they can handles different kind of work.

EVALUATION:
1. Classify computers by size and degree of versatility.
2. State and discuss five general characteristics of computers.
READING ASSIGNMENT:
Read: ‘handbook on computer studies (practical guide) for schools and colleges ‘Book 2, pages 14-16, By Niyi Adekolegan.
ASSIGNMENT:
1. Computers that are small enough to be held in hands are called_____
(a)Palmtop (b) Desktop (c) Laptop (d) Notebook.
2. Medium-sized computers are also known as _______ computers.
(a)Mini-computers (b) Micro-computers (c) Mainframe computers (d) Workstations
3. Another for micro-computers is______
(a) Compaq computers (b) Micro-computers (c) Mainframe computers (d) Apple computers
4. Mainframe computers generate large amount of heat because;
(a) They are very big (b) They consume too much electricity (c) They occupy so much room space (d) They are very small
5. Computers designed to solve special class of problems are called______
(a) General purpose computers (b) Special purpose computers
(c) Workstations (d) EDSAC Computers
TOPIC: CLASSIFICATION OF COMPUTERS: By Sizes and Degree of versatility
OBJECTIVE:
At the end of the lesson students should be able to;
- Classify computers by purpose and degree of versality
- Classify computer by size and capacity
CLASSIFICATION OF COMPUTERS BY SIZE AND CAPABILITIES
Computer classification according to the size and capacity are grouped into four (4) categories. These are: micro computers, mini computers, mainframe and super computers.
MICRO COMPUTERS
This is the smallest and most popular class of computers.
Micro computers are also called personal computers (PC) or desktop computers. They are the most widely used and the fastest growing type of computers. They are accessible, relatively cheap and interactive. It is an example of general purpose computers.

CLASSES OR SIZE OF MICRO COMPUTERS
Micro computers came in different sizes ranging from desktop, laptop, palmtop, notebook computers etc.

DESKTOP
This category of micro computer can be set on the top of a desk “Desktop”. It supports other peripherals and has a very high storage capacity and speed.

LAPTOP COMPUTER
This type of computer can be placed on the lap and also in a belief case. They can be either AC powered, battery powered or both. They combine the power of the PC with mobility.

NOTEBOOK COMPUTERS
These are very high PCs but have all the capacities of a PC.
Palm top: They are small enough to be held in the palm of your hand: They are equally as powerful as the Desktop.

WORK STATIONS
These are more powerful than the PCs. They are used by the engineers and scientists who process a lot of data. It is a kind of special purpose computer.

MINICOMPUTER
This is a medium size general purpose digital.
It is a multi-user i.e. it allows many users at once and has the ability to perform many tasks simultaneously. The distinguished features of mini from micro computers are: memory size, speed of operation, faster input and output devices and higher cost. They are specially designed to solve and handle wide variety of commuting problems. It has become a popular and powerful network server to help manage large internet web sites, corporate intranet and client server networks.

MAINFRAME COMPUTER
These are multi-user and multi-tasking general purpose computers.
They have large storage capacity and cost more than typical mini computers. They are used by large organizations such as banks, universities, central bank, national population commission etc.

SUPER COMPUTER
This can be seen as technological improvement on mainframe computers. It is used in the scientific environment such as for space studies and weather forecast.
They have higher processing powers and large storage capacities.

CLASSIFICATION OF COMPUTER BY PURPOSES
Classification of computer according to purpose can be grouped into two, namely:
1. General purpose computers
2. Special purposes computers
SPECIAL PURPOSE COMPUTERS
These are computers designed solely to solve a restricted class of problems e.g. computer for medical diagnosis, weapon guidance, traffic control, wealth study and forecast, control of airplanes and production control of refinery and guidance etc.
GENERAL PURPOSE COMPUTER
This class of computers is also called multi-purpose computers and are used for variety of works. They have the ability to store various programs of instructions and perform variety of operations such as graphics, database inventory and sales analysis.
Most computers are general purpose computers and they can handles different kind of work.

EVALUATION:
1. Classify computers by size and degree of versatility.
2. State and discuss five general characteristics of computers.
READING ASSIGNMENT:
Read: ‘handbook on computer studies (practical guide) for schools and colleges ‘Book 2, pages 14-16, By Niyi Adekolegan.
ASSIGNMENT:
1. Computers that are small enough to be held in hands are called_____
(a)Palmtop (b) Desktop (c) Laptop (d) Notebook.
2. Medium-sized computers are also known as _______ computers.
(a)Mini-computers (b) Micro-computers (c) Mainframe computers (d) Workstations
3. Another for micro-computers is______
(a) Compaq computers (b) Micro-computers (c) Mainframe computers (d) Apple computers
4. Mainframe computers generate large amount of heat because;
(a) They are very big (b) They consume too much electricity (c) They occupy so much room space (d) They are very small
5. Computers designed to solve special class of problems are called______
(a) General purpose computers (b) Special purpose computers
(c) Workstations (d) EDSAC Computers
WEEK 3
LESSON 4
TOPIC: THE COMPUTER SYSTEMS: The Concept of computer
Systems, And Component of computer Systems
OBJECTIVES
At the end of the lesson, students should be able to
- Explain the term computer system
- State the components of a computer system
THE CONCEPT OF COMPUTER SYSTEMS
What is a system? A system is a group of interrelated components working together towards a common goal by accepting inputs and producing outputs in an organized transformation process.
A computer is an example of a system made of input device, processing device and output device working together to produce the desire result.
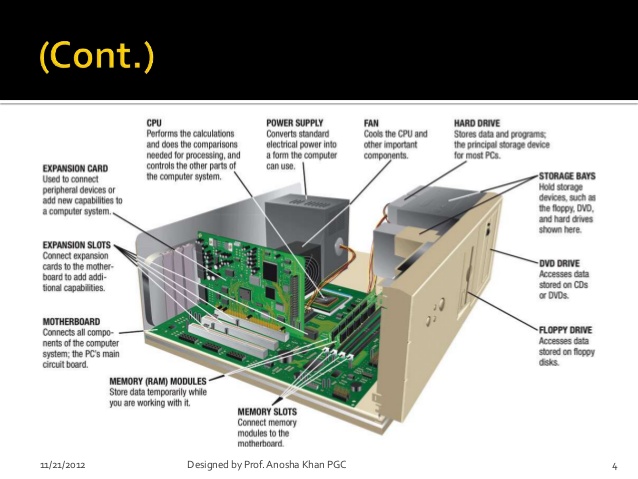
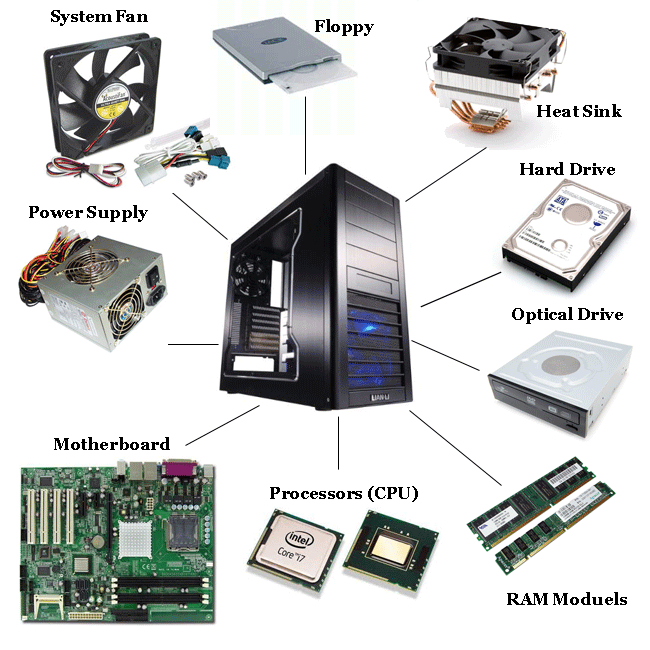
THE SYSTEM UNIT: System unit is the major part of a computer system. It consists of system board or power supply, system board or mother board, drives, memory and the processor.
Collection of all these components inside a single case or housing is called system unit. Some people refer to it as CPU. The CPU is an acronym for Central Processing Unit and the component parts of the system unit. The system unit came in different sizes, mini tower, full tower or desktop depending on its physical shape and architectural design.
THE CONSTITUENT PARTS OF A COMPUTER SYSTEM.
A computer system consists of three main parts otherwise called components. These are:
1. Hardware.
2. Software.
3. Human ware.
Hard ware component: computer hardware could be defined as the physical parts of the computer that we can see, feel and handle Computer hardwire includes the main parts and its peripheral. The main parts are the two devices: processor and memory unit make up the central processing unit. The CPU is responsible for all the processing responsible for feeding data into the system and collecting information from the system.
CPU is the brain of the computer system and sub-divided into the control unit (CU), Arithmetic and logic unit (ALU) and storage of memory unit.
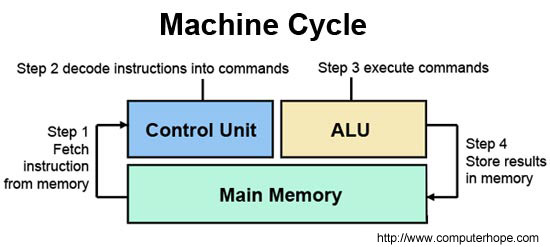
1. Control unit: This is the unit of the computer system that fetches instructions from the main storage, interprets them and issues all the necessary signals to the components making up the system. Control unit direct all hardware operation necessary in obeying instructions.
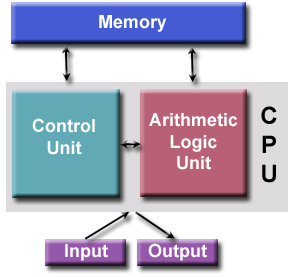
2. Arithmetic and logic unit: This part of the CPU is where all the arithmetic is carried out in the computer. These are adding up, subtracting, multiplication, division etc. It also carries out any logic functions that are necessary. Logic functions are decisions which have to be made such as less than <, equal to (=), greater than etc. Its operations consist of comparisons.
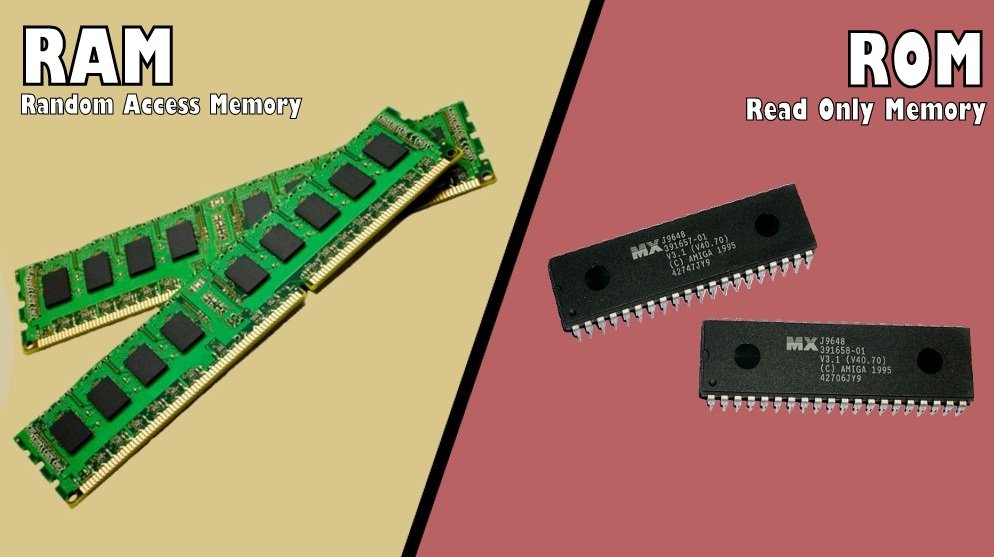
3. Storage or memory unit: The memory or storage is the place in the computer where the program and the data are stored. The computer memory is divided into two, namely:
1. Random Access Memory (RAM)
2. Read Only Memory (ROM)
ROM: Is used by the manufacturer to store general purpose and permanent instructions as operating system and program utilities to start and test the computer. You can only read from ROM but cannot write into it as it is write protected. The information here are permanent and cannot be lost when the computer is shut down.
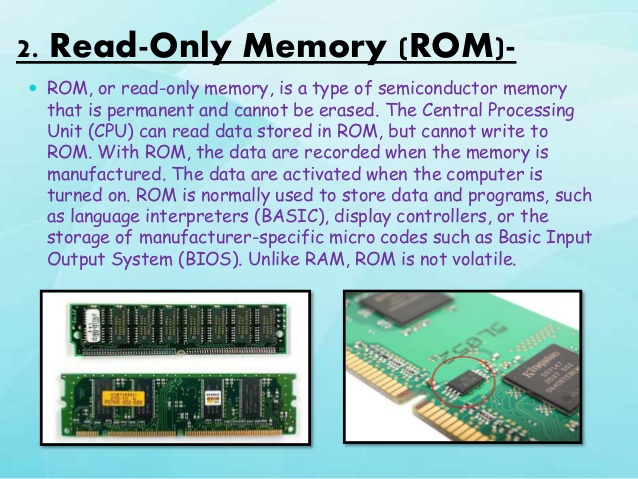
RAM: Data can be written into RAM and erased to enable fresh data to come in. This is the work area for the computer user when the program is being run.
RAM is electric power dependent and stored data is lost when power goes off. Information in the RAM is said to be volatile and read faster by the computer than information stored in the external storage devices. (Read more on storage devices in chapter six.)
PERIPHERALS
The general name for all input and output devices are called computer peripherals.
THE PERIPHERALS ARE IN THREE CATEGORIES
(1). Input devices
(2) Output device
(3) Auxiliary storage device.
They are the devices attached to the computer system in order to transfer information into and out of the system.
Input device: these are the medium through which we can communicate textual and graphic data etc. with the computer input devices such as keyboard, joystick, scanner etc. (see book one for more information).

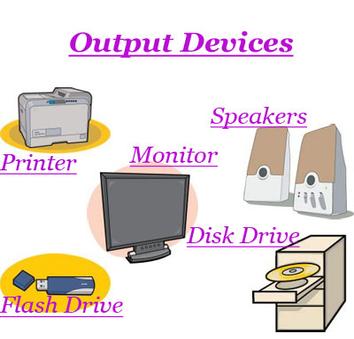
Output devices: These are the computer devices that bring out the result of processed data or information from the computer e.g. Video display unit or monitor, printer, speaker etc.
Auxiliary/secondary storage devices:
The auxiliary storage devices are an additional memory or external storage device. It is otherwise called BACK STORE or BACKUP storage device. This storage device holds large amount of data, information or program on a big term basis. They are less expensive than that of main or primary memory. They also serve as an input and output device i.e. Floppy, CD ROM, ZIP DISK, FLASH DISK etc.

EVALUATION:
1. State the sizes of the the system unit you know and explain any one of them
2. Define the term ‘System’
READING ASSIGNMENT:
Read ‘handbook on computer studies (practical guide) for schools and colleges ‘Book 2, pages 17-20, By Niyi Adekolegan.
ASSIGNMENT:
1. A group of inter-related components working together towards a common goal in an organized transformation process is called______
(a)System (b) Computer (c) Couple (d) Devices
2.______ is not a size of the system unit.
(a) Full tower (b) Mini-tower (c) micro-tower (d) Flat tower
3._____ is not a constituent part of a computer system.
(a) Hardware (b) Software (c) People ware (d) Sector ware
4. The Computer memory is divided into ______
(a) 2 (b) 4 (c) 6 (d) 7
5. The general name for all input and output devices is
called____
(a) Overall devices (b) Computer basics (c) Computer Peripherals (d) Group devices
TOPIC: THE COMPUTER SYSTEMS: The Concept of computer
Systems, And Component of computer Systems
OBJECTIVES
At the end of the lesson, students should be able to
- Explain the term computer system
- State the components of a computer system
THE CONCEPT OF COMPUTER SYSTEMS
What is a system? A system is a group of interrelated components working together towards a common goal by accepting inputs and producing outputs in an organized transformation process.
A computer is an example of a system made of input device, processing device and output device working together to produce the desire result.
THE SYSTEM UNIT: System unit is the major part of a computer system. It consists of system board or power supply, system board or mother board, drives, memory and the processor.
Collection of all these components inside a single case or housing is called system unit. Some people refer to it as CPU. The CPU is an acronym for Central Processing Unit and the component parts of the system unit. The system unit came in different sizes, mini tower, full tower or desktop depending on its physical shape and architectural design.

THE CONSTITUENT PARTS OF A COMPUTER SYSTEM.
A computer system consists of three main parts otherwise called components. These are:
1. Hardware.
2. Software.
3. Human ware.
Hard ware component: computer hardware could be defined as the physical parts of the computer that we can see, feel and handle Computer hardwire includes the main parts and its peripheral. The main parts are the two devices: processor and memory unit make up the central processing unit. The CPU is responsible for all the processing responsible for feeding data into the system and collecting information from the system.

CPU is the brain of the computer system and sub-divided into the control unit (CU), Arithmetic and logic unit (ALU) and storage of memory unit.
1. Control unit: This is the unit of the computer system that fetches instructions from the main storage, interprets them and issues all the necessary signals to the components making up the system. Control unit direct all hardware operation necessary in obeying instructions.

2. Arithmetic and logic unit: This part of the CPU is where all the arithmetic is carried out in the computer. These are adding up, subtracting, multiplication, division etc. It also carries out any logic functions that are necessary. Logic functions are decisions which have to be made such as less than <, equal to (=), greater than etc. Its operations consist of comparisons.

3. Storage or memory unit: The memory or storage is the place in the computer where the program and the data are stored. The computer memory is divided into two, namely:
1. Random Access Memory (RAM)
2. Read Only Memory (ROM)
ROM: Is used by the manufacturer to store general purpose and permanent instructions as operating system and program utilities to start and test the computer. You can only read from ROM but cannot write into it as it is write protected. The information here are permanent and cannot be lost when the computer is shut down.

RAM: Data can be written into RAM and erased to enable fresh data to come in. This is the work area for the computer user when the program is being run.
RAM is electric power dependent and stored data is lost when power goes off. Information in the RAM is said to be volatile and read faster by the computer than information stored in the external storage devices. (Read more on storage devices in chapter six.)

PERIPHERALS
The general name for all input and output devices are called computer peripherals.
THE PERIPHERALS ARE IN THREE CATEGORIES
(1). Input devices
(2) Output device
(3) Auxiliary storage device.
They are the devices attached to the computer system in order to transfer information into and out of the system.
Input device: these are the medium through which we can communicate textual and graphic data etc. with the computer input devices such as keyboard, joystick, scanner etc. (see book one for more information).

Output devices: These are the computer devices that bring out the result of processed data or information from the computer e.g. Video display unit or monitor, printer, speaker etc.

Auxiliary/secondary storage devices:
The auxiliary storage devices are an additional memory or external storage device. It is otherwise called BACK STORE or BACKUP storage device. This storage device holds large amount of data, information or program on a big term basis. They are less expensive than that of main or primary memory. They also serve as an input and output device i.e. Floppy, CD ROM, ZIP DISK, FLASH DISK etc.

EVALUATION:
1. State the sizes of the the system unit you know and explain any one of them
2. Define the term ‘System’
READING ASSIGNMENT:
Read ‘handbook on computer studies (practical guide) for schools and colleges ‘Book 2, pages 17-20, By Niyi Adekolegan.
ASSIGNMENT:
1. A group of inter-related components working together towards a common goal in an organized transformation process is called______
(a)System (b) Computer (c) Couple (d) Devices
2.______ is not a size of the system unit.
(a) Full tower (b) Mini-tower (c) micro-tower (d) Flat tower
3._____ is not a constituent part of a computer system.
(a) Hardware (b) Software (c) People ware (d) Sector ware
4. The Computer memory is divided into ______
(a) 2 (b) 4 (c) 6 (d) 7
5. The general name for all input and output devices is
called____
(a) Overall devices (b) Computer basics (c) Computer Peripherals (d) Group devices
WEEK 4
LESSON 5
TOPIC: THE COMPUTER SYSTEMS: Software
Component
OBJECTIVES
At the end of the lesson, students should be able to
- Explain term hardware, software and human ware or people ware.
- Explain the relationship between each of the three components of a computer system.
SOFTWARE COMPONENT
Computer hardware without software can be likened to a vehicle without fuel. A system can only perform based on a set of given instructions that are to be followed in sequence called program.
Software refers to the collections of all the programs available on a computer. Basically there are two types of software. These are system software and application software.
System Software: These are programs written by the computer manufacturer to control the internal operations of the computer system. Operating system is an example.
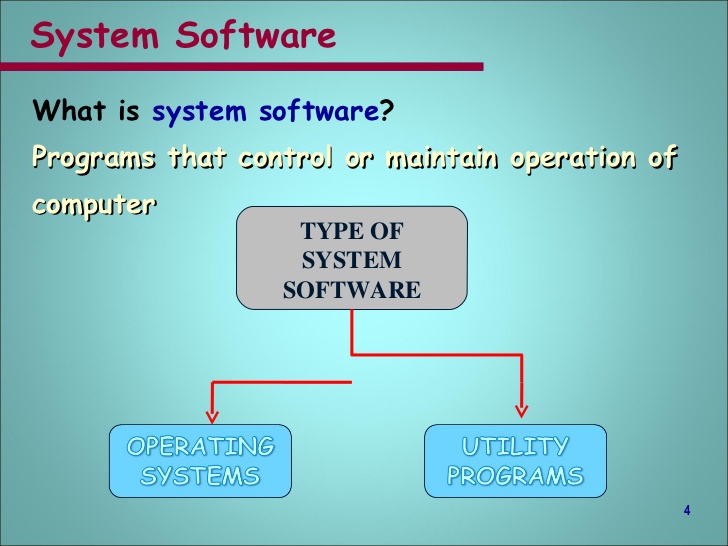
Application software: These are the programs written by the software expert. They are referred to as application software because they are applied to solve our problems. These software come in form of package such as MS-WORD, MS-EXCEL, MS-POWERPOINT etc. Another part of application software is referred to as users’ software. User software is a program written by the computer operator or user of the system to meet his immediate needs. Read more on this topic in the next chapter.
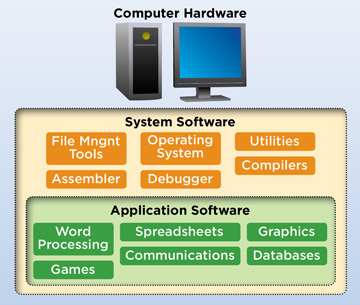
Human ware component
A computer system is more that just the machine alone; includes all the other things that make the computer to function. The human aspect of computer is called peoples ware or human ware. Computer cannot be treated in isolation without the people that actually operates it. Human ware is the people working with the computer. It ranges from the professional users like system analyst, engineer, programmer to operational users such as data entry operators. Computer professionals are those who have undergone one form of formal computer training or the other and are certificated.

EVALUATION:
1. Write short note on the following;
(i) System software
(ii) Application package
2. Explain the term people ware
READING ASSIGNMENT:
Read ‘handbook on computer studies (practical guide) for schools and colleges ‘Book 2, pages 17-20, By Niyi Adekolegan.
ASSIGNMENT:
1. Auxilliary/Secondary storage devices are otherwise known as______
(a) Backup storage device (b) Expensive storage device (c) Soft store (d) Zip store
2._____ is not an auxiliary storage device
(a) Flash drive (b) Compact disc (c) Floppy disk (d) Hard disk
3._____ and _____ are two types software;
(a) System software and application software
(b) System software and Chigozie software
© Application software and planned software
(d) None of the above
4. Example of Application software includes all, except_____
(a) MS-WORD (b) MS-EXCEL (c) MS-POWERPOINT (d)
QuickBasic
5. Which of these is not an operating system?
(a) Operating system (b)Centralized system (c) Coordinating system (d) Logical system
LESSON 6
TOPIC: THE COMPUTER SOFTWARE: Definition of computer
Software, Types of computer software
OBJECTIVES:
At the end of the lesson, students should be able to;
Explain the term software and give examples to differentiate between system software and Application software.
Software is the term used to describe computer programs; it is the blood that flows through the computer system. Compared with the hardware, the software used on a given computer is relatively easy to change and it is the attributes, which give computer their flexibility.
Just as there are two types of blood cells in human beings performing different functions in the computer system. The first is referred to as System software and the other is the application software. All other forms of software come under these two board divisions.
Software component of the computer system.

Computer hardware without software can be linked to a vehicle without fuel. A system can only perform based on a set of given instructions that are to be followed in sequence, called program. Software refers to the collection of all the programs available on a computer system or in a computer installation. Software can be divided into two main classes namely;
1. System Software
2. application Software
System Software: These are programs written by the manufacturer to ensure the smooth running of the computer. They are programs that enhance the performance operations of computer. It is divided into four classes of the system namely;
1. Operating system
2. Translators
3. Database management system (DBMS)
4. Utilities and service programmers
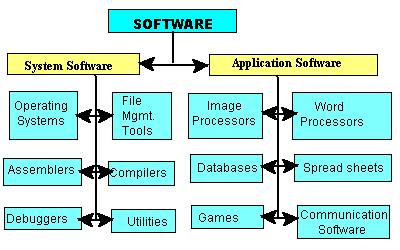
Application Software: This can be classified into two namely;
1. User application program, 2. Application Packages
The tree below summarizes the classes of software

EVALUATION:
1. Distinguish between system software and application software
2. List five application packages you know
READING ASSIGNMENT:
Read ‘handbook on computer studies (practical guide) for schools and colleges ‘Book 2, pages 23-25, By Niyi Adekolegan.
ASSIGNMENT:
1. How many class of application package do we have?
(a) 2 (b) 3 (c) 7 (d) 8
2. Which of these software is written by the manufacturer?
(a) System software (b) application software (c) E-learning software (d) Language software
3. ______ Can be used to described the software
(a) Blood (b) Water (c) Toner (d) Anti-virus
4. System software can be divided into how many parts?
(a) 6 (b) 8 (c) 4 (d) 1
5. An application package that can be used to communicate textual data to the user is called ______
(a) Power point (b) Corel draw (c) MS-WORD (d) Excel
6. A collection of all the program available in the computer system or set of instructions guiding the operation of the computer is called_______
(a) Software (b) Firmware (c) People ware (d) Hard ware
TOPIC: THE COMPUTER SYSTEMS: Software
Component
OBJECTIVES
At the end of the lesson, students should be able to
- Explain term hardware, software and human ware or people ware.
- Explain the relationship between each of the three components of a computer system.
SOFTWARE COMPONENT
Computer hardware without software can be likened to a vehicle without fuel. A system can only perform based on a set of given instructions that are to be followed in sequence called program.
Software refers to the collections of all the programs available on a computer. Basically there are two types of software. These are system software and application software.
System Software: These are programs written by the computer manufacturer to control the internal operations of the computer system. Operating system is an example.

Application software: These are the programs written by the software expert. They are referred to as application software because they are applied to solve our problems. These software come in form of package such as MS-WORD, MS-EXCEL, MS-POWERPOINT etc. Another part of application software is referred to as users’ software. User software is a program written by the computer operator or user of the system to meet his immediate needs. Read more on this topic in the next chapter.

Human ware component
A computer system is more that just the machine alone; includes all the other things that make the computer to function. The human aspect of computer is called peoples ware or human ware. Computer cannot be treated in isolation without the people that actually operates it. Human ware is the people working with the computer. It ranges from the professional users like system analyst, engineer, programmer to operational users such as data entry operators. Computer professionals are those who have undergone one form of formal computer training or the other and are certificated.

EVALUATION:
1. Write short note on the following;
(i) System software
(ii) Application package
2. Explain the term people ware
READING ASSIGNMENT:
Read ‘handbook on computer studies (practical guide) for schools and colleges ‘Book 2, pages 17-20, By Niyi Adekolegan.
ASSIGNMENT:
1. Auxilliary/Secondary storage devices are otherwise known as______
(a) Backup storage device (b) Expensive storage device (c) Soft store (d) Zip store
2._____ is not an auxiliary storage device
(a) Flash drive (b) Compact disc (c) Floppy disk (d) Hard disk
3._____ and _____ are two types software;
(a) System software and application software
(b) System software and Chigozie software
© Application software and planned software
(d) None of the above
4. Example of Application software includes all, except_____
(a) MS-WORD (b) MS-EXCEL (c) MS-POWERPOINT (d)
QuickBasic
5. Which of these is not an operating system?
(a) Operating system (b)Centralized system (c) Coordinating system (d) Logical system
LESSON 6
TOPIC: THE COMPUTER SOFTWARE: Definition of computer
Software, Types of computer software
OBJECTIVES:
At the end of the lesson, students should be able to;
Explain the term software and give examples to differentiate between system software and Application software.
Software is the term used to describe computer programs; it is the blood that flows through the computer system. Compared with the hardware, the software used on a given computer is relatively easy to change and it is the attributes, which give computer their flexibility.
Just as there are two types of blood cells in human beings performing different functions in the computer system. The first is referred to as System software and the other is the application software. All other forms of software come under these two board divisions.
Software component of the computer system.

Computer hardware without software can be linked to a vehicle without fuel. A system can only perform based on a set of given instructions that are to be followed in sequence, called program. Software refers to the collection of all the programs available on a computer system or in a computer installation. Software can be divided into two main classes namely;
1. System Software
2. application Software
System Software: These are programs written by the manufacturer to ensure the smooth running of the computer. They are programs that enhance the performance operations of computer. It is divided into four classes of the system namely;
1. Operating system
2. Translators
3. Database management system (DBMS)
4. Utilities and service programmers

Application Software: This can be classified into two namely;
1. User application program, 2. Application Packages
The tree below summarizes the classes of software

EVALUATION:
1. Distinguish between system software and application software
2. List five application packages you know
READING ASSIGNMENT:
Read ‘handbook on computer studies (practical guide) for schools and colleges ‘Book 2, pages 23-25, By Niyi Adekolegan.
ASSIGNMENT:
1. How many class of application package do we have?
(a) 2 (b) 3 (c) 7 (d) 8
2. Which of these software is written by the manufacturer?
(a) System software (b) application software (c) E-learning software (d) Language software
3. ______ Can be used to described the software
(a) Blood (b) Water (c) Toner (d) Anti-virus
4. System software can be divided into how many parts?
(a) 6 (b) 8 (c) 4 (d) 1
5. An application package that can be used to communicate textual data to the user is called ______
(a) Power point (b) Corel draw (c) MS-WORD (d) Excel
6. A collection of all the program available in the computer system or set of instructions guiding the operation of the computer is called_______
(a) Software (b) Firmware (c) People ware (d) Hard ware
WEEK 5
LESSON 7
TOPIC: OPERATING SYSTEM: Definition of operating system (OS), Examples of Operating system.
OBJECTIVES:
At the end of the lesson, students should be able to;
- Define the term operation system
- Give examples of operating system
- State the functions of operating system
- Differentiate between DOS operating system and window operating system.
DEFINITION OF AN OPERATING SYSTEM
A set of instruction or programs designed to efficiently manage the resources of the computer system is referred to as operating system. It is the operating system that makes the computer understands the user’s instructions and command. It is the life-wire of a computer system. It does the loading and schedule of all activities going on in a computer system some examples of operating system are Disk operating system (DOS), Windows Operating System, Linux Operating System, UNIX and Xenix Operating System. Etc.

WHAT IS AN OPERATING SYSTEM?
An operating system can be defined as the collection of programs which are resident in the computer memory. It controls the general operations of the computer system.

TYPES OF OPERATING SYSTEM
There are different types of operating system as specified by their operational performance. The most commonly used operating system are:
1. Single user operating system
2. Multi user operating system
3. Networking operating system
Single user operating system allows only a single task performed at a time. It allows a single user to operate the machine time in an interactive mode and allows one user program to be in the main store and processed at a time. It does not allow users program. Examples of a single user operating system includes MSDOS, PCDOS etc.
Multi- User Operating System permits the execution of more than one task at a time. It shares the system resources to more than one user by connecting the individual user on the system. Examples are window 98, windows me, zenix os/2etc.
Networking operating system is used in network environment where users form different locations are interconnected. Computers connected to a large network, such as WAN & INTERNET. Examples of a networking operating system includes window NT, window 2000, window XP, novel Netware. Etc.

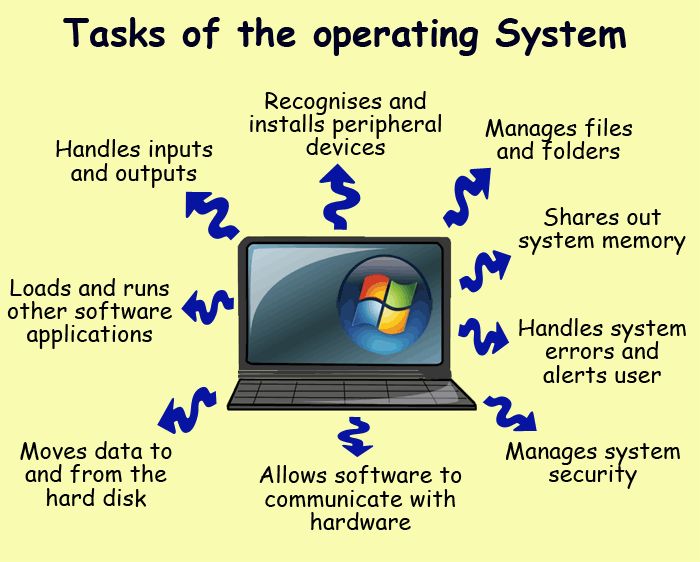
FUNCTIONS OF AN OPERATING SYSTEM
The general functions of the operation system include the following among others.
1. It helps in loading and scheduling of programs to provide continuous processing and give appropriate response to events
2. It protects software, hardware and data from improper use.
3. It manages hardware resources.
4. It performs the loading of programs from external memory to the main memory.
5. It provide error correction routine
6. It makes communication possible between the users and computer system
7. It passes control from one job to another in a multi programming environment.
8. It handles interrupts and computer language malfunctioning.
EVALUATION:
1. List five functions of the operating system
2. Write short note on the following;
(i) Single user operating system
(ii)Multi-user operating system
(iii)Network operating system
LESSON 8
DISK OPERATING SYSTEM
Disk operating system is the master program of computer, which can be located in the computer temporary memory called RAM. It allows the various parts of the computer to communicate with one another. It allows the computer users to copy files, format disk and print etc. examples of DOS are: MSDOS (Microsoft Disk Operating System), PCDOS, DOS is a single user operating system.

DOS COMMAND
There are two types of DOS command and they are:
1. Internal DOS command
2. External DOS command
Internal DOS command:
These are command that comes with the new computer; they are the simplest most commonly used command. It is an invisible command that resides in the memory of the computer. Examples of DOS are CLS. DATE, DIR, DEL, CD prompt MD, VER, File copy etc.
External command
The external DOS command are read from the disk and loaded into the memory of the computer before they can be executed. They are commands that have to be purchased and stored in the hard disk. Examples of External command are Format Disk copy, Back up, Restore, print etc.
Windows Operating system
A window operating system is a graphical user interface that enables you to communicate with your computer through ICON, MENU, dialog box and application programs.
Window operating system is the major part of the system software that controls the interface between the computer and users. It communicates with the CPU and gives result on the screen. The different versions of window are as follows; window 95, 98, 2000, millennium and window XP. The latter versions are more interactive compared to the former. More of latest versions of windows are coming as technology is advancing daily.

ADVANTAGES OF WINDOW OPERATING SYSTEM OVER DOS
The window operating system has the following advantages over DOS. The window operating system has the following advantages over DOS.
- Window packages are more interactive compared to DOS
- Window packages are easier to learn compared to DOS package (ie once you know about window package you can train yourself on the other window packages).
- Date and time are easier to correct or change on wind system compared to DOS.

EVALUATION:
1. What do you understand by the ‘Disk operating system’?
2. state any 3 Advantages of windows operating system over disk operating
3. In tabular form, differentiate between Disk Operating System and window Operating System
4. List four types of Operating System with examples
READING ASSIGNMENT:
Read ‘handbook on computer studies (practical guide) for schools and colleges ‘Book 2, pages 31-42, By Niyi Adekolegan.
ASSIGNMENT:
1. DBMS stands for
(a) Data base management system
(b) Data bank monitoring system
(c) Data base marking system
(d) None of the above
2. There are ______ types of DOS
(a) 3 (b) 2 (c) 6 (d) 5
3._______ packages are more interactive than the DOS
(a) Windows OS (b) Single OS (c) Double OS (d) None
4. Which of these is the master program of the computer
(a) DOS (b) SOS (c) VLSIC (d) DBMS
5. MSDOS stands for
(a) Microsoft disk operating system
(b) Micro stand disk operating system
© Micro disk operating system
(d)None
TOPIC: OPERATING SYSTEM: Definition of operating system (OS), Examples of Operating system.
OBJECTIVES:
At the end of the lesson, students should be able to;
- Define the term operation system
- Give examples of operating system
- State the functions of operating system
- Differentiate between DOS operating system and window operating system.
DEFINITION OF AN OPERATING SYSTEM
A set of instruction or programs designed to efficiently manage the resources of the computer system is referred to as operating system. It is the operating system that makes the computer understands the user’s instructions and command. It is the life-wire of a computer system. It does the loading and schedule of all activities going on in a computer system some examples of operating system are Disk operating system (DOS), Windows Operating System, Linux Operating System, UNIX and Xenix Operating System. Etc.

WHAT IS AN OPERATING SYSTEM?
An operating system can be defined as the collection of programs which are resident in the computer memory. It controls the general operations of the computer system.

TYPES OF OPERATING SYSTEM
There are different types of operating system as specified by their operational performance. The most commonly used operating system are:
1. Single user operating system
2. Multi user operating system
3. Networking operating system
Single user operating system allows only a single task performed at a time. It allows a single user to operate the machine time in an interactive mode and allows one user program to be in the main store and processed at a time. It does not allow users program. Examples of a single user operating system includes MSDOS, PCDOS etc.
Multi- User Operating System permits the execution of more than one task at a time. It shares the system resources to more than one user by connecting the individual user on the system. Examples are window 98, windows me, zenix os/2etc.
Networking operating system is used in network environment where users form different locations are interconnected. Computers connected to a large network, such as WAN & INTERNET. Examples of a networking operating system includes window NT, window 2000, window XP, novel Netware. Etc.

FUNCTIONS OF AN OPERATING SYSTEM
The general functions of the operation system include the following among others.
1. It helps in loading and scheduling of programs to provide continuous processing and give appropriate response to events
2. It protects software, hardware and data from improper use.
3. It manages hardware resources.
4. It performs the loading of programs from external memory to the main memory.
5. It provide error correction routine
6. It makes communication possible between the users and computer system
7. It passes control from one job to another in a multi programming environment.
8. It handles interrupts and computer language malfunctioning.

EVALUATION:
1. List five functions of the operating system
2. Write short note on the following;
(i) Single user operating system
(ii)Multi-user operating system
(iii)Network operating system
LESSON 8
DISK OPERATING SYSTEM
Disk operating system is the master program of computer, which can be located in the computer temporary memory called RAM. It allows the various parts of the computer to communicate with one another. It allows the computer users to copy files, format disk and print etc. examples of DOS are: MSDOS (Microsoft Disk Operating System), PCDOS, DOS is a single user operating system.

DOS COMMAND
There are two types of DOS command and they are:
1. Internal DOS command
2. External DOS command
Internal DOS command:
These are command that comes with the new computer; they are the simplest most commonly used command. It is an invisible command that resides in the memory of the computer. Examples of DOS are CLS. DATE, DIR, DEL, CD prompt MD, VER, File copy etc.
External command
The external DOS command are read from the disk and loaded into the memory of the computer before they can be executed. They are commands that have to be purchased and stored in the hard disk. Examples of External command are Format Disk copy, Back up, Restore, print etc.
Windows Operating system
A window operating system is a graphical user interface that enables you to communicate with your computer through ICON, MENU, dialog box and application programs.
Window operating system is the major part of the system software that controls the interface between the computer and users. It communicates with the CPU and gives result on the screen. The different versions of window are as follows; window 95, 98, 2000, millennium and window XP. The latter versions are more interactive compared to the former. More of latest versions of windows are coming as technology is advancing daily.

ADVANTAGES OF WINDOW OPERATING SYSTEM OVER DOS
The window operating system has the following advantages over DOS. The window operating system has the following advantages over DOS.
- Window packages are more interactive compared to DOS
- Window packages are easier to learn compared to DOS package (ie once you know about window package you can train yourself on the other window packages).
- Date and time are easier to correct or change on wind system compared to DOS.

EVALUATION:
1. What do you understand by the ‘Disk operating system’?
2. state any 3 Advantages of windows operating system over disk operating
3. In tabular form, differentiate between Disk Operating System and window Operating System
4. List four types of Operating System with examples
READING ASSIGNMENT:
Read ‘handbook on computer studies (practical guide) for schools and colleges ‘Book 2, pages 31-42, By Niyi Adekolegan.
ASSIGNMENT:
1. DBMS stands for
(a) Data base management system
(b) Data bank monitoring system
(c) Data base marking system
(d) None of the above
2. There are ______ types of DOS
(a) 3 (b) 2 (c) 6 (d) 5
3._______ packages are more interactive than the DOS
(a) Windows OS (b) Single OS (c) Double OS (d) None
4. Which of these is the master program of the computer
(a) DOS (b) SOS (c) VLSIC (d) DBMS
5. MSDOS stands for
(a) Microsoft disk operating system
(b) Micro stand disk operating system
© Micro disk operating system
(d)None
WEEK 6
LESSON 9
TOPIC: NUMBER BASES: (i) Decimal (ii) Binary (iii) Octal (iv)
Hexadecimal
OBJECTIVES: At the end of this lesson, student should be able to:
- Describe how data and information are represented and communicated to the computer.
- Add numbers together in base two, base eight, base ten and base sixteen.
- Covert decimal numbers to binary and hexadecimal number based and vice-versa.
NUMBER SYSTEM
To effectively use the computer, it is therefore necessary to know how data is represented and communicated to it.
The Decimal Numbers. These are numbers in everyday use. They are also denary number or numbers in base 10. Any denary number will contain any of the 10 symbols i.e “0. 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9” where (n<10).
Addition in base ten
Addition of numbers in base ten is accomplished in a very simple way. The digits with the same positional or place value are added together. Starting from the right.
Find the following sums in base ten

Subtraction in base ten:
In subtraction, digits from the subtraction are subtracted from the corresponding digits form the minuend with the same positional values.
If digits from the subtraction are greater that the corresponding minuend, one is borrowed from the immediate neighbor on the left and that one counts as ten.
Example 4
Evaluate each of the following

PLACE OR POSITIONAL VALUE
Consider the numbers 777. Ordinarily, the 3 digits are the same i.e.7, but when their positional value are considered one is 7 hundred, another is 70 and the last is ordinary 7. The position of a digit affects its value or meaning.
Positional value plays an important role in converting a number from one base to another.
Example
777 = 700 + 70 + 7
= 7 x 100 + 7 x 10 + 7
= 7 x 102 + 7 x 101 + 7 x 1
= 7 x 102 + 7 x 101 + 7 x 100
Examples
6345 = 6000 + 300 + 40 + 5
= 6 x 1000 + 3 x 100 + 4 x 10 + 5 x 1
= 6 x 10 + 3 x 10 + 4 x 10 x 5 x 10
BINARY SYSTEM
The binary system is a system of numbers, which has two as its base. the digits in base two are 0and 1.computer is made on the mechanism of a two – way device system.
A two-way device system is a system, which can make a decision that has two alternatives like;
(1) True or false statement (2) yes or No (3) Switch ON or OFF in electrical circuits e.t.c.
In an electro-magnetic device for instance, I can stand for magnetize while 0 stands for demagnetize or in an electrical circuits for switch off. it is for this reason that the binary systems dominate other number system in computer.
Binary Addition
When adding these digits together, the result will also be 1’s and 0’s. The following examples indicate all possible combinations.
(1) 0+0=0 (2) 0+1=1 (3) 1+0=1 (4) 1+1=0(plus a carryover of 1)
Here are some examples of binary addition
Example

Binary Subtraction
Subtraction is the inverse operation of addition. To subtract, it is necessary to establish a procedure for subtracting a large number from a smaller digit. The table for the binary subtraction is as follows;
1. 0-0=0 2. 1-0=0 3. 1-1=0 4. 0-1=1 with a barrow of 1
Example
Evaluate each of the following in base two.
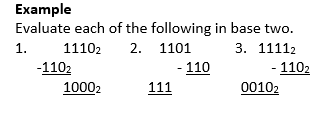
Conversion from binary to denary/ decimal
The following examples illustrate the conversion of binary number the decimal system. the same type of positional notation is used in the binary number as in the decimal system.
Example

Conversion from decimal to binary
The decimal numbers is repeating divided by 2, and the remainder after each division is used to indicate the coefficient of the binary number to be formed. It should therefore be noted that binary number is from bottom to the top.
Example
Convert the following denary numbers to binary
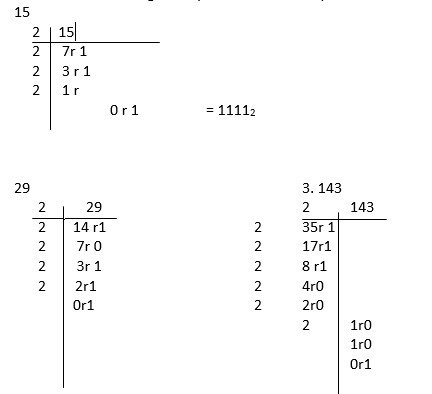
EVALUATION:
1. Convert 1012 to a number in base 10.
TOPIC: NUMBER BASES: (i) Decimal (ii) Binary (iii) Octal (iv)
Hexadecimal
OBJECTIVES: At the end of this lesson, student should be able to:
- Describe how data and information are represented and communicated to the computer.
- Add numbers together in base two, base eight, base ten and base sixteen.
- Covert decimal numbers to binary and hexadecimal number based and vice-versa.
NUMBER SYSTEM
To effectively use the computer, it is therefore necessary to know how data is represented and communicated to it.
The Decimal Numbers. These are numbers in everyday use. They are also denary number or numbers in base 10. Any denary number will contain any of the 10 symbols i.e “0. 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9” where (n<10).
Addition in base ten
Addition of numbers in base ten is accomplished in a very simple way. The digits with the same positional or place value are added together. Starting from the right.
Find the following sums in base ten

Subtraction in base ten:
In subtraction, digits from the subtraction are subtracted from the corresponding digits form the minuend with the same positional values.
If digits from the subtraction are greater that the corresponding minuend, one is borrowed from the immediate neighbor on the left and that one counts as ten.
Example 4
Evaluate each of the following

PLACE OR POSITIONAL VALUE
Consider the numbers 777. Ordinarily, the 3 digits are the same i.e.7, but when their positional value are considered one is 7 hundred, another is 70 and the last is ordinary 7. The position of a digit affects its value or meaning.
Positional value plays an important role in converting a number from one base to another.
Example
777 = 700 + 70 + 7
= 7 x 100 + 7 x 10 + 7
= 7 x 102 + 7 x 101 + 7 x 1
= 7 x 102 + 7 x 101 + 7 x 100
Examples
6345 = 6000 + 300 + 40 + 5
= 6 x 1000 + 3 x 100 + 4 x 10 + 5 x 1
= 6 x 10 + 3 x 10 + 4 x 10 x 5 x 10
BINARY SYSTEM
The binary system is a system of numbers, which has two as its base. the digits in base two are 0and 1.computer is made on the mechanism of a two – way device system.
A two-way device system is a system, which can make a decision that has two alternatives like;
(1) True or false statement (2) yes or No (3) Switch ON or OFF in electrical circuits e.t.c.
In an electro-magnetic device for instance, I can stand for magnetize while 0 stands for demagnetize or in an electrical circuits for switch off. it is for this reason that the binary systems dominate other number system in computer.
Binary Addition
When adding these digits together, the result will also be 1’s and 0’s. The following examples indicate all possible combinations.
(1) 0+0=0 (2) 0+1=1 (3) 1+0=1 (4) 1+1=0(plus a carryover of 1)
Here are some examples of binary addition
Example

Binary Subtraction
Subtraction is the inverse operation of addition. To subtract, it is necessary to establish a procedure for subtracting a large number from a smaller digit. The table for the binary subtraction is as follows;
1. 0-0=0 2. 1-0=0 3. 1-1=0 4. 0-1=1 with a barrow of 1
Example
Evaluate each of the following in base two.
Conversion from binary to denary/ decimal
The following examples illustrate the conversion of binary number the decimal system. the same type of positional notation is used in the binary number as in the decimal system.
Example

Conversion from decimal to binary
The decimal numbers is repeating divided by 2, and the remainder after each division is used to indicate the coefficient of the binary number to be formed. It should therefore be noted that binary number is from bottom to the top.
Example
Convert the following denary numbers to binary

EVALUATION:
1. Convert 1012 to a number in base 10.
WEEK 7
LESSON 10
OCTAL NUMBERS
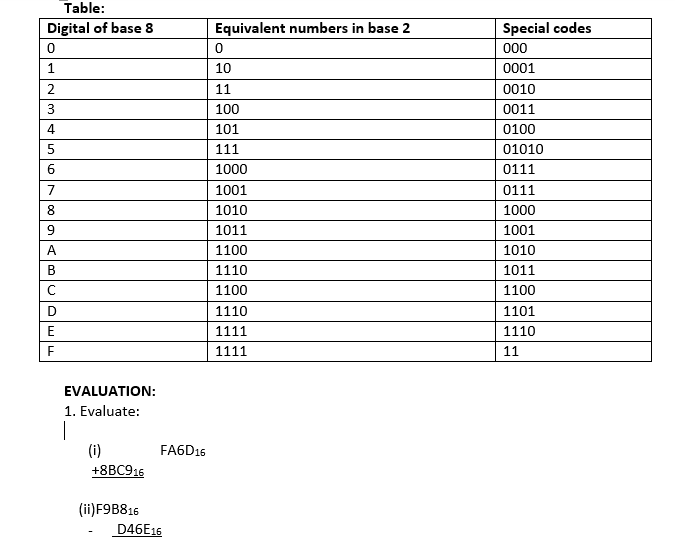
The Octal number system has a base or radix of 8. eight different symbols are used to represent Octal numbers are 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6,and 7. Generally, it could be express as (n < 8) which implies 0, 1, 2, ………………. n-1
EXAMPLE
Convert the following octal numbers to denary number 1) 4078 2) 6348 3) 1748
To covert an octal number to a decimal numbers, we use the same sort of polynomial as used in the binary case, except that we now have radix of 8 instead of 2.
1) 4078
4 x 82x0x81x7x80
= 4x64+0+8+7x1
= 256+0+7 =26310
2)
6348
=6x82+3x81+4x80
= 6x64+3x8+4x1
=384+24+4= 41210
3) 1748
= 1x82+7x81+4x80
=1x64+7x8+4x1
=64+56+4
= 64+60=12410
CONVERSION FROM OCTAL TO DENARY
The decimal numbers are repeatedly divided by 8 and the remainder after each division is used to indicate the co-efficient of the octal number to be formed. Note that the octal number is derived by written from bottom to the up binary number as in the decimal system.
EXAMPLE
Convert the following binary number to denary
1)
101=1x22+0x21+1x20
= 1x4+0x2x1x1
= 4x0x1=510
2)
110112=1x24+1x23x022x1x21x1x20
= 16x1+1x8+0x4+1x2+2+1x1
=16+8+0+2+1
= 24+3 = 2710
3)
1001102 = 1x25 + 0x24 +0x23x1x22+0x20
= 1x 32+0x16+0x8+1x4+2+0x1
= 32+0+0+4+2+1
= 32+7
= 3910
4)
11011101112
= 1x29 +1x28+0x27+1x26+1x25+1x24+0x23+1x22+1x21+1x20
= 1x512+1x256+1x64+1x32+1x16+1x4+1x2+1x1
= 512+256+64+32+16+4+2+1
= 88710
CONVERSION FROM DECIMAL TO BINARY
The decimal numbers is repeating divided by 2, and the remainder after each division is used to indicate the coefficient of the binary number to be formed. It should be therefore noted that binary number is written from button to the top.
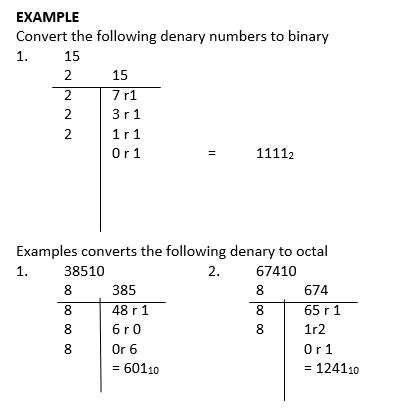
Conversion between Octal and Binary
Now 8 = 23, so each group of 3 binary digit from right to left an be changed to the corresponding octal number and vice – versa
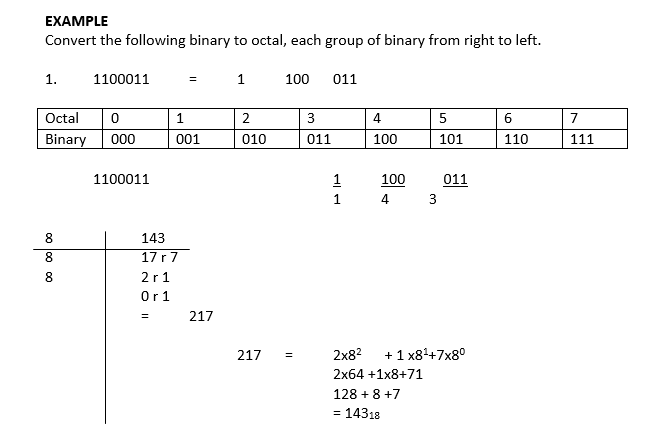
EXAMPLE
Convert the following binary to octal, each group of binary from right to left.
Note: Any one digital in octal represents 3 digital in binary

Note:
(1) Remember that 3 binary digits is equivalent to one octal digit.
(2) The table is just guide to see the relationship between octal and binary number.
(3) All necessary working must be shown.
Evaluate each of the followings in base 8
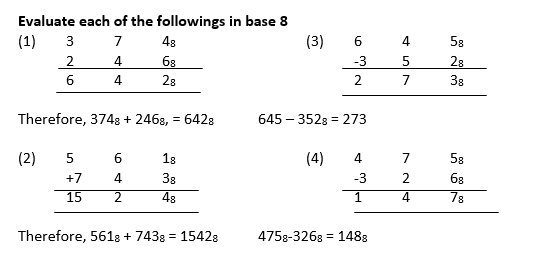
Relationship between binary and octal numbers
Note: That 8 = 23. For this reason, there is a close relationship between number in base 2 and 8.
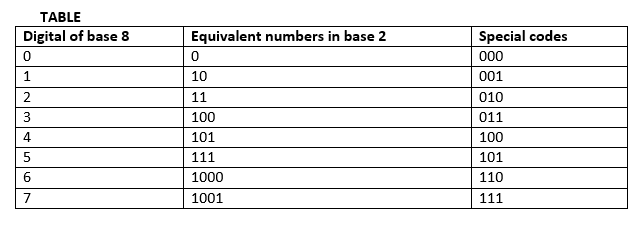
The digits of octal number have been given special codes
TABLE
EVALUATION:
1. Convert the following octal numbers to denary number
1.
407
2.
6348
3.
1748
2. Convert the following denary numbers to binary
(i) 16 (ii) 20 (iii) 32
LESSON 11
HEXADECIMALS
The special codes for 8 digits are called 3-bit equivalent forms. Hexadecimal Numbers (HEX).
A number system using 16 as its base is called a hexadecimal system. The hexadecimal system has the following digits:
0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,A,B,C,D,Eand F.
Where A=10, B=11,C=12,D=13,E=14,and F=15
Example: Write each of the following numbers using the expanded notations;

conversion between hexadecimal and denary

Relationship between Binary, Octal and Hexadecimal numbers
Recall that 16 and 8 are multiple of 2 for this reason; there is a close relationship between numbers in base2, base 8 and base 16. Similar the digits of hexadecimal numbers are given special codes.
READING ASSIGNMENT:
Read ‘handbook on computer studies (practical guide) for schools and colleges ‘Book 2, pages 43-48, By Niyi Adekolegan.
ASSIGNMENT:
ATTEMPT REVISION EXERCISE IN PAGE 42 OF STUDENTS TEXT BOOK, BY NIYI ADEKOLEGAN
OCTAL NUMBERS
The Octal number system has a base or radix of 8. eight different symbols are used to represent Octal numbers are 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6,and 7. Generally, it could be express as (n < 8) which implies 0, 1, 2, ………………. n-1
EXAMPLE
Convert the following octal numbers to denary number 1) 4078 2) 6348 3) 1748
To covert an octal number to a decimal numbers, we use the same sort of polynomial as used in the binary case, except that we now have radix of 8 instead of 2.
1) 4078
4 x 82x0x81x7x80
= 4x64+0+8+7x1
= 256+0+7 =26310
2)
6348
=6x82+3x81+4x80
= 6x64+3x8+4x1
=384+24+4= 41210
3) 1748
= 1x82+7x81+4x80
=1x64+7x8+4x1
=64+56+4
= 64+60=12410
CONVERSION FROM OCTAL TO DENARY
The decimal numbers are repeatedly divided by 8 and the remainder after each division is used to indicate the co-efficient of the octal number to be formed. Note that the octal number is derived by written from bottom to the up binary number as in the decimal system.
EXAMPLE
Convert the following binary number to denary
1)
101=1x22+0x21+1x20
= 1x4+0x2x1x1
= 4x0x1=510
2)
110112=1x24+1x23x022x1x21x1x20
= 16x1+1x8+0x4+1x2+2+1x1
=16+8+0+2+1
= 24+3 = 2710
3)
1001102 = 1x25 + 0x24 +0x23x1x22+0x20
= 1x 32+0x16+0x8+1x4+2+0x1
= 32+0+0+4+2+1
= 32+7
= 3910
4)
11011101112
= 1x29 +1x28+0x27+1x26+1x25+1x24+0x23+1x22+1x21+1x20
= 1x512+1x256+1x64+1x32+1x16+1x4+1x2+1x1
= 512+256+64+32+16+4+2+1
= 88710
CONVERSION FROM DECIMAL TO BINARY
The decimal numbers is repeating divided by 2, and the remainder after each division is used to indicate the coefficient of the binary number to be formed. It should be therefore noted that binary number is written from button to the top.

Conversion between Octal and Binary
Now 8 = 23, so each group of 3 binary digit from right to left an be changed to the corresponding octal number and vice – versa
EXAMPLE
Convert the following binary to octal, each group of binary from right to left.

Note: Any one digital in octal represents 3 digital in binary

Note:
(1) Remember that 3 binary digits is equivalent to one octal digit.
(2) The table is just guide to see the relationship between octal and binary number.
(3) All necessary working must be shown.
Evaluate each of the followings in base 8

Relationship between binary and octal numbers
Note: That 8 = 23. For this reason, there is a close relationship between number in base 2 and 8.
The digits of octal number have been given special codes
TABLE

EVALUATION:
1. Convert the following octal numbers to denary number
1.
407
2.
6348
3.
1748
2. Convert the following denary numbers to binary
(i) 16 (ii) 20 (iii) 32
LESSON 11
HEXADECIMALS
The special codes for 8 digits are called 3-bit equivalent forms. Hexadecimal Numbers (HEX).
A number system using 16 as its base is called a hexadecimal system. The hexadecimal system has the following digits:
0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,A,B,C,D,Eand F.
Where A=10, B=11,C=12,D=13,E=14,and F=15
Example: Write each of the following numbers using the expanded notations;

conversion between hexadecimal and denary

Relationship between Binary, Octal and Hexadecimal numbers
Recall that 16 and 8 are multiple of 2 for this reason; there is a close relationship between numbers in base2, base 8 and base 16. Similar the digits of hexadecimal numbers are given special codes.

READING ASSIGNMENT:
Read ‘handbook on computer studies (practical guide) for schools and colleges ‘Book 2, pages 43-48, By Niyi Adekolegan.
ASSIGNMENT:
ATTEMPT REVISION EXERCISE IN PAGE 42 OF STUDENTS TEXT BOOK, BY NIYI ADEKOLEGAN
WEEK 8
LESSON 12
TOPIC: UNITS OF STORAGE IN COMPUTER:
Units of Storage; Bits, Nibble, Byte, Kilobyte, Gigabyte, etc.
OBJECTIVES:
At the end of the lesson, students should be able to:
- State the various units of storage and their values
- Convert from one unit to another
- Differentiate between Kilometer, Kilogram and Kilobyte
- Distinguish between Kilobyte, Megabyte and gigabyte.
THE COMPUTER MEMORY
The memory or storage is that part of the computer system that stores data for later use. Computer has types of memory namely; main or internal memory and the auxiliary or external memory. The main memory is referred to as the computer primary storage and resides in the computer casing or system unit. The computer has two kinds of main memory. One is permanently stored and cannot be affected when the machine is turned off and there can be no loss of information. This memory kind is called Read Only Memory (ROM). It is mostly used by the computer manufacturer to store general purpose and permanent instructions on the computer, e.g operating system. The other memory is temporary. The temporary memory is affected when the machine is turned off and there is loss of information. This kind of memory is called Random Access
Memory (RAM), it is the memory that holds data input and the users software while working on them. The amount of RAM varies from one computer to the other.
Auxiliary memory is a secondary storage unit. It is to supplement the main memory. It is also called backing memory or external memory. It is a mass storage unit because it stored large amount of information. Secondary storage is needed due to the volatile nature of RAM and its inability to store large volume of data.
DIFFERENCES BETWEEN ROM AND RAM
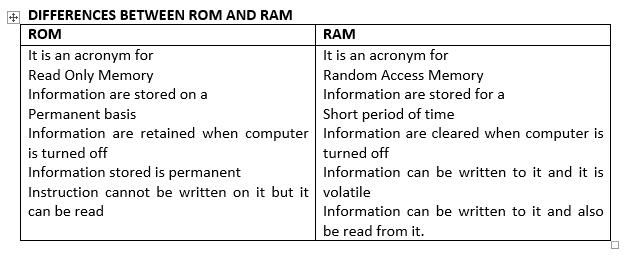
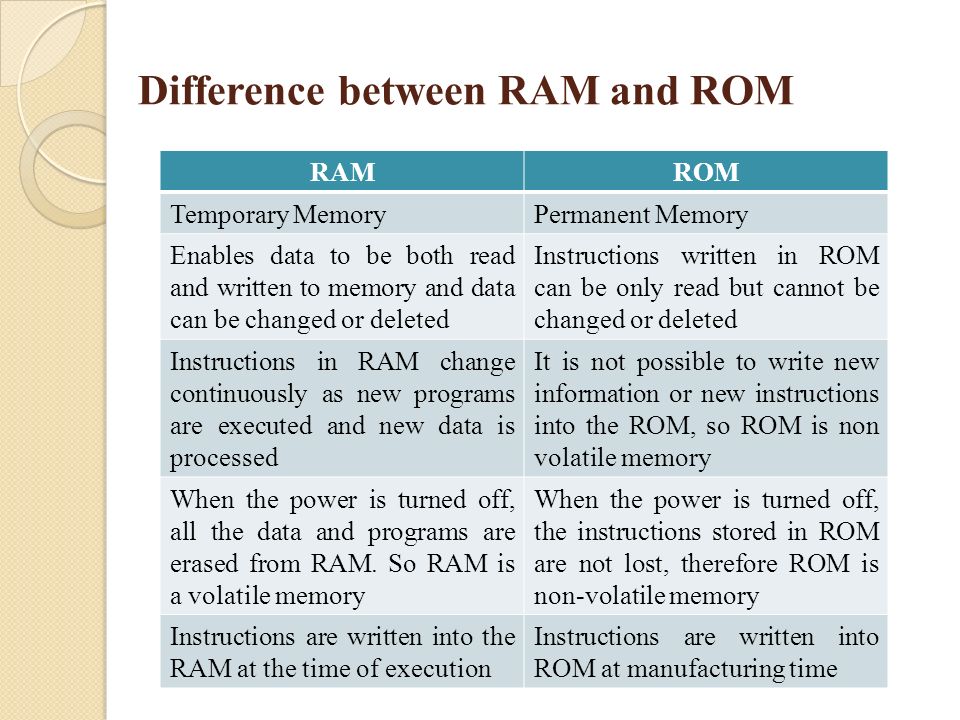
TYPES OF SECONDARY MEMORY
There are different types of secondary memory. Some of them are.
(1) Magnetic tapes (2) Magnetic disk (3) Optical disk.
MAGNETIC DISK
Magnetic disk is another form or auxiliary storage device. It is used to write and data on a disk called disk drive.
There are two types of magnetic disks. These are floppy disk and hard disk.

OPTICAL DISK
CD ROM is an example of optical disk. It is usually driven by the CD ROM Drive, CD ROM has a larger storage capacity. There are two types of CD ROM. Writable CD and Re-writable CD ROM. Writable CD ROM are used to store data or information which does not require alternations as the contents of the medium cannot be altered while the content of RE- writable CD ROM can be altered and written CD ROM is an acronym for Compact Disk Read Only Memory.
EVALUATION:
1. What is computer memory?
2. Mention two types of computer memory. Give examples.
LESSON 13
DIFFERENCE BETWEEN MAIN MEMORY AND AUXILIARY MEMORY
MAIN MEMORY AUXILIARY MEMORY
1. It is primary storage ..... it is secondary storage
2. It is internal storage ..... it is external storage
3. It acts as main memory .....it acts as backup for main memory
4. It is volatile .....it is non volatile
5. It is expensive ..... it is less expensive
6. It has small memory capacity ..... it has less memory capacity

MAGNETIC TAPE: This is similar to the tape used in audio tape recorder. Magnetic tapes are made of a long thin film covered with iron oxide. The thin film is wound round a plastic container in a form of a reel. Data can be written from tape to tape and placed into the main memory. It performs the function of an input and output devices. It is a sequential access storage device.
BIT: This is a binary digit i.e. binary digit i.e. 0 and 1
BYTE: byte is a bit of eight digit i.e. 01011101, 11110110, 01010110 etc
NIBBLE: This is half of a byte (i.e. 4 bits 0101, 1110, 0101, 1101, 1001 etc) it is also called a group of two words.
WORD: A word is a group of fixed numbers of bits in a given computer. It is also described as a group of two.
BYTES:
KILOBYTE: This is equivalent of 210 =1024
MEGABYTE: A megabyte is equivalent to 210x 210 1024 kilobyte= I MB.
GIGABYTE: A gigabyte is equivalent to 210x 210x 210 megabytes
TERABYTE: A terabyte is 240 =1,099,511,628,000, thus 240=1,099,511,628,000 bytes
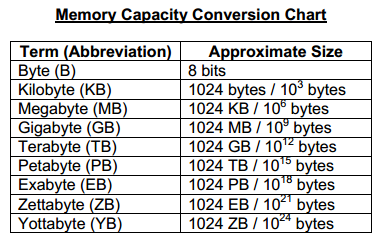
WORKING EXAMPLES
A byte = 8 bit
1 kilobyte (KB)=210=1024
1 megabyte (MB) = 210 x210 x210=220=1,048,576 bytes
I gigabyte (GB) = 210 x 210x 210=1,073,741,824 bytes
I terabyte (TB)= 210x210x210x210=240 thus 240=1,099,511,628,000 bytes
FURTHER WORKINGS
Bit = 0 or 1
4 bits = I nibble
2 nibbles = 8 bit and 8 bit = 1 byte
3 nibbles = (3 x4) bits = 12bit
4 nibbles = (4x4) bits = 16 bit
5 nibbles = (5 x4) bits = 20 bits
Conversion of bytes to bits
1 bytes = 8 bits
2 bytes = 16 bits
3 bytes = 24 bits
5 bytes = 40 bits
Unlike the metric system where I kilometer (km) is equal to 1000 meter the sub-units of byte are converted as follows.
EXAMPLES 1
Converts 2 kilobytes to byte
1 KM = 1024bytes = 2048 bytes
2 KM = 2(1024) bytes = 2048 bytes.
Convert 4KM to Byte
Note IKB = 1024 bytes
4KB = 4(1024) bytes
4096 bytes
EXAMPLES 3
Convert 2048 bytes to kilobytes
Recall 1024 bytes = IKB
2048 bytes = 2048bytes
1024bytes = 2 kilobyte.
EXAMPLES 4
Change 3 megabytes to byte
IMB = 1048, 576 bytes
3 MB = 3(1048, 576 bytes) =3,145,728 bytes
3 145, 728 bytes = 3 MB
1048 576 bytes
Convert words to bytes
Recall I word = group of 2 bytes
1 word = 2 bytes
2 bytes = 16bytes
2 word = 2(2bytes = 2x 16bits)
= 32 bits
4 word = 4(2 bytes)
= 8bytes
8 bytes = 64 bits
Change 3, 145, 728 Byte to MB
Solution: To change 3, 145, 728 to MB
1, 048,576B = 1MB
3, 145,728 = 3,145, 728
1,048,576
3MB
EVALUATION;
I. Explain the following terms
(a) Nibble (b) Word (c) Double words (d) word nipple (e) Byte (f) Kilobyte (g) Megabyte (h) Gigabyte
2. Convert, (i) 3 bytes to bits (ii) 5 nibbles to bit (c) 2word to byte
3. Convert the followings: (i) megabyte to kilobyte (ii) kilobyte to byte (iii) 6bytes to nibble.
READING ASSIGNMENT:
Read to revise this lesson again, and be prepared for questions on it.
ASSIGNMENT:
1. A type of memory that supplements the main memory is called______
(a)Main memory (b) Auxiliary memory (c) Active memory (d)
None
2. A type of memory that cannot be affected by power failure is called______
(a) RAM (b) ROM (c) Optical disk (d) Magnetic disk
3. A group of fixed numbers of bits in a given computer is called_____
(a) Word (b) Nibble (c) Bit (d) Bytes
4. 4 kilobytes is equivalent to ____ bytes
(a) 3096 (b) 4096 (c) 9069 (d) 1000
5. Which of the following storage device is used to store data or information that does not require alteration
(a)Writable CD-ROM (b) RE-Writable CD-ROM(c) Optical disk
(d)Magnetic disk
TOPIC: UNITS OF STORAGE IN COMPUTER:
Units of Storage; Bits, Nibble, Byte, Kilobyte, Gigabyte, etc.
OBJECTIVES:
At the end of the lesson, students should be able to:
- State the various units of storage and their values
- Convert from one unit to another
- Differentiate between Kilometer, Kilogram and Kilobyte
- Distinguish between Kilobyte, Megabyte and gigabyte.
THE COMPUTER MEMORY
The memory or storage is that part of the computer system that stores data for later use. Computer has types of memory namely; main or internal memory and the auxiliary or external memory. The main memory is referred to as the computer primary storage and resides in the computer casing or system unit. The computer has two kinds of main memory. One is permanently stored and cannot be affected when the machine is turned off and there can be no loss of information. This memory kind is called Read Only Memory (ROM). It is mostly used by the computer manufacturer to store general purpose and permanent instructions on the computer, e.g operating system. The other memory is temporary. The temporary memory is affected when the machine is turned off and there is loss of information. This kind of memory is called Random Access
Memory (RAM), it is the memory that holds data input and the users software while working on them. The amount of RAM varies from one computer to the other.
Auxiliary memory is a secondary storage unit. It is to supplement the main memory. It is also called backing memory or external memory. It is a mass storage unit because it stored large amount of information. Secondary storage is needed due to the volatile nature of RAM and its inability to store large volume of data.
DIFFERENCES BETWEEN ROM AND RAM


TYPES OF SECONDARY MEMORY
There are different types of secondary memory. Some of them are.
(1) Magnetic tapes (2) Magnetic disk (3) Optical disk.
MAGNETIC DISK
Magnetic disk is another form or auxiliary storage device. It is used to write and data on a disk called disk drive.
There are two types of magnetic disks. These are floppy disk and hard disk.

OPTICAL DISK
CD ROM is an example of optical disk. It is usually driven by the CD ROM Drive, CD ROM has a larger storage capacity. There are two types of CD ROM. Writable CD and Re-writable CD ROM. Writable CD ROM are used to store data or information which does not require alternations as the contents of the medium cannot be altered while the content of RE- writable CD ROM can be altered and written CD ROM is an acronym for Compact Disk Read Only Memory.
EVALUATION:
1. What is computer memory?
2. Mention two types of computer memory. Give examples.
LESSON 13
DIFFERENCE BETWEEN MAIN MEMORY AND AUXILIARY MEMORY
MAIN MEMORY AUXILIARY MEMORY
1. It is primary storage ..... it is secondary storage
2. It is internal storage ..... it is external storage
3. It acts as main memory .....it acts as backup for main memory
4. It is volatile .....it is non volatile
5. It is expensive ..... it is less expensive
6. It has small memory capacity ..... it has less memory capacity

MAGNETIC TAPE: This is similar to the tape used in audio tape recorder. Magnetic tapes are made of a long thin film covered with iron oxide. The thin film is wound round a plastic container in a form of a reel. Data can be written from tape to tape and placed into the main memory. It performs the function of an input and output devices. It is a sequential access storage device.

BIT: This is a binary digit i.e. binary digit i.e. 0 and 1
BYTE: byte is a bit of eight digit i.e. 01011101, 11110110, 01010110 etc
NIBBLE: This is half of a byte (i.e. 4 bits 0101, 1110, 0101, 1101, 1001 etc) it is also called a group of two words.
WORD: A word is a group of fixed numbers of bits in a given computer. It is also described as a group of two.
BYTES:
KILOBYTE: This is equivalent of 210 =1024
MEGABYTE: A megabyte is equivalent to 210x 210 1024 kilobyte= I MB.
GIGABYTE: A gigabyte is equivalent to 210x 210x 210 megabytes
TERABYTE: A terabyte is 240 =1,099,511,628,000, thus 240=1,099,511,628,000 bytes

WORKING EXAMPLES
A byte = 8 bit
1 kilobyte (KB)=210=1024
1 megabyte (MB) = 210 x210 x210=220=1,048,576 bytes
I gigabyte (GB) = 210 x 210x 210=1,073,741,824 bytes
I terabyte (TB)= 210x210x210x210=240 thus 240=1,099,511,628,000 bytes
FURTHER WORKINGS
Bit = 0 or 1
4 bits = I nibble
2 nibbles = 8 bit and 8 bit = 1 byte
3 nibbles = (3 x4) bits = 12bit
4 nibbles = (4x4) bits = 16 bit
5 nibbles = (5 x4) bits = 20 bits
Conversion of bytes to bits
1 bytes = 8 bits
2 bytes = 16 bits
3 bytes = 24 bits
5 bytes = 40 bits
Unlike the metric system where I kilometer (km) is equal to 1000 meter the sub-units of byte are converted as follows.
EXAMPLES 1
Converts 2 kilobytes to byte
1 KM = 1024bytes = 2048 bytes
2 KM = 2(1024) bytes = 2048 bytes.
Convert 4KM to Byte
Note IKB = 1024 bytes
4KB = 4(1024) bytes
4096 bytes
EXAMPLES 3
Convert 2048 bytes to kilobytes
Recall 1024 bytes = IKB
2048 bytes = 2048bytes
1024bytes = 2 kilobyte.
EXAMPLES 4
Change 3 megabytes to byte
IMB = 1048, 576 bytes
3 MB = 3(1048, 576 bytes) =3,145,728 bytes
3 145, 728 bytes = 3 MB
1048 576 bytes
Convert words to bytes
Recall I word = group of 2 bytes
1 word = 2 bytes
2 bytes = 16bytes
2 word = 2(2bytes = 2x 16bits)
= 32 bits
4 word = 4(2 bytes)
= 8bytes
8 bytes = 64 bits
Change 3, 145, 728 Byte to MB
Solution: To change 3, 145, 728 to MB
1, 048,576B = 1MB
3, 145,728 = 3,145, 728
1,048,576
3MB
EVALUATION;
I. Explain the following terms
(a) Nibble (b) Word (c) Double words (d) word nipple (e) Byte (f) Kilobyte (g) Megabyte (h) Gigabyte
2. Convert, (i) 3 bytes to bits (ii) 5 nibbles to bit (c) 2word to byte
3. Convert the followings: (i) megabyte to kilobyte (ii) kilobyte to byte (iii) 6bytes to nibble.
READING ASSIGNMENT:
Read to revise this lesson again, and be prepared for questions on it.
ASSIGNMENT:
1. A type of memory that supplements the main memory is called______
(a)Main memory (b) Auxiliary memory (c) Active memory (d)
None
2. A type of memory that cannot be affected by power failure is called______
(a) RAM (b) ROM (c) Optical disk (d) Magnetic disk
3. A group of fixed numbers of bits in a given computer is called_____
(a) Word (b) Nibble (c) Bit (d) Bytes
4. 4 kilobytes is equivalent to ____ bytes
(a) 3096 (b) 4096 (c) 9069 (d) 1000
5. Which of the following storage device is used to store data or information that does not require alteration
(a)Writable CD-ROM (b) RE-Writable CD-ROM(c) Optical disk
(d)Magnetic disk