SCHEME OF WORK
WEEK TOPIC
1. Revision of second term work.
2. Constitution: (a) what is constitution – (i) Definition of a constitution (ii) Sources of constitution; - written document, unwritten document, judicial pronouncements.
3. Types of Constitution: (a) Types: Federal, Unitary, and Con- Federal (b) Explanation of each of them with examples of countries operating each type of constitution.
4. Human Rights: (a) Fundamental Human Rights; (i) meaning and examples, (ii) shelter, (iii) education, (iv) life, (v) association, (vi) protection, etc.
5. Human Rights (cont’d): (b) Human Rights Abuse: (i) Forms of Abuses, (ii) Effects of abuse on individuals and society. (c) Ways of preventing the abuse of Human Rights. (d) Checks/control on human rights.
6. Types of Human Rights: (i) Civic Rights of Nigerian Citizens. (ii) Economic Rights of Nigerian Citizens. (iii) Political Rights of Nigerian Citizens
7. Obligations of Citizens: (a) Economic/Financial obligations (b) Civic Political obligations
8. Obligations of Citizens (cont’d): © Social obligations (d) consequences of failure of citizen’s performance of obligations to the Community, the State and the Nation.
9. Social Issues: (i) Traffic Rules and Regulations: Road signs and traffic lights, Causes of road accidents. (ii) Consequences of disobeying traffic rules and regulations, e.g. Traffic hold-ups, loss of man-hours, loss of life and property.
10. Revision.
3RD TERM
WEEK 1
LESSON 1
TOPIC: CONSTITUTION
CONTENT:
a. Definition of a constitution
b. Sources of a constitution: written document, unwritten document, judicial pronouncements.
DEFINITION OF A CONSTITUTION
A Constitution is an established body of laws and principles by which a country or organization is governed. It can also be seen as a body of fundamental rules and regulations that guards the conduct of people and their leader in a given state. It is a document that contains the rules and regulations that governs a country.

The Constitution

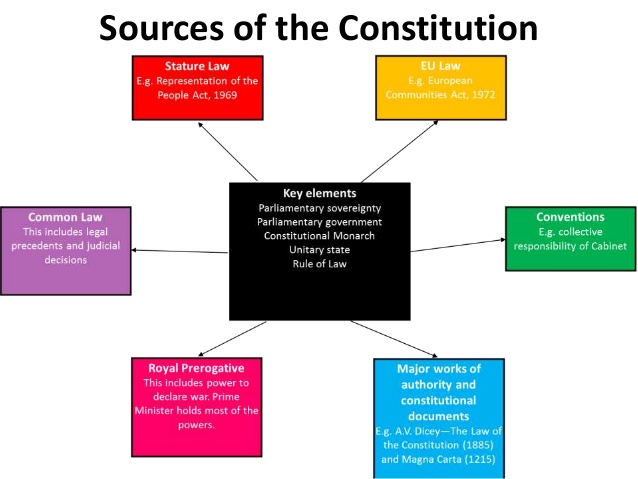
SOURCES OF A CONSTITUTION – WRITTEN DOCUMENT, UNWRITTEN DOCUMENT, JUDICIAL PRONOUNCEMENTS.
The source of a Constitution refers to the materials or body of knowledge from which the constitution can be drawn. These include written sources and unwritten sources.
WRITTEN SOURCES OF THE CONSTITUTION
These are materials which have been put into writing. They contain information and evidence that serves as an official record of the rules and regulations binding people. These include:-
1. JUDICIAL PRONOUCEMENTS OR PRECEDENTS:-
The decisions of the court and their records through judicial reviews could
be used as source of the constitution.

Court pronouncements form a source of a constitution
2. LEGISLATION: Legislation is a set of laws. A constitution can be derived from numerous laws passed by the members of the parliament.
3. CONSTITUTIONAL CONFERENCES:- These are peaceful gatherings where people of various interest groups meet to discuss important and delicate national issues before a new constitution is formed. The decisions of such conferences usually form part of the new constitution.
4. INTERNATIONAL DOCUMENTS:- The official documents of international organizations usually form significant inputs in the making of a country’s constitution.
5. WRITINGS OF RENOWNED LAWYERS, POLITICAL THINKERS, JURISTS AND HISTORICAL DOCUMENTS: - These can also form part of the constitution.
UNWRITTEN SOURCES OF THE CONSTITUTION
These are materials that provide information on rules and regulations but are not recorded in writing. These include:-
1. CUSTOMS AND TRADITIONS
The constitution could be sourced by oral means which means that past stories or sayings, that is people’s beliefs, norms and values could be a source of a constitution.
2. CONVENTION
These are acceptable political rules and practices which often form parts of a Country’s constitution.

EVALUATION
1. Define a Constitution
2. List four written sources of a constitution
3. Mention two unwritten sources of a constitution.
ASSIGNMENT
1. A ……………………………… is a document that contains the rules and regulations that governs a country.
a. Pronouncement
b. Constitution
c. Conference
d. Convention
2. A constitution may be written or ………………………..
a. Written
b. Unwritten
c. Taken
d. Spoken
3. A constitution can emerge from ………………………. Source
a. Written
b. Custom
c. Traditional
d. Conventional
4. One of this is not a written source
a. Legislation
b. Constitutional conferences
c. Customs
d. Judicial
5. All except one is unwritten source of a constitution
a. Custom
b. Traditional practices
c. Conventions
d. Legislation
6. Judicial decisions and precedents are got from the …………………….
a. Court
b. Hospital
c. Church
d. Conferences
7. ………………… is a law or set of laws
a. Precedents
b. Legislation
c. Conferences
d. Documents
ESSAY QUESTIONS
1. Define a constitution.
2. List three written sources of a constitution.
3. Mention two unwritten sources of a constitution.
TOPIC: CONSTITUTION
CONTENT:
a. Definition of a constitution
b. Sources of a constitution: written document, unwritten document, judicial pronouncements.
DEFINITION OF A CONSTITUTION
A Constitution is an established body of laws and principles by which a country or organization is governed. It can also be seen as a body of fundamental rules and regulations that guards the conduct of people and their leader in a given state. It is a document that contains the rules and regulations that governs a country.

The Constitution

SOURCES OF A CONSTITUTION – WRITTEN DOCUMENT, UNWRITTEN DOCUMENT, JUDICIAL PRONOUNCEMENTS.
The source of a Constitution refers to the materials or body of knowledge from which the constitution can be drawn. These include written sources and unwritten sources.
WRITTEN SOURCES OF THE CONSTITUTION
These are materials which have been put into writing. They contain information and evidence that serves as an official record of the rules and regulations binding people. These include:-
1. JUDICIAL PRONOUCEMENTS OR PRECEDENTS:-
The decisions of the court and their records through judicial reviews could
be used as source of the constitution.

Court pronouncements form a source of a constitution
2. LEGISLATION: Legislation is a set of laws. A constitution can be derived from numerous laws passed by the members of the parliament.
3. CONSTITUTIONAL CONFERENCES:- These are peaceful gatherings where people of various interest groups meet to discuss important and delicate national issues before a new constitution is formed. The decisions of such conferences usually form part of the new constitution.
4. INTERNATIONAL DOCUMENTS:- The official documents of international organizations usually form significant inputs in the making of a country’s constitution.
5. WRITINGS OF RENOWNED LAWYERS, POLITICAL THINKERS, JURISTS AND HISTORICAL DOCUMENTS: - These can also form part of the constitution.

UNWRITTEN SOURCES OF THE CONSTITUTION
These are materials that provide information on rules and regulations but are not recorded in writing. These include:-
1. CUSTOMS AND TRADITIONS
The constitution could be sourced by oral means which means that past stories or sayings, that is people’s beliefs, norms and values could be a source of a constitution.
2. CONVENTION
These are acceptable political rules and practices which often form parts of a Country’s constitution.

EVALUATION
1. Define a Constitution
2. List four written sources of a constitution
3. Mention two unwritten sources of a constitution.
ASSIGNMENT
1. A ……………………………… is a document that contains the rules and regulations that governs a country.
a. Pronouncement
b. Constitution
c. Conference
d. Convention
2. A constitution may be written or ………………………..
a. Written
b. Unwritten
c. Taken
d. Spoken
3. A constitution can emerge from ………………………. Source
a. Written
b. Custom
c. Traditional
d. Conventional
4. One of this is not a written source
a. Legislation
b. Constitutional conferences
c. Customs
d. Judicial
5. All except one is unwritten source of a constitution
a. Custom
b. Traditional practices
c. Conventions
d. Legislation
6. Judicial decisions and precedents are got from the …………………….
a. Court
b. Hospital
c. Church
d. Conferences
7. ………………… is a law or set of laws
a. Precedents
b. Legislation
c. Conferences
d. Documents
ESSAY QUESTIONS
1. Define a constitution.
2. List three written sources of a constitution.
3. Mention two unwritten sources of a constitution.
WEEK 2
LESSON 2
TOPIC: TYPES OF CONSTITUTION
CONTENTS
a. Federal, Unitary and Confederal
b. Explanation of each of them with examples of countries operating them.
TYPES OF CONSTITUTION
1. Federal Constitution
2. Unitary Constitution
3. Confederal Constitution
EXPLANATIONS OF EACH OF THE TYPES OF CONSTITUTION WITH EXAMPLES OF COUNTRIES OPERATING THEM.
1. FEDERAL CONSTITUTION
This is a type of constitution in which the powers of the state are shared between two or more levels of government.
Countries that operate Federal Constitution are Nigeria, Canada, United States, Switzerland etc.
2. UNITARY CONSTITUTION
This is a type of Constitution in which it is clearly stated that all the
powers of a state are vested in the central government. Countries that practice Unitary Constitution are Britain, France, Ghana, Italy etc.
3. CONFEDERAL CONSTITUTION
A confederal constitution is formed when independent and sovereign
Member states come together for some common purposes such as defense, currency, foreign affairs etc. Countries that operate confederal constitution are U.S.A, Switzerland, Senegal, Ghana etc.

EVALUATION
List two types of Constitution
Mention and explain three types of Constitution.
List two countries that practice unitary constitution
Further Study
ASSIGNMENT
OBJECTIVE QUESTIONS
1. Federal constitution is practiced in all these places except ………………
a. Nigeria
b. U.S.A
c. Switzerland
d. Britain
2. Unitary constitution is practiced in ……………………..
a. Switzerland
b. U.S.A
c. Nigeria
d. Italy
3. The type of constitution that concentrates or vests all the powers of government in the central government is called
a. Unitary
b. Federal
c. Confederal
d. Written
4. ………………………… constitution shares powers with the components states
a. Unitary
b. Federal
c. Confederal
d. Unwritten
ESSAY QUESTIONS
1. Mention three countries that have Federal constitution
2. List three types of constitution and explain two of them
TOPIC: TYPES OF CONSTITUTION
CONTENTS
a. Federal, Unitary and Confederal
b. Explanation of each of them with examples of countries operating them.
TYPES OF CONSTITUTION
1. Federal Constitution
2. Unitary Constitution
3. Confederal Constitution

EXPLANATIONS OF EACH OF THE TYPES OF CONSTITUTION WITH EXAMPLES OF COUNTRIES OPERATING THEM.
1. FEDERAL CONSTITUTION
This is a type of constitution in which the powers of the state are shared between two or more levels of government.

Countries that operate Federal Constitution are Nigeria, Canada, United States, Switzerland etc.
2. UNITARY CONSTITUTION
This is a type of Constitution in which it is clearly stated that all the
powers of a state are vested in the central government. Countries that practice Unitary Constitution are Britain, France, Ghana, Italy etc.

3. CONFEDERAL CONSTITUTION
A confederal constitution is formed when independent and sovereign
Member states come together for some common purposes such as defense, currency, foreign affairs etc. Countries that operate confederal constitution are U.S.A, Switzerland, Senegal, Ghana etc.

EVALUATION
List two types of Constitution
Mention and explain three types of Constitution.
List two countries that practice unitary constitution
Further Study
ASSIGNMENT
OBJECTIVE QUESTIONS
1. Federal constitution is practiced in all these places except ………………
a. Nigeria
b. U.S.A
c. Switzerland
d. Britain
2. Unitary constitution is practiced in ……………………..
a. Switzerland
b. U.S.A
c. Nigeria
d. Italy
3. The type of constitution that concentrates or vests all the powers of government in the central government is called
a. Unitary
b. Federal
c. Confederal
d. Written
4. ………………………… constitution shares powers with the components states
a. Unitary
b. Federal
c. Confederal
d. Unwritten
ESSAY QUESTIONS
1. Mention three countries that have Federal constitution
2. List three types of constitution and explain two of them
WEEK 3
LESSON 3
TOPIC: HUMAN RIGHT
CONTENT:-
a. Meaning of Fundamental Human Rights
b. Examples of Fundamental Human Rights.
MEANING OF FUNDAMENTAL HUMAN RIGHTS:-
Fundamental Human Rights are legal claims or entitlements which every citizen enjoys in a country and which the state has duty to protect and guarantee.
The United Nations Organization in 1948 made a Universal declaration of fundamental human rights and the resolution made it compulsory for all states to include such rights in their constitutions. The declaration is aimed at committing governments of various countries to protect basic human rights of their people.


Scales of Justice
EXAMPLES OF FUNDAMENTAL HUMAN RIGHTS:-
1. Right to life
2. Right to dignity of human person
3. Right to fair hearing
4. Right to private life
5. Right to freedom of expression and the press
6. Right to peaceful assembly and association
7. Right to freedom from discrimination
8. Right to freedom of movement
9. Right to freedom of acquisition of property
10. Right to personal liberty
11. Right to education; etc

https://www.slideshare.net/jeganraj/uni ... man-rights
EVALUATION:
Explain the meaning of Fundamental Human Rights.
List five fundamental human rights of a Nigerian citizen.
https://www.slideshare.net/nsihag/funda ... nstitution
ASSIGNMENT
1. Basic rights which individuals are allowed to have as human beings in the society is known as ………………………………………
a. Human Privilege
b. Human basic
c. Fundamental human rights
d. Privilege human rights
2. Human rights are entrenched in the …………………… of countries
a. Fundamental place
b. Constitution
c. Immigration
d. Politics
3. Human rights …………… could help to achieve change in the society
a. Activities
b. Activists
c. Actions
d. Acquisition
4. Who is responsible for protecting people’s rights in the state?
a. The parents
b. The vigilante groups
c. The youth leaders
d. The state government
ESSAY QUESTIONS
1. Explain the meaning of human rights
2. List seven fundamental human rights of a Nigerian citizen
3. Explain three of these rights.
TOPIC: HUMAN RIGHT
CONTENT:-
a. Meaning of Fundamental Human Rights
b. Examples of Fundamental Human Rights.
MEANING OF FUNDAMENTAL HUMAN RIGHTS:-
Fundamental Human Rights are legal claims or entitlements which every citizen enjoys in a country and which the state has duty to protect and guarantee.
The United Nations Organization in 1948 made a Universal declaration of fundamental human rights and the resolution made it compulsory for all states to include such rights in their constitutions. The declaration is aimed at committing governments of various countries to protect basic human rights of their people.


Scales of Justice
EXAMPLES OF FUNDAMENTAL HUMAN RIGHTS:-
1. Right to life
2. Right to dignity of human person
3. Right to fair hearing
4. Right to private life
5. Right to freedom of expression and the press
6. Right to peaceful assembly and association
7. Right to freedom from discrimination
8. Right to freedom of movement
9. Right to freedom of acquisition of property
10. Right to personal liberty
11. Right to education; etc

https://www.slideshare.net/jeganraj/uni ... man-rights
EVALUATION:
Explain the meaning of Fundamental Human Rights.
List five fundamental human rights of a Nigerian citizen.
https://www.slideshare.net/nsihag/funda ... nstitution
ASSIGNMENT
1. Basic rights which individuals are allowed to have as human beings in the society is known as ………………………………………
a. Human Privilege
b. Human basic
c. Fundamental human rights
d. Privilege human rights
2. Human rights are entrenched in the …………………… of countries
a. Fundamental place
b. Constitution
c. Immigration
d. Politics
3. Human rights …………… could help to achieve change in the society
a. Activities
b. Activists
c. Actions
d. Acquisition
4. Who is responsible for protecting people’s rights in the state?
a. The parents
b. The vigilante groups
c. The youth leaders
d. The state government
ESSAY QUESTIONS
1. Explain the meaning of human rights
2. List seven fundamental human rights of a Nigerian citizen
3. Explain three of these rights.
WEEK 4
LESSON 4
TOPIC: HUMAN RIGHTS
CONTENTS
a. Human Rights Abuses:
(i) Forms of Abuses (ii) Effects of abuses on individuals and society
b. Ways of preventing the abuse of Human Rights
c. Checks/control on human rights
HUMAN RIGHTS ABUSES:-
Most often, the rights of individuals are abused either by the government or by the citizens themselves.


FORMS OF HUMAN RIGHTS ABUSES:-
1. Torture and indecent treatment by the law enforcement agents e.g. police brutality.
2. Seizure of properties by the government without payment of adequate compensation.
3. People being arrested, imprisoned, without trail.
4. Prevention from voting and being voted for at elections.
5. Making of laws or rules and regulations to punish opponents.
6. Non access to decent shelter, education and health facilities.
7. Denial of press freedom by the government.
8. Secret trials of accused persons etc.

Police brutality
EFFECTS OF HUMAN RIGHTS ABUSES ON INDIVIDUALS AND SOCIETY:-
1. People may suffer losses especially when they are deprived of certain rights.
2. It may lead to destruction of lives and properties.
3. When people are denied of their political right, wrong people will find themselves in power.
4. It may lead to political instability in the society as people may engage in a form of rivalry in their effort at getting redress.
5. It will also give the government of the day bad or negative image locally and internationally and sanctions may be established against such states.
6. People may disobey the law in order to protest the abuse of their rights.

https://www.slideshare.net/zmiers/human ... esentation
WAYS OF PREVENTING THE ABUSE OF HUMAN RIGHTS:-
The abuse of human rights can be prevented through the following ways:-
1. People should be educated on their fundamental human rights so that they would not be deprived of their rights.
2. Government should uphold the principle of the rule of law to guarantee the right of the citizens.
3. Government should also obey and carry out court orders in order to have an orderly society.
4. People should be given the opportunity to challenge any violation of their rights in the court of law.
5. The fundamental human rights should be entrenched in the constitution so that it could be respected and referred to.
6. There should be independence of the judiciary because the court is the last hope of the common man.
7. The press should not be gagged but should be allowed to keep reporting issues without fear or favour.

Education helps us to know our right

The law court assists citizens whose rights are abused.
CHECKS OR CONTROL OF HUMAN RIGHTS:-
The fundamental human rights of the citizens can be checked or controlled through the following ways:-
1. Rights can be controlled by the legislature as they are the representatives of the people, by making laws against human right abuses.
2. The press as the watch dog of the government can also check abuse of rights, by making known of cases of human right abuses.
3. Some human rights commissions established by non-governmental agencies can assist to check abuse of rights.
4. Government agencies such as the police, public complaints commission can also check abuses of rights.
5. People can check abuse of rights by criticizing government agencies which violate human rights in the news media.
6. The court is the best agency of government that can check abuse of fundamental human rights as it is the last hope of the common man.

EVALUATION
1. Explain three instances of abuse of human rights.
2. State three effects of the abuse of human rights.
3. Suggest three ways of preventing the abuse of human rights
4. Mention three ways of checking or controlling human rights.
ASSIGNMENT
OBJECTIVE QUESTIONS
1. A citizen who abuses the rights of others can be charged to ……………………
a. Court
b. School
c. Hospital
d. Church
2. ………………. Helps us to know our rights
a. Complaining
b. Fighting
c. Quarrelling
d. Education
3. Citizens dignity can be curtailed if the person is a ………………
a. Patriot
b. Nationalist
c. Criminal
d. Chief judge
4. Cases of abuse can be exposed through the mass media except ……………..
a. Television
b. Radio
c. Magazine
d. School
5. The rights that guard against inhuman treatment is known as ………………
a. Right to life
b. Right to privacy and family life
c. Right to personal liberty
d. Right to dignity of human person.
ESSAY QUESTIONS
1. Explain three instances of abuse of human rights
2. State two effects of the abuse of human rights
3. Mention two ways of preventing human rights abuses
TOPIC: HUMAN RIGHTS
CONTENTS
a. Human Rights Abuses:
(i) Forms of Abuses (ii) Effects of abuses on individuals and society
b. Ways of preventing the abuse of Human Rights
c. Checks/control on human rights
HUMAN RIGHTS ABUSES:-
Most often, the rights of individuals are abused either by the government or by the citizens themselves.


FORMS OF HUMAN RIGHTS ABUSES:-
1. Torture and indecent treatment by the law enforcement agents e.g. police brutality.
2. Seizure of properties by the government without payment of adequate compensation.
3. People being arrested, imprisoned, without trail.
4. Prevention from voting and being voted for at elections.
5. Making of laws or rules and regulations to punish opponents.
6. Non access to decent shelter, education and health facilities.
7. Denial of press freedom by the government.
8. Secret trials of accused persons etc.

Police brutality
EFFECTS OF HUMAN RIGHTS ABUSES ON INDIVIDUALS AND SOCIETY:-
1. People may suffer losses especially when they are deprived of certain rights.
2. It may lead to destruction of lives and properties.
3. When people are denied of their political right, wrong people will find themselves in power.
4. It may lead to political instability in the society as people may engage in a form of rivalry in their effort at getting redress.
5. It will also give the government of the day bad or negative image locally and internationally and sanctions may be established against such states.
6. People may disobey the law in order to protest the abuse of their rights.

https://www.slideshare.net/zmiers/human ... esentation
WAYS OF PREVENTING THE ABUSE OF HUMAN RIGHTS:-
The abuse of human rights can be prevented through the following ways:-
1. People should be educated on their fundamental human rights so that they would not be deprived of their rights.
2. Government should uphold the principle of the rule of law to guarantee the right of the citizens.
3. Government should also obey and carry out court orders in order to have an orderly society.
4. People should be given the opportunity to challenge any violation of their rights in the court of law.
5. The fundamental human rights should be entrenched in the constitution so that it could be respected and referred to.
6. There should be independence of the judiciary because the court is the last hope of the common man.
7. The press should not be gagged but should be allowed to keep reporting issues without fear or favour.

Education helps us to know our right

The law court assists citizens whose rights are abused.
CHECKS OR CONTROL OF HUMAN RIGHTS:-
The fundamental human rights of the citizens can be checked or controlled through the following ways:-
1. Rights can be controlled by the legislature as they are the representatives of the people, by making laws against human right abuses.
2. The press as the watch dog of the government can also check abuse of rights, by making known of cases of human right abuses.
3. Some human rights commissions established by non-governmental agencies can assist to check abuse of rights.
4. Government agencies such as the police, public complaints commission can also check abuses of rights.
5. People can check abuse of rights by criticizing government agencies which violate human rights in the news media.
6. The court is the best agency of government that can check abuse of fundamental human rights as it is the last hope of the common man.

EVALUATION
1. Explain three instances of abuse of human rights.
2. State three effects of the abuse of human rights.
3. Suggest three ways of preventing the abuse of human rights
4. Mention three ways of checking or controlling human rights.
ASSIGNMENT
OBJECTIVE QUESTIONS
1. A citizen who abuses the rights of others can be charged to ……………………
a. Court
b. School
c. Hospital
d. Church
2. ………………. Helps us to know our rights
a. Complaining
b. Fighting
c. Quarrelling
d. Education
3. Citizens dignity can be curtailed if the person is a ………………
a. Patriot
b. Nationalist
c. Criminal
d. Chief judge
4. Cases of abuse can be exposed through the mass media except ……………..
a. Television
b. Radio
c. Magazine
d. School
5. The rights that guard against inhuman treatment is known as ………………
a. Right to life
b. Right to privacy and family life
c. Right to personal liberty
d. Right to dignity of human person.
ESSAY QUESTIONS
1. Explain three instances of abuse of human rights
2. State two effects of the abuse of human rights
3. Mention two ways of preventing human rights abuses
WEEK 5
LESSON 5
TOPIC: TYPES OF HUMAN RIGHTS
CONTENTS:
1. Civic Rights of Nigerian Citizens.
2. Economic Rights of Nigerian Citizens.
3. Political Rights of Nigerian Citizens.
CIVIC RIGHTS OF NIGERIAN CITIZENS
These are the rights that enable a citizen to live a decent life and relate with other members of the community. Such rights include:-
1. RIGHTS TO LIFE: Every person has a right to life and no one shall be deprived intentionally of his life, unless in execution of the sentence of a court in respect of a criminal offence which the person is found guilty of in Nigeria.
2. RIGHT TO EDUCATION: Every Nigerian Citizen has the right to enjoy basic education.
3. RIGHT TO DIGNITY OF HUMAN PERSON: This means that every human being must be respected and accorded the honour befitting a human person. A citizen should not be subjected to torture or inhuman treatment.
4. RIGHT TO PERSONAL LIBERTY: Every citizen is entitled to freedom from unlawful arrests and intimidation.
5. RIGHT TO FAIR HEARING: Every citizen is entitled to the right of being listened to in an independent and impartial court of law within a reasonable time.
6. RIGHT TO PRIVACY AND FAMILY LIFE: This means that every citizen is entitled to enjoy family life, private discussion, personal correspondences, telephone conversations and other general communication without disturbance or intrusion.

Citizens have rights to their private life
ECONOMIC RIGHTS OF NIGERIAN CITIZENS
These are the rights which a citizen enjoys, that enable him to be engaged in a profitable business in order to earn a living. These include:-
1. RIGHT TO EMPLOYMENT: Every Nigerian Citizen has the right to be gainfully employed or engaged in lawful business.
2. RIGHT TO ACQUIRE AND OWN PROPERTY: Section 43 of the 1999 constitution allows every citizen in Nigeria to acquire and own property anywhere in Nigeria. This includes right to own house, land, car, etc.
3. RIGHT TO FREEDOM OF MOVEMENT: Citizens are free to move from place to place. Workers are also free to work and live in places of their choices.
4. RIGHT TO A JUST AND FAVOURABLE CONDITION OF WORK: Every Nigerian citizen is entitled to a just and favourable condition of work.
5. Freedom from all forms of discrimination in employment due to sex, race or colour.
6. Right to social security, especially in the event of unemployment, sickness, disability or old age.

Citizens have the right to own property
POLITICAL RIGHTS OF NIGERIAN CITIZENS:
These are the rights that enable us to participate in government. These includes:-
1. RIGHT TO VOTE AND BE VOTED FOR: This means that you can vote for any candidate of your choice and someone can also vote for you if you contest during elections provided you meet the qualifications for it.
2. RIGHT TO CONSTRUCTIVE CRITICISM: Every citizen of Nigeria has the right to constructively question the government on certain issues.
3. RIGHT TO FREEDOM FROM DISCRIMINATION: Citizens should not be denied their rights based on their religion, tribe, sex, physical features etc.
4. RIGHT TO PEACEFUL ASSEMBLY: Citizens have the right to come together to interact peacefully with other people to pursue the same interest provided it is not a bad or illegal assembly.

https://www.slideshare.net/iamnotangeli ... f-citizens
EVALUATION
1. Outline three political rights of a Nigerian citizen.
2. Explain two political rights of a Nigerian citizen.
https://www.slideshare.net/saurav_mic/what-is-rights
ASSIGNMENT
OBJECTIVE QUESTIONS
1. Civic rights are created and protected by the
a. Citizens
b. States
c. Individuals
d. Officers
2. All citizen should be gainfully ……………………
a. Satisfied
b. Liberated
c. Sacrificed
d. Employed
3. Citizens can own the following things except ………………………
a. Land
b. House
c. Sky
d. Car
4. Citizens have right to ……………………
a. Life
b. Death
c. Swim
d. Fly
5. All citizens deserve fair …………………..
a. Discussion
b. Hearing
c. Movement
d. Freedom
ESSAY QUESTIONS
1. state three civic rights of a Nigerian citizen
2. List three economic rights of a citizen.
TOPIC: TYPES OF HUMAN RIGHTS
CONTENTS:
1. Civic Rights of Nigerian Citizens.
2. Economic Rights of Nigerian Citizens.
3. Political Rights of Nigerian Citizens.
CIVIC RIGHTS OF NIGERIAN CITIZENS
These are the rights that enable a citizen to live a decent life and relate with other members of the community. Such rights include:-
1. RIGHTS TO LIFE: Every person has a right to life and no one shall be deprived intentionally of his life, unless in execution of the sentence of a court in respect of a criminal offence which the person is found guilty of in Nigeria.
2. RIGHT TO EDUCATION: Every Nigerian Citizen has the right to enjoy basic education.
3. RIGHT TO DIGNITY OF HUMAN PERSON: This means that every human being must be respected and accorded the honour befitting a human person. A citizen should not be subjected to torture or inhuman treatment.
4. RIGHT TO PERSONAL LIBERTY: Every citizen is entitled to freedom from unlawful arrests and intimidation.
5. RIGHT TO FAIR HEARING: Every citizen is entitled to the right of being listened to in an independent and impartial court of law within a reasonable time.
6. RIGHT TO PRIVACY AND FAMILY LIFE: This means that every citizen is entitled to enjoy family life, private discussion, personal correspondences, telephone conversations and other general communication without disturbance or intrusion.

Citizens have rights to their private life
ECONOMIC RIGHTS OF NIGERIAN CITIZENS
These are the rights which a citizen enjoys, that enable him to be engaged in a profitable business in order to earn a living. These include:-
1. RIGHT TO EMPLOYMENT: Every Nigerian Citizen has the right to be gainfully employed or engaged in lawful business.
2. RIGHT TO ACQUIRE AND OWN PROPERTY: Section 43 of the 1999 constitution allows every citizen in Nigeria to acquire and own property anywhere in Nigeria. This includes right to own house, land, car, etc.
3. RIGHT TO FREEDOM OF MOVEMENT: Citizens are free to move from place to place. Workers are also free to work and live in places of their choices.
4. RIGHT TO A JUST AND FAVOURABLE CONDITION OF WORK: Every Nigerian citizen is entitled to a just and favourable condition of work.
5. Freedom from all forms of discrimination in employment due to sex, race or colour.
6. Right to social security, especially in the event of unemployment, sickness, disability or old age.

Citizens have the right to own property
POLITICAL RIGHTS OF NIGERIAN CITIZENS:
These are the rights that enable us to participate in government. These includes:-
1. RIGHT TO VOTE AND BE VOTED FOR: This means that you can vote for any candidate of your choice and someone can also vote for you if you contest during elections provided you meet the qualifications for it.
2. RIGHT TO CONSTRUCTIVE CRITICISM: Every citizen of Nigeria has the right to constructively question the government on certain issues.
3. RIGHT TO FREEDOM FROM DISCRIMINATION: Citizens should not be denied their rights based on their religion, tribe, sex, physical features etc.
4. RIGHT TO PEACEFUL ASSEMBLY: Citizens have the right to come together to interact peacefully with other people to pursue the same interest provided it is not a bad or illegal assembly.

https://www.slideshare.net/iamnotangeli ... f-citizens
EVALUATION
1. Outline three political rights of a Nigerian citizen.
2. Explain two political rights of a Nigerian citizen.
https://www.slideshare.net/saurav_mic/what-is-rights
ASSIGNMENT
OBJECTIVE QUESTIONS
1. Civic rights are created and protected by the
a. Citizens
b. States
c. Individuals
d. Officers
2. All citizen should be gainfully ……………………
a. Satisfied
b. Liberated
c. Sacrificed
d. Employed
3. Citizens can own the following things except ………………………
a. Land
b. House
c. Sky
d. Car
4. Citizens have right to ……………………
a. Life
b. Death
c. Swim
d. Fly
5. All citizens deserve fair …………………..
a. Discussion
b. Hearing
c. Movement
d. Freedom
ESSAY QUESTIONS
1. state three civic rights of a Nigerian citizen
2. List three economic rights of a citizen.
WEEK 6
LESSON 6
TOPIC: OBLIGATIONS OF CITIZENS
CONTENT:
1. ECONOMIC AND FINANCIAL OBLIGATIONS
2. CIVIC AND POLITICAL OBLIGATIONS
ECONOMIC AND FINANCIAL OBLIGATIONS
OBLIGATIONS OF CITIZENS
Obligations are the duties or responsibilities that the citizens own not only to the state but also to themselves for the smooth functioning of the state.
TYPES OF OBLIGATIONS
Economic/financial Obligations: it is the duties of citizen’s contributions towards the progress of the state or country. Examples of Economic/Financial obligations of a citizen include – payment of taxes: the tax may be direct or indirect.
Direct tax: Such as income tax, company, while indirect tax includes such tax as water rate, electricity bill, custom, duties, exercise duties. This payment will help the country in carrying out its functions such as provision of Pipe- borne water, good roads, electricity, schools and hospitals.

POLITICAL & CIVIC OBLIGATION
Political Obligations
The political obligations of citizens include:
- Voting during elections- citizen of a country are expected to vote for people who will be part of the government during elections.
They can also be voted for if they present themselves as candidates for elective position. Refusing to vote during election means contributing to the promotion of an unpopular government.

Civic Obligations
Civic Obligations of citizens include:
(1) Having respect and obedience to oneself, the community and the government.
(2) To maintain peace and order in the State.
(3) Obeying the Laws of the State.
(4) Enlisting in the armed forces when military service is compulsory to defense one’s Nation.
(5) Protecting the good name of one’s country.
(6) Assisting in keeping the state secure by reporting, criminals and law breaker to police.


https://www.slideshare.net/maheshjp05/p ... obligation
EVALUATION
1. State three civic rights of Nigerian citizens.
2. List three economic rights of Nigerian Citizens.
3. Explain two of the economic rights of a Nigerian citizen.
4. Name and give example of the two types of tax you know.
5. What are the Civic responsibilities of a citizen?
6. What is Political obligation?
Further Study
TOPIC: OBLIGATIONS OF CITIZENS
CONTENT:
1. ECONOMIC AND FINANCIAL OBLIGATIONS
2. CIVIC AND POLITICAL OBLIGATIONS
ECONOMIC AND FINANCIAL OBLIGATIONS
OBLIGATIONS OF CITIZENS
Obligations are the duties or responsibilities that the citizens own not only to the state but also to themselves for the smooth functioning of the state.
TYPES OF OBLIGATIONS
Economic/financial Obligations: it is the duties of citizen’s contributions towards the progress of the state or country. Examples of Economic/Financial obligations of a citizen include – payment of taxes: the tax may be direct or indirect.
Direct tax: Such as income tax, company, while indirect tax includes such tax as water rate, electricity bill, custom, duties, exercise duties. This payment will help the country in carrying out its functions such as provision of Pipe- borne water, good roads, electricity, schools and hospitals.

POLITICAL & CIVIC OBLIGATION
Political Obligations
The political obligations of citizens include:
- Voting during elections- citizen of a country are expected to vote for people who will be part of the government during elections.
They can also be voted for if they present themselves as candidates for elective position. Refusing to vote during election means contributing to the promotion of an unpopular government.

Civic Obligations
Civic Obligations of citizens include:
(1) Having respect and obedience to oneself, the community and the government.
(2) To maintain peace and order in the State.
(3) Obeying the Laws of the State.
(4) Enlisting in the armed forces when military service is compulsory to defense one’s Nation.
(5) Protecting the good name of one’s country.
(6) Assisting in keeping the state secure by reporting, criminals and law breaker to police.


https://www.slideshare.net/maheshjp05/p ... obligation
EVALUATION
1. State three civic rights of Nigerian citizens.
2. List three economic rights of Nigerian Citizens.
3. Explain two of the economic rights of a Nigerian citizen.
4. Name and give example of the two types of tax you know.
5. What are the Civic responsibilities of a citizen?
6. What is Political obligation?
Further Study
WEEK 7
LESSON 7
Topic: OBLIGATIONS OF CITIZENS (cont’d)
Content: (a) Social Obligations
(b) Consequences of failure of Citizens performance of obligations
Social Obligations
Social Obligation refers to those duties required of us by common sense. Nobody actually forces us to do it.
Social responsibilities (obligations) of the citizens includes
1. Environmental cleanliness- keeping the environment clean is the responsibility of every citizen.
2. Taking good care of public property.
3. Helping and old woman or children cross a busy express way.
4. Assisting the needy members of the society.
5. Taking accident victims to the hospital.

CONSEQUENCES OF NON PERFORMANCE OF OBLIGATIONS
Our community, state and country stand to gain much when citizens perform their duties. By so doing, they are contributing their own quota towards achieving peace, order and governance.
When Citizens fail to carry out their responsibilities, the following may likely happen.
i. A total break-down of law and order;
ii. Absence of peace and harmony in the Nation;
iii. Corruption and embezzlement of public funds (money)
iv. Poverty
v. Loss of confidence in the nation;
vi. Suppression of individual initiatives
vii. Environmental pollution; and discrimination
viii. Lack of patriotism
ix. Economic sabotage.

Evaluation
(1) Mention four consequences of failure of citizens to perform their obligation.
(2) State three social responsibilities of a citizen you know.
https://www.slideshare.net/gooheer/soci ... y-51435575
Topic: OBLIGATIONS OF CITIZENS (cont’d)
Content: (a) Social Obligations
(b) Consequences of failure of Citizens performance of obligations
Social Obligations
Social Obligation refers to those duties required of us by common sense. Nobody actually forces us to do it.
Social responsibilities (obligations) of the citizens includes
1. Environmental cleanliness- keeping the environment clean is the responsibility of every citizen.
2. Taking good care of public property.
3. Helping and old woman or children cross a busy express way.
4. Assisting the needy members of the society.
5. Taking accident victims to the hospital.

CONSEQUENCES OF NON PERFORMANCE OF OBLIGATIONS
Our community, state and country stand to gain much when citizens perform their duties. By so doing, they are contributing their own quota towards achieving peace, order and governance.
When Citizens fail to carry out their responsibilities, the following may likely happen.
i. A total break-down of law and order;
ii. Absence of peace and harmony in the Nation;
iii. Corruption and embezzlement of public funds (money)
iv. Poverty
v. Loss of confidence in the nation;
vi. Suppression of individual initiatives
vii. Environmental pollution; and discrimination
viii. Lack of patriotism
ix. Economic sabotage.

Evaluation
(1) Mention four consequences of failure of citizens to perform their obligation.
(2) State three social responsibilities of a citizen you know.
https://www.slideshare.net/gooheer/soci ... y-51435575
WEEK 8
LESSON 8
TOPIC: SOCIAL ISSUES
CONTENT: i. TRAFFIC RULES AND REGULATIONS
ii. CONSEQUENCES OF DISOBEYING TRAFFIC RULES AND
REGULATIONS
TRAFFIC RULES AND REGULATIONS
Traffic rules and regulations refer to a set of laws prepared for road users on how to behave on the road.
ROAD SIGNS AND TRAFFIC LIGHTS
Every day, we come across many signs on our roads.
Such signs include:
1. Traffic Lights: This is usually located at cross-roads junctions. Traffic lights have three colours, which are green, amber and red.
E.g. Amber ( Yellow light) = get ready to go
Green= go
red = stop.

TRAFFIC LIGHT
2. Zebra Crossing: This is used to indicate where pedestrians (people walking) can safely cross the road. Once a pedestrian steps on the zebra line, motorists, motorcyclists and bicycle riders are expected to stop. Zebra crossing are usually constructed in front of schools, hospital, markets and busy spots.

3. Road Diversion: it is a roads sign that prepares road users for a change in the direction of the road.

4. Hill Sign: The hill sign means to inform road users about the hill nature of the road ahead.

5. Road Block: Are stops on the road usually for security checks e.g. the police check point, customs, immigration and federal Road safely commission ( FRSC)
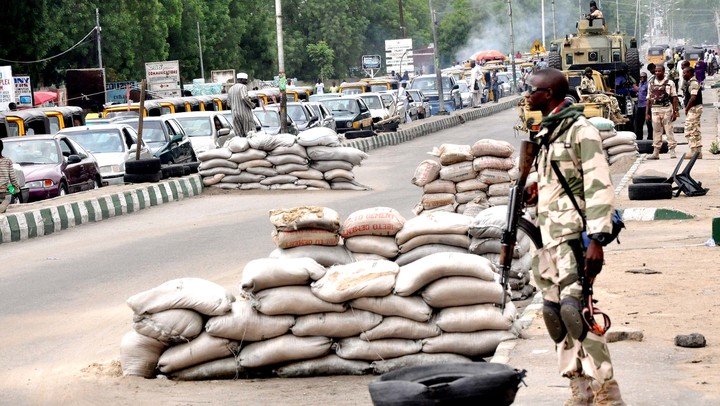

CAUSES OF ROAD ACCIDENTS
Road accidents are caused by a number of factors.
These include:
1. Over-speeding- many motorists are usually in a hurry and the drive at high speed in disregard for the official speed limit.

2. Bad-roads: poor condition of road, either as a result of not Tarred or lack of proper maintenance may leads to road accident. E.g. bumps, pot-hole and dangerous sport on the road.

3. Under-aged driver: Another cause of road accident is the abuse of driving regulations by under-aged children.
Such children take their parent’s vehicles without permission. Thereby constituting hazard to other road users

4. Ignorance- Some road users cannot read and interpret road signs. This is risky for other road users. There are some drivers who never attended any driving school before getting on the road. Such drivers are easily involved in road accidents.

5. Drunkenness: Accidents in most cases, occur on our roads as a result of some drivers who drinks alcohol before embarking on trip. It is very dangerous to drinks before and when driving.
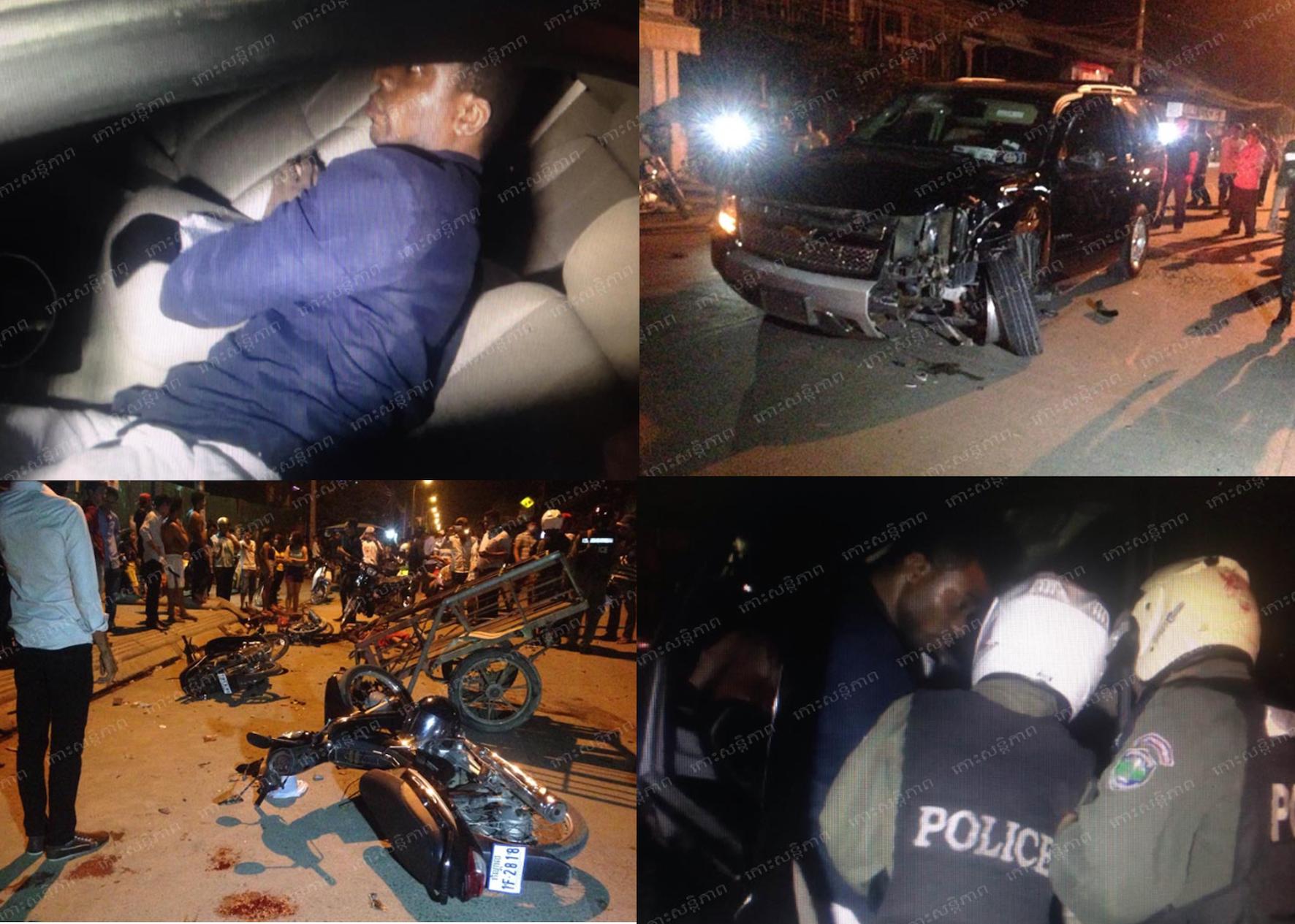

CONSEQUENCES OF NOT OBEYING TRAFFIC RULES
Traffic rules and regulations are meant to act as guide to all road users.
1. Road accidents
2. Disabilities
3. Loss of valuable property
4. Economic depression
5. Traffic jams
6. Loss of valuable man-hour
Traffic rules and regulations
These are rules and regulations made by government to ensure safety of all road users. Some of the rules are
(a) Motorists should obey speed limit
(b) Drivers should obey traffic lights
(c) Motorists should not drive when drunk
(d) Pedestrians should use foot bridges where available
(e) Vehicles should be properly parked when the need arises
(f) Motorist should obey traffic controllers such as traffic, police, and federal road safety corps.

Evaluation
1. Mention three causes of road accident?
2. Explain what each colour in the traffic light mans
3. What are traffic rules and regulation
4. Mention three rules and regulations that users should obey
5. List four consequences of disobeying Traffic rules.
Objective Question
1. Road accidents occur as a result of ___________ rules and regulation
(a) Disobeying traffic (b) respecting traffic (c) responding to traffic controller (d) controlling speed limits
2. The traffic light red colour means that vehicle should __________
(a) Keeping moving (b) parked (c) continue (d) stop
3. Obligations are the ________ of a citizen
(a) Commitment (b) right (c) duties (d) failure
4. The civic responsibilities of a citizen includes all expect
(a) Obeying the laws of the state (b) maintain peace and order (c) protecting criminal (d) enlisting in the armed forces
5. Failure to performance one’s duty leads to
(a) Promotion of unity and peace (b) total breakdown of law and order (c) embezzlement of public funds (d) Economic sabotage
TOPIC: SOCIAL ISSUES
CONTENT: i. TRAFFIC RULES AND REGULATIONS
ii. CONSEQUENCES OF DISOBEYING TRAFFIC RULES AND
REGULATIONS
TRAFFIC RULES AND REGULATIONS
Traffic rules and regulations refer to a set of laws prepared for road users on how to behave on the road.
ROAD SIGNS AND TRAFFIC LIGHTS
Every day, we come across many signs on our roads.
Such signs include:
1. Traffic Lights: This is usually located at cross-roads junctions. Traffic lights have three colours, which are green, amber and red.
E.g. Amber ( Yellow light) = get ready to go
Green= go
red = stop.

TRAFFIC LIGHT
2. Zebra Crossing: This is used to indicate where pedestrians (people walking) can safely cross the road. Once a pedestrian steps on the zebra line, motorists, motorcyclists and bicycle riders are expected to stop. Zebra crossing are usually constructed in front of schools, hospital, markets and busy spots.

3. Road Diversion: it is a roads sign that prepares road users for a change in the direction of the road.

4. Hill Sign: The hill sign means to inform road users about the hill nature of the road ahead.

5. Road Block: Are stops on the road usually for security checks e.g. the police check point, customs, immigration and federal Road safely commission ( FRSC)

CAUSES OF ROAD ACCIDENTS
Road accidents are caused by a number of factors.
These include:
1. Over-speeding- many motorists are usually in a hurry and the drive at high speed in disregard for the official speed limit.

2. Bad-roads: poor condition of road, either as a result of not Tarred or lack of proper maintenance may leads to road accident. E.g. bumps, pot-hole and dangerous sport on the road.

3. Under-aged driver: Another cause of road accident is the abuse of driving regulations by under-aged children.
Such children take their parent’s vehicles without permission. Thereby constituting hazard to other road users

4. Ignorance- Some road users cannot read and interpret road signs. This is risky for other road users. There are some drivers who never attended any driving school before getting on the road. Such drivers are easily involved in road accidents.

5. Drunkenness: Accidents in most cases, occur on our roads as a result of some drivers who drinks alcohol before embarking on trip. It is very dangerous to drinks before and when driving.

CONSEQUENCES OF NOT OBEYING TRAFFIC RULES
Traffic rules and regulations are meant to act as guide to all road users.
1. Road accidents
2. Disabilities
3. Loss of valuable property
4. Economic depression
5. Traffic jams
6. Loss of valuable man-hour
Traffic rules and regulations
These are rules and regulations made by government to ensure safety of all road users. Some of the rules are
(a) Motorists should obey speed limit
(b) Drivers should obey traffic lights
(c) Motorists should not drive when drunk
(d) Pedestrians should use foot bridges where available
(e) Vehicles should be properly parked when the need arises
(f) Motorist should obey traffic controllers such as traffic, police, and federal road safety corps.

Evaluation
1. Mention three causes of road accident?
2. Explain what each colour in the traffic light mans
3. What are traffic rules and regulation
4. Mention three rules and regulations that users should obey
5. List four consequences of disobeying Traffic rules.
Objective Question
1. Road accidents occur as a result of ___________ rules and regulation
(a) Disobeying traffic (b) respecting traffic (c) responding to traffic controller (d) controlling speed limits
2. The traffic light red colour means that vehicle should __________
(a) Keeping moving (b) parked (c) continue (d) stop
3. Obligations are the ________ of a citizen
(a) Commitment (b) right (c) duties (d) failure
4. The civic responsibilities of a citizen includes all expect
(a) Obeying the laws of the state (b) maintain peace and order (c) protecting criminal (d) enlisting in the armed forces
5. Failure to performance one’s duty leads to
(a) Promotion of unity and peace (b) total breakdown of law and order (c) embezzlement of public funds (d) Economic sabotage